Researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina have formulated a vitamin K-based compound that, due to its unique structure and mechanism, eliminates medication-resistant epileptic seizures in mice tested to date. Credit: Sarah Pack, Medical University of South Carolina In the cover article of the June 11 issue of the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a...
Tag: <span>BMC Biotechnology.</span>
DRUG SHOWS PROMISE FOR FIGHTING RARE ALS
An experimental drug for a rare, inherited form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis has shown promise in a phase 1/phase 2 clinical trial, researchers report. The trial indicated that the experimental drug, known as tofersen, shows evidence of safety that warrants further investigation and lowers levels of a disease-causing protein in people with a type of...
Scientists scoff at Indian agency’s plan to have COVID-19 vaccine ready for use next month
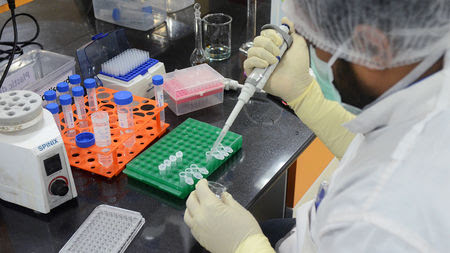
A scientist at work at the Serum Institute of India, which is working on COVID-19 vaccines. Two Indian companies have received the green light to start human trials of their candidate vaccines. By Sanjay KumarJul. 6, 2020 , 4:55 PM Science’s COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Pulitzer Center. NEW DELHI—The apparent speed at which...
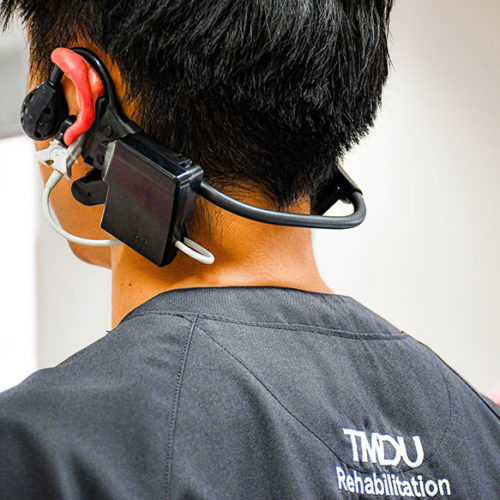
Kyocera Helps Develop Wearable for Remote Rehab Monitoring During COVID Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a slew of new challenges for clinical facilities, including how to deliver as much care as possible at a distance. The Department of Cardiovascular Medicine at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) Medical Hospital is working with Kyocera to be able to deliver rehab therapy to patients while closely monitoring...
Molecules that reduce ‘bad’ gut bacteria reverse narrowing of arteries in animal study
by The Scripps Research Institute Scientists at Scripps Research have developed molecules that can remodel the bacterial population of intestines to a healthier state and they have shown—through experiments in mice—that this reduces cholesterol levels and strongly inhibits the thickened-artery condition known as atherosclerosis. The scientists, who report their findings in Nature Biotechnology, created a...
Wearable patch may provide new treatment option for skin cancer
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Conventional melanoma therapies, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, suffer from the toxicity and side effects of repeated treatments due to the aggressive and recurrent nature of melanoma cells. Less invasive topical chemotherapies have emerged as alternatives, but their widespread uses have been hindered by both the painful size of the microneedles and...
Lancet Neurology publishes results of AFFiRiS’ Phase 1 trial with PD01A in Parkinson’s
Vienna, Austria, June 18, 2020 – AFFiRiS AG, a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing novel disease-modifying specific active immunotherapies (SAITs), today announced that detailed results of the phase 1 clinical program with its lead candidate PD01 in early Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients were published in the peer-reviewed journal The Lancet Neurology. The results of the long-term...
Research shows electroceutical fabric eradicates coronaviruses on contact
by Nicole Wilkins, Indiana University The electroceutical technology offers clinicians a non-antibiotic solution for infection risk reduction and potentially increases its value for use in face masks and possibly other surface treatments. Credit: Chandan Sen With the number of novel coronavirus infections at 4 million and growing as of May 10, use of personal protective...
Designing vaccines from artificial proteins
by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Vaccines are one of the most effective interventions to prevent the spreading of infectious diseases. They trigger the immune system to produce antibodies that protect the body against infection. However, we still lack efficacious vaccines for many important pathogens like the flu or dengue fever. “When a vaccine doesn’t...
Tiny RNA that should attack coronavirus diminish with age, disease
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University A group of tiny RNA that should attack the virus causing COVID-19 when it tries to infect the body are diminished with age and chronic health problems, a decrease that likely helps explain why older individuals and those with preexisting medical conditions are vulnerable populations, investigators report....