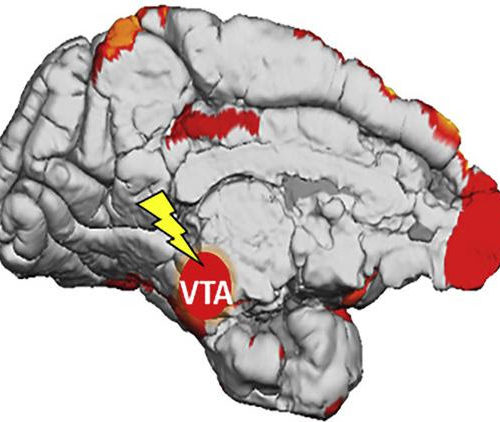
KU LEUVEN IMAGE: THE VENTRAL TEGMENTAL AREA CONTAINS, AMONG OTHERS, CELLS THAT PRODUCE DOPAMINE. CREDIT: NEURON Researchers uncovered for the first time what happens in animals’ brains when they learn from subconscious, visual stimuli. In time, this knowledge can lead to new treatments for a number of conditions. The study, a collaboration between KU Leuven, Massachusetts...
Tag: <span>brain</span>
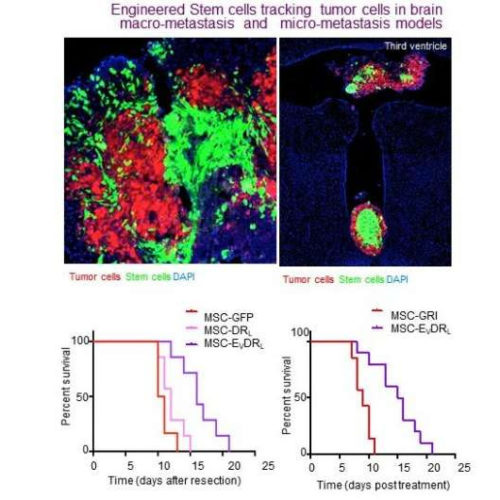
Engineered ‘off the shelf’ stem cells target breast cancer that metastasizes to the brain
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital Tumor cells (red) stem cells (green) and DAPI (blue) Credit: Khalid Shah lab, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Approximately 15-to-30 percent of patients with metastatic breast cancer have brain metastasis (BM), with basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) metastasizing to the brain most frequently. The prognosis for BLBC-BM patients is poor, as the blood-brain...
A new theory for how memories are stored in the brain
by University of Kent Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Research from the University of Kent has led to the development of the MeshCODE theory, a revolutionary new theory for understanding brain and memory function. This discovery may be the beginning of a new understanding of brain function and in treating brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s. In a...
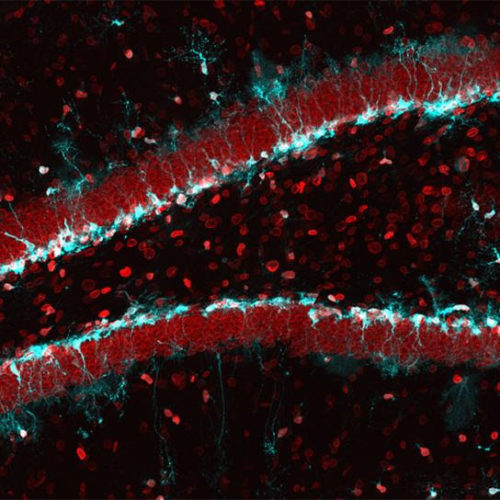
Reactivating aging stem cells in the brain
UNIVERSITY OF ZURICH IMAGE: STEM CELLS IN THE MOUSE HIPPOCAMPUS (IN BLUE): WITH INCREASING AGE, THEIR ABILITY TO FORM NEW NEURONS DECREASES AS THE AMOUNT OF THE NUCLEAR PROTEIN LAMIN B1 (IN RED) DROPS. CREDIT: KHADEESH BIN IMTIAZ, UNIVERSITY OF ZURICH The stem cells in our brain generate new neurons throughout life, for example in...
