As interest in the application of plasma medicine — the use of low-temperature plasma (LTP) created by an electrical discharge to address medical problems — continues to grow, so does the need for research advancements proving its capabilities and potential impacts on the health care industry. Across the world, many research groups are investigating plasma...
Tag: <span>Biomedical</span>
Focused ultrasound opening brain to previously impossible treatments
University of Virginia’s School of Medicine and School of Engineering, is using focused soundwaves to overcome the natural ‘blood-brain barrier,’ which protects the brain from harmful pathogens. Credit: Dan Addison | UVA Communications University of Virginia researchers are pioneering the use of focused ultrasound to defy the brain’s protective barrier so that doctors could, at...
Earbud-like nerve stimulator shows promise for relieving indigestion
Bethesda, MD – People who suffer frequent indigestion may find relief with a small device that hooks onto the ear known as a transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulator, or taVNS. People who used taVNS showed significant improvements in their stomach’s ability to accommodate and process a meal, according to a new study. The research was...
Nutrient deficiency in tumor cells attracts cells that suppress the immune system
by IDIBELL-Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute Some solid tumors have a very high growth rate, which often leads to a lack of vascularization due to the impossibility to develop, at the same time, the blood vessels that accompany and nourish it. The team of Dr. Cristina Muñoz Pinedo, from the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) and...
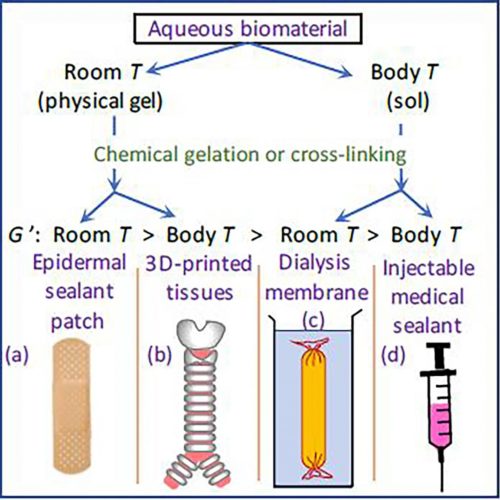
Adjusting processing temperature results in better hydrogels for biomedical applications
Using different temperatures creates sturdier hydrogels for tissue repair, surgical sealants and 3D printing AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS WASHINGTON, March 24, 2020 — Biohydrogels — biomaterials composed of polymer chains dispersed in water — have been studied closely by researchers for their potential use in biomedical applications, such as in tissue repair, as surgical sealants,...
Glimpse: How Electronic Tattoos Will Change The World — And Ourselves
It’s the stuff of cyberpunk science fiction — tattoos adorned with flashing lights and sophisticated circuitry. They’ll monitor our vitals, we’re told, and feed us personalized health advice in real time. They’ll wire our biology to the web, and put the internet of things at — on, in — our fingertips. They’ll enhance our five...
Stretchable, Conductive Hydrogel as a Biomedical Sensor
Researchers at King Abdullah University of Science & Technology in Saudi Arabia have developed an electrically conductive hydrogel that can flex, stretch, and self-heal when cut and reattached. The versatile material has potential in a variety of applications including wound healing patches, wearable electronics, and touch-sensitive robotics. The research team developed the new material by...
MELISA utilizes a smartphone for biomedical testing
In order to get bloodwork or urinalysis done, samples obtained from patients are typically sent off to a lab. Thanks to a new device that’s being developed at the University of South Florida, however, it may soon be possible to perform such analyses right in a doctor’s office. Presently, if a physician wants to test...