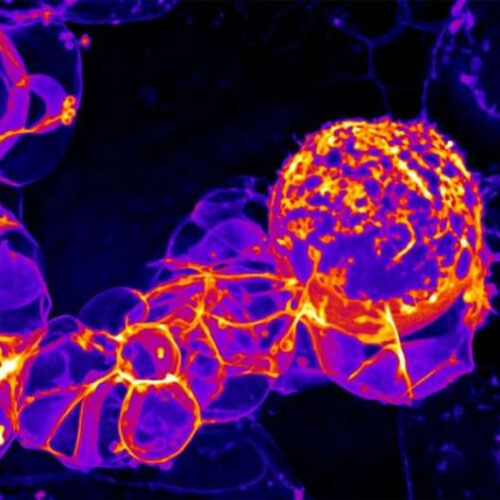
by University of Oregon A neural stem cell and its progeny are seen under high-resolution imagery of their cell membranes in research at the University of Oregon. The stem cell is the large cell shown near the center with progeny from previous divisions, like grapes in a cluster, trailing to the left. The image is shown in false...
Tag: <span>brain cells</span>
Salk scientists reveal how brain cells in Alzheimer’s go awry, lose their identity
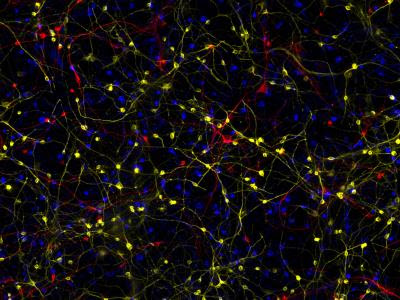
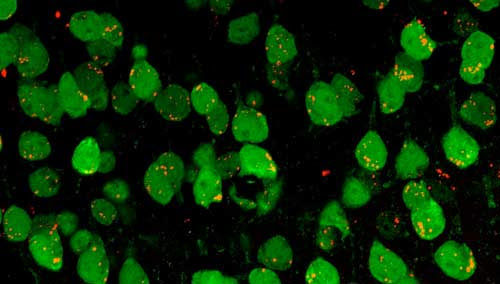
SALK INSTITUTE IMAGE: THIS IMAGE IS A COMPOSITE OF INDUCED NEURONS (BRAIN CELLS) FROM DIFFERENT INDIVIDUALS WITH ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE. CREDIT: SALK INSTITUTE LA JOLLA–(April 27, 2021) Despite the prevalence of Alzheimer’s, there are still no treatments, in part because it has been challenging to study how the disease develops. Now, scientists at the Salk Institute...
Brain cells decide on their own when to release pleasure hormone
by NYU Langone Health Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain In addition to smoothing out wrinkles, researchers have found that the drug Botox can reveal the inner workings of the brain. A new study used it to show that feedback from individual nerve cells controls the release of dopamine, a chemical messenger involved in motivation, memory, and movement. Such “self-regulation,”...
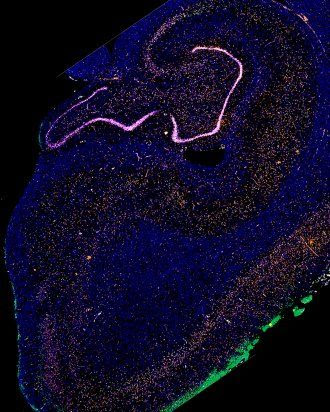
Targeting brain cells with light halts epileptic activity in mice
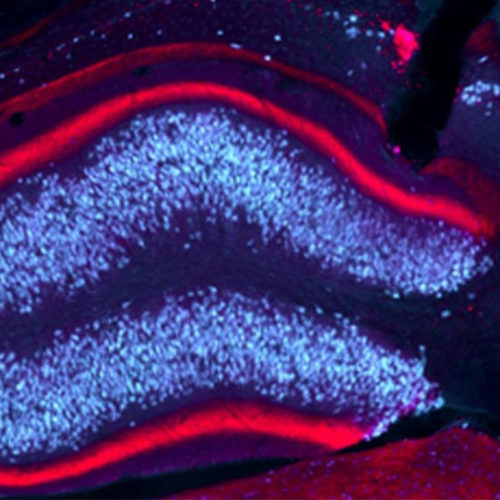
By Nick Lavars February 22, 2021 Image of the hippocampus in a mouse model of epilepsy, which researchers successfully targeted with light to prevent epileptic activity and its spread to other brain regionsMedical Center – University of Freiburg/AG HaasVIEW 1 IMAGES One of the ways scientists hope to deliver more precise and effective treatments for conditions afflicting...
