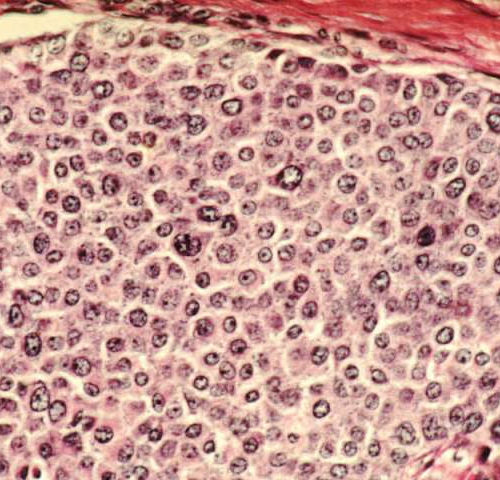
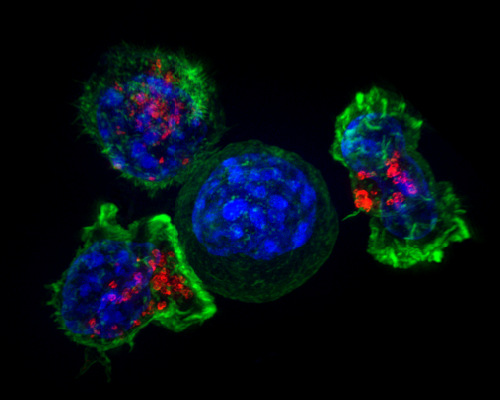
by University of Southern California The research team has discovered that akt-type cancer cells, which are common in breast cancer, above, can be killed by a common milk sugar, galactose. Credit: Wikimedia Commons Like any cells in the body, cancer cells need sugar—namely glucose—to fuel cell proliferation and growth. Cancer cells in particular metabolize glucose...
Tag: <span>cancer cells</span>
How cells’ ‘lava lamp’ effect could make cancer drugs more powerful
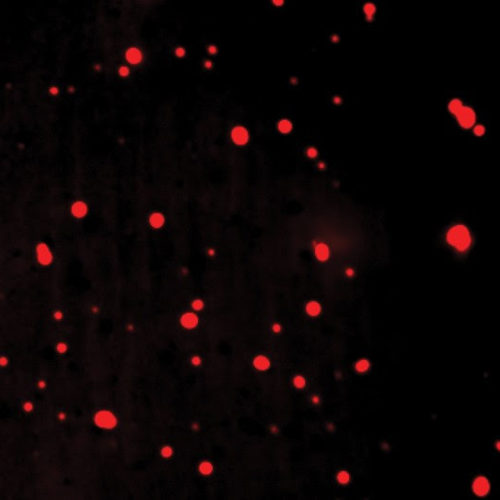
Discovery that synthetic compounds form concentrated droplets inside cells could shake up drug development — including the hunt for coronavirus treatments. Fluorescently tagged molecules of the cancer drug cisplatin clump up inside droplets in cells.Credit: Isaac Klein/Whitehead Institute There’s a long-standing assumption in the pharmaceutical industry that when drug molecules enter a cell, they spread...
Early clinical trial supports tumor cell-based vaccine for mantle cell lymphoma
by Rockefeller University Press A phase I/II clinical trial by researchers at Stanford University suggests that vaccines prepared from a patient’s own tumor cells may prevent the incurable blood cancer mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) from returning after treatment. The study, which will be published June 19 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), reveals that...
Cancer cells adapt to lack of key nutrient, posing potential problems for drugmakers
Cancer can adapt its metabolism in a way that could overcome lipid-focused therapies being developed by drug companