Scientists have developed a simple clinical test that can assess the lower limb strength of patients to predict their risk of falls. STAFFORDSHIRE UNIVERSITY DESIGNED BY STAFFORDSHIRE UNIVERSITY CARTOON AND COMIC ARTS STUDENT JOSH THOMAS WHO WON A COMPETITION TO ILLUSTRATE THE STUDY. view more CREDIT: STAFFORDSHIRE UNIVERSITY/JOSH THOMAS The “enhanced paper grip test” validated...
Tag: <span>Biomedical</span>
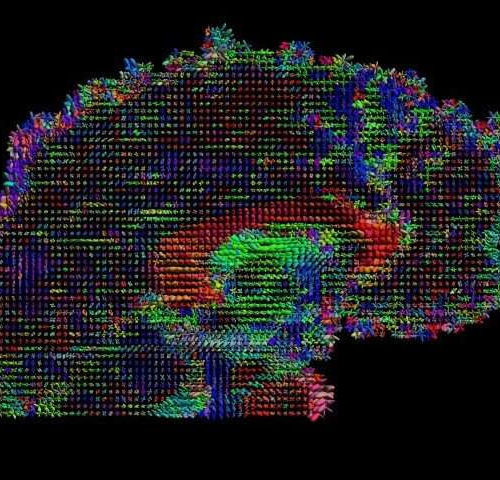
Brain thickness and connectivity, not just location, correlate with behavior
by Matt Swayne, Pennsylvania State University New techniques and technologies of big data are helping researchers better understand the brain. In this study, a Penn State team studied data from the Human Connectome Project to better understand the correlations between brain features, such as cortical thickness and connectivity, and various behaviors. Credit: David Shattuck and...
Scientists work to freeze-dry synthetic platelets
A Case Western Reserve University scientist, who has for more than a decade pioneered research into synthetic platelet substitutes, has been awarded a $3.8 million grant by the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to develop freeze-dried artificial platelets that can treat bleeding in wounded soldiers in the battlefield before they can be taken to a...
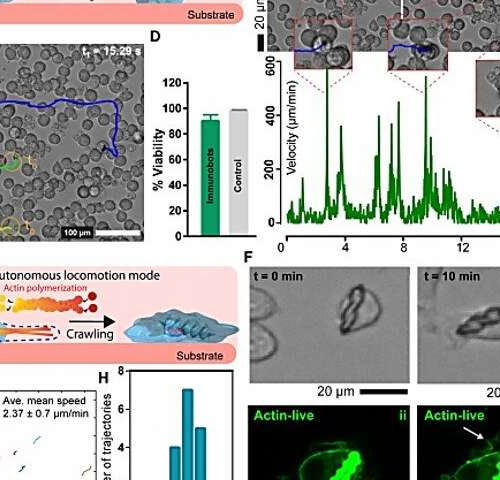
Interaction dynamics between designer microrobots and the immune system
by Thamarasee Jeewandara , Medical Xpress Optimization of microswimmer shape for targeted drug delivery. Illustration of a future use case for the medical microrobots emphasizing an important design tradeoff. Double-helical magnetic microswimmers with filled internal cores are 3D-printed as concentrated drug-carrying bodies. Three morphological derivatives of the same design are tested with the same body...
Restoring mobility by identifying the neurons that make it possible
ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Researchers at EPFL are able to get paralyzed rodents walking again by stimulating the animals’ damaged spinal cords. This promising treatment has already helped paraplegics regain mobility during clinical trials at Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV). Now, using artificial intelligence, the researchers can pinpoint which neurons are involved in the gait...
Apathy not depression helps to predict dementia
Apathy offers an important early warning sign of dementia in individuals with cerebrovascular disease, but depression does not, new research led by the University of Cambridge suggests. Depression is often thought to be a risk factor for dementia but this may be because some depression scales used by clinicians and researchers partially assess apathy, say...
New vitamin K-based drug shows promise against medication-resistant epilepsy
Researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina have formulated a vitamin K-based compound that, due to its unique structure and mechanism, eliminates medication-resistant epileptic seizures in mice tested to date. Credit: Sarah Pack, Medical University of South Carolina In the cover article of the June 11 issue of the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a...
Better vaccines are in our blood
by Harvard University Red blood cells do more than shuttle oxygen from our lungs to our organs: they also help the body fight off infections by capturing pathogens on their surfaces, neutralizing them, and presenting them to immune cells in the spleen and liver. Now, a team of researchers from Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically...
Widely used blood test could advance heart failure treatment
NEW YORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Biomedical experts believe that half of heart failure patients likely have low levels of the thyroid hormone T3 in their cardiac tissue. While heart failure symptoms are commonly attributed to cardiovascular conditions like coronary artery disease and high blood pressure, a growing number of studies suggest that low cardiac T3...
New vitamin K-based drug shows promise against medication-resistant epilepsy
Researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina have formulated a vitamin K-based compound that, due to its unique structure and mechanism, eliminates medication-resistant epileptic seizures in mice tested to date. Credit: Sarah Pack, Medical University of South Carolina In the cover article of the June 11 issue of the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a...