by Adam D Hines, The Conversation MAY 18, 2024 Credit: CC0 Public Domain Over 350 million surgeries are performed globally each year. For most of us, it’s likely at some point in our lives we’ll have to undergo a procedure that needs general anesthesia. Even though it is one of the safest medical practices, we...
Tag: <span>brain</span>
Dancing cells show how the brain awakens from anesthesia
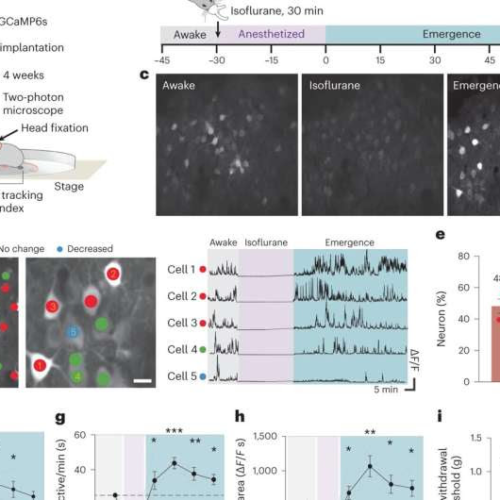
by Alison Satake, Mayo Clinic Neuronal hyperactivity occurs during emergence from general anesthesia. Credit: Nature Neuroscience (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01537-8According to a Mayo Clinic study published in Nature Neuroscience, the cells that act as the central nervous system’s first line of defense against harm also play a role in helping the brain awaken from anesthesia. This discovery...
Neurons help flush waste out of brain during sleep
Findings could lead to new approaches for Alzheimer’s, other neurological conditions by Marta Wegorzewska GETTY IMAGESResearchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that brain cell activity during sleep is responsible for propelling fluid into, through and out of the brain, cleaning it of debris. There lies a paradox in sleep....
A new model for understanding the brain and its interaction with the environment paves the way for more accurate diagnoses and treatments
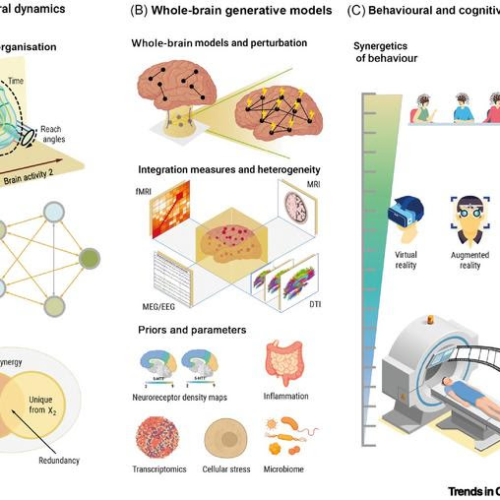
The study defines a new neuroscientific paradigm (synergistic model), which allows to better understand the complexity of the interactions between brain, body and environment and paves the way to being able to integrate different levels of brain diseases.Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITAT POMPEU FABRA – BARCELONA SYNERGETIC FRAMEWORK.CREDIT: TRENDS IN COGNITIVE SCIENCES How does our brain interact...
Drug repairs systems that remove Alzheimer’s-causing waste from the brain, study shows
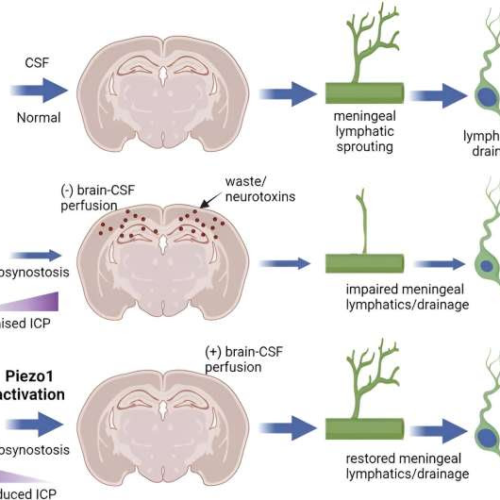
by Andrew Smith, Rutgers University Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Clinical Investigation (2023). DOI: 10.1172/JCI171468A team of Rutgers undergraduates has shown that an experimental drug known as Yoda1 may help drain cranial waste plus neurotoxins that cause Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. “The brain’s lymphatic system is one of the hottest research areas in...
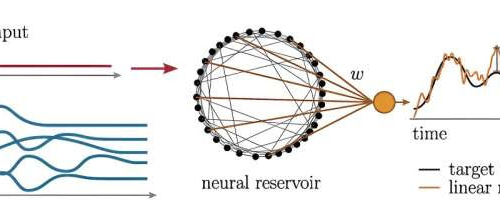
Neuronal diversity impacts the brain’s information processing
by Melissa Rohman, Northwestern University Spike threshold heterogeneity affects the function generation properties of spiking neural networks. (A) Reservoir computing architecture used for function generation. A pulse is fed into a recurrent neural network and a linear readout is trained to minimize the mean squared error between a target time-dependent function and a network output obtained...
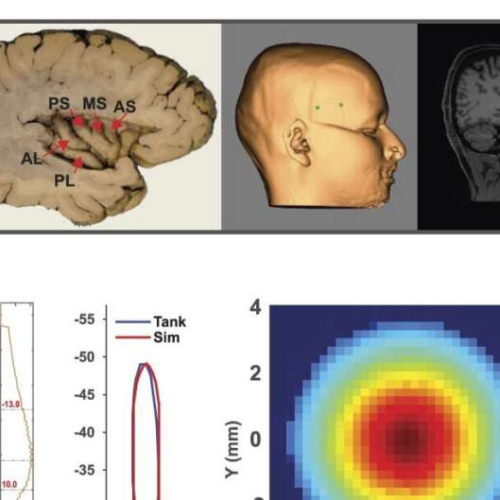
Scientists show focused ultrasound can reach deep into the brain to relieve pain
by Matt Chittum, Virginia Tech Targeting & acoustic modeling. Credit: Pain (2024). DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003171You feel a pain, so you pop a couple of ibuprofen or acetaminophen. If the pain is severe or chronic, you might be prescribed something stronger—an opioid pain killer that can be addictive under some circumstances. But what if you could ease pain...
Firing nerve fibers in the brain are supplied with energy on demand, shows study
by Kurt Bodenmüller, University of Zurich Cross section of nerve fibers in the mouse optic nerve. Credit: Zoe Looser and Aiman Saab, University of ZurichBrain function depends on the swift movement of electrical signals along axons, the long extensions of nerve cells that connect billions of brain cells. The nerve fibers are insulated by a fatty...
Old area in the brain turns out to be more important for vision than expected
by Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience Superior colliculus is involved in figure detection. (A) The stimulus types that were used for the figure detection task. The stimulus consisted of a static grating that differed from the background in either contrast (top left), orientation (top right), or phase (bottom). (B) Two example stimuli (both orientation task). Licking on...
Scientists Extend Life Span in Mice by Restoring This Brain-Body Connection
By Shelly Fan It’s easy to vilify body fat as just a layer of unwanted padding sitting silently beneath the skin. But these cells are surprisingly active. Beyond being storage containers for energy, they pump out a wide range of hormones that interact with multiple organs to control metabolism, immune responses, and even reproduction. They...