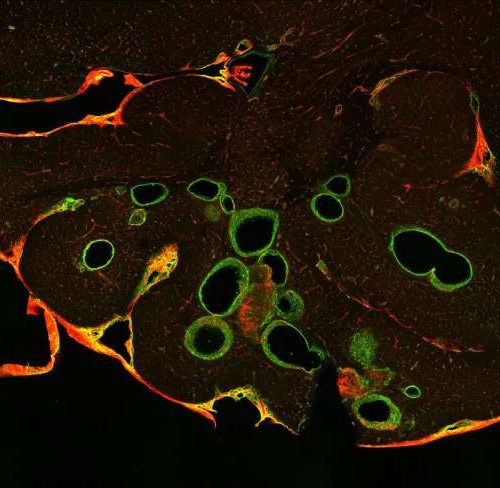
Beta blockers can repair malformed blood vessels in the brain
by Uppsala University Propranolol treatment contributes to reduced number and size of cerebral cavernous malformations. Panel A shows a brain section of vehicle treated mouse. The lesions are outlined in green. Credit: Joppe Oldenburg Propranolol, a drug that is efficacious against infantile haemangiomas (“strawberry naevi,” resembling birthmarks), can also be used to treat cerebral cavernous malformations,...
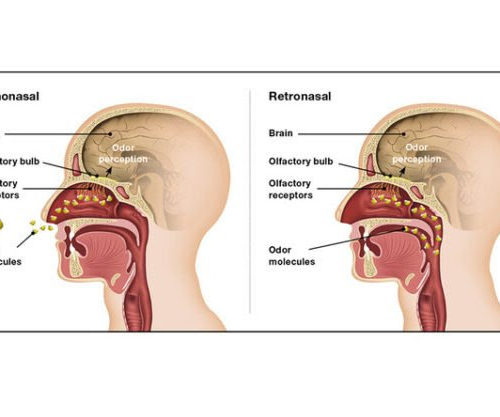
Taste and its two ways to the brain
There are a few ways we perceive food, and not all are particularly well-understood. We know that much of it happens in the olfactory bulb, a small lump of tissue between the eyes and behind the nose, but how the stimuli arrive at this part of the brain is still being worked out. How these...
How the ‘noise’ in our brain influences our behavior
by Max Planck Society Neural variability may provide a unique window into brain function. Credit: NomeVisualizzato & Cassidy Dickens, CC0 The brain’s neural activity is irregular, changing from one moment to the next. To date, this apparent “noise” has been thought to be due to random natural variations or measurement error. However, researchers at the Max Planck Institute...
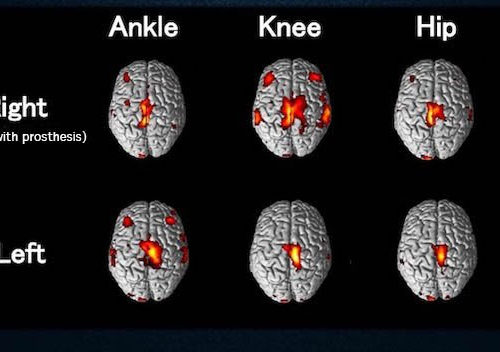
How having a disability can spur the brain to develop new abilities
Professor Kimitaka Nakazawa, a specialist in neurorehabilitation, first had the opportunity to study the brain activity of a Paralympic gold medalist in January 2016, when he visited a university pool in the United States as part of an NHK television program called “Chojin-tachi no Paralympic” [The superhuman Paralympians]. He was struck by what he could...
Brain’s ‘Background Noise’ May Hold Clues to Persistent Mysteries
By digging out signals hidden within the brain’s electrical chatter, scientists are getting new insights into sleep, aging and more. Olena Shmahalo/Quanta Magazine; noise generated by Thomas Donoghue Elizabeth Landau February 8, 2021 At a sleep research symposium in January 2020, Janna Lendner presented findings that hint at a way to look at people’s brain activity for signs of...
How the brain makes sense of touch
by Giorgia Guglielmi, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Credit: CC0 Public Domain EPFL researchers have identified specific neurons that help activate sensory processing in nearby nerve cells—a finding that could explain how the brain integrates signals necessary for tactile perception and learning. The ability to perceive touch sensations gives our brains a wealth of information about the environment,...