by Diego E. Rincon-Limas and Aaron N. Johnson, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Infectious or chronic diseases such as long COVID, Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury can cause inflammation in the brain, or neuroinflammation, that weakens muscles. While scientists are aware of this link between inflammation and muscle weakness, the molecules and processes involved have...
Tag: <span>brain inflammation</span>
New study shows COVID-19 can cause brain inflammation and small bleeds
By Rich Haridy April 03, 2022 The researchers found evidence of mild SARS-CoV-2 infections causing neuroinflammation, small bleeds in the brain and neuron damage Depositphotos A new study published in Nature Communications has offered the most comprehensive investigation to date into the effects of COVID-19 on the brain using nonhuman primates. The study found SARS-CoV-2 infection, regardless...
Study: New drug candidate reduced brain inflammation, protected against cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s mouse model
by National Institutes of Health Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain An anti-inflammatory drug candidate, known as 3,6′-dithiopomalidomide (DP) and designed by researchers at the National Institute on Aging (NIA), protected lab mice against cognitive decline by reducing brain inflammation. An international research team led by the NIA scientists has published their findings in Alzheimer’s and Dementia: The Journal...
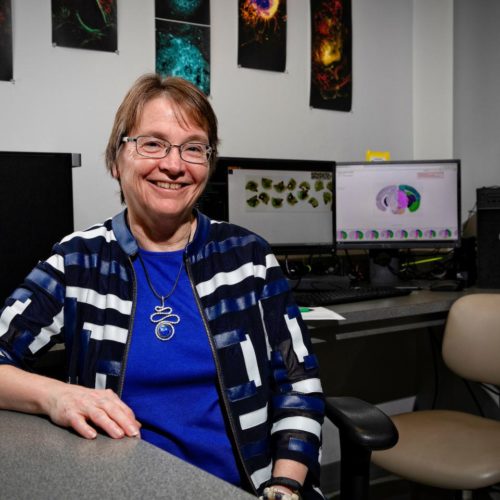
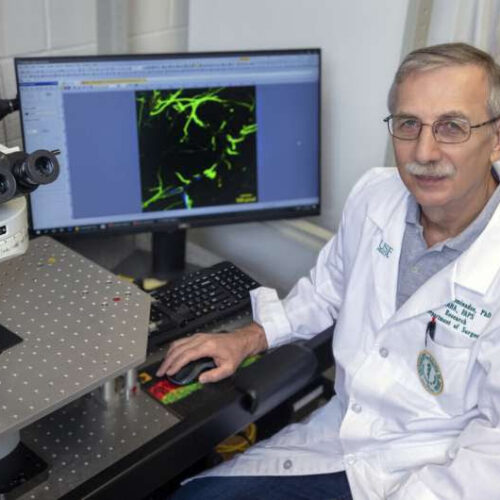
Blood plasma protein fibrinogen interacts directly with nerve cells to cause brain inflammation
by Anne Delotto Baier, University of South Florida David Lominadze, Ph.D., a professor of surgery and molecular pharmacology and physiology at the University of South Florida Health (USF Health) Morsani College of Medicine, investigates how microvascular changes induced by neuroinflammation may damage cognition, including short-term memory. Credit: USF Health/University of South Florida Neuroinflammatory diseases, including...
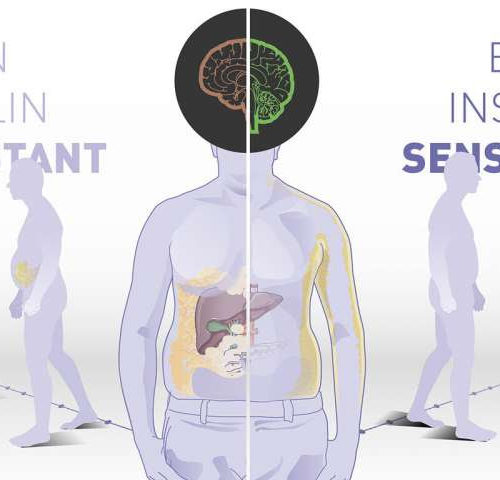
Brain insulin sensitivity determines body weight and fat distribution
by Deutsches Zentrum fuer Diabetesforschung DZD Just where fat is deposited in the body and to what degree a person may benefit from a lifestyle intervention depends, among other things, on how sensitive the brain is to insulin. If the person’s brain responds sensitively to the hormone, a significant amount of weight can be lost,...
First in-human study of drug targeting brain inflammation supports further development
University of Kentucky UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY LEXINGTON, Ky. (April 9, 2020) — Linda J. Van Eldik, director of the Sanders-Brown Center on Aging at the University of Kentucky, co-authored a paper reporting the first human clinical study of a drug candidate that suppresses injury and disease-induced inflammation of the brain. The paper was accepted in...
Brain Inflammation in Patients with Fibromyalgia
By Osman Shabir, M.Sc. Reviewed by Dr. Jennifer Logan, MD, MPH Fibromyalgia is a condition in which there is extensive chronic pain across the body with an increased pain response to pressure, which would normally not be painful. Central to the pathogenesis of fibromyalgia is impaired nociceptive (pain) signal processing in the nervous system. Therefore, fibromyalgia in its pure form is...
How does your brain take out the trash?
By Tim Newman Fact checked by Gianna D’Emilio In this Spotlight, we introduce the glymphatic system: the brain’s dedicated waste clearance system. Now implicated in various conditions, it is high time that we became acquainted. Many of us are relatively familiar with the lymphatic system; it performs a number of roles, one of which is...
Promising novel treatment against Alzheimer disease
New research conducted at the Lady Davis Institute (LDI) at the Jewish General Hospital reveals that a novel drug reverses memory deficits and stops Alzheimer disease pathology (AD) in an animal model. Importantly, this drug has already proven to be non-toxic for humans in a clinical setting and could, therefore, be brought quickly to trials...
Malicious brain cell identified
Surprising finding fills gap in understanding astrocytes’ role in brain disease SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INSTITUTE Astrocytes–the star-shaped cells of our brain–are very busy. Their job description includes maintaining the blood-brain barrier, removing excess neurotransmitters, repairing brain tissue and more. IMAGE: THIS IS JEROLD CHUN, M.D., PH.D., PROFESSOR AND SENIOR VICE PRESIDENT OF NEUROSCIENCE...
- 1
- 2