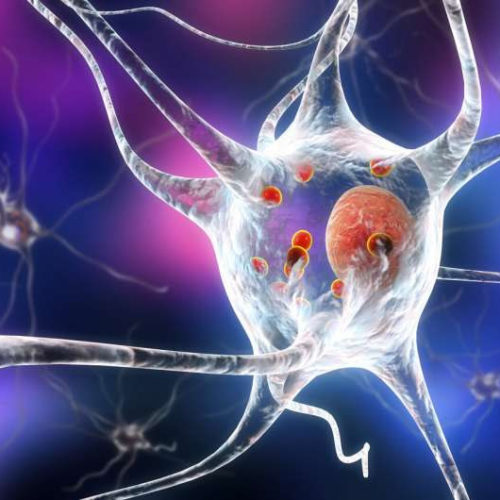
Function identified of ‘mystery protein’ that kills brain cells of people with Parkinson’s
by University of Cambridge 3D illustration showing neurons containing Lewy bodies small red spheres which are deposits of proteins accumulated in brain cells that cause their progressive degeneration. Credit: Kateryna Kon via Shutterstock A study published in Nature Communications today presents a compelling new evidence about what a key protein called alpha-synuclein actually does in neurons in the...
Study links brain cells to depression
by Frontiers Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new study further highlighting a potential physiological cause of clinical depression could guide future treatment options for this serious mental health disorder. Published in Frontiers in Psychiatry, researchers show differences between the cellular composition of the brain in depressed adults who died by suicide and non-psychiatric individuals who died suddenly by other...
Newly discovered subset of brain cells fight inflammation with instructions from the gut
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Astrocytes are the most abundant type of cells within the central nervous system (CNS), but they remain poorly characterized. Researchers have long assumed that astrocytes’ primary function is to provide nutrients and support for the brain’s more closely scrutinized nerve cells; over the years, however, increasing evidence has shown...
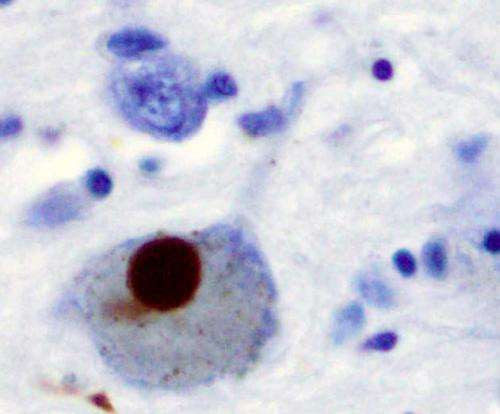
New Parkinson’s disease therapeutics discovered
by American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Immunohistochemistry for alpha-synuclein showing positive staining (brown) of an intraneural Lewy-body in the Substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Credit: Wikipedia Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers have discovered that the protein BMP5/7 offers promising therapeutics that could slow down or halt the progression of Parkinson’s disease. The findings were published...
Brain Cells Most Vulnerable to Alzheimer’s Disease Identified by Scientists
A major mystery in Alzheimer’s disease research is why some brain cells succumb to the creeping pathology of the disease years before symptoms first appear, while others seem impervious to the degeneration surrounding them until the disease’s final stages. Now, in a study published in Nature Neuroscience, a team of molecular biologists and neuropathologists from the UCSF Weill Institute for...
Could a nasal spray repair brain cells?
An inexpensive, accessible and non-invasive therapy for diseases and injuries of the brain may be slowly emerging: tiny particles called extracellular vesicles (EVs). Unlike stem cell therapies for repairing brain damage — which can be unsafe when tested in humans — EVs may safely regenerate brain cells and reduce inflammation, according to a recent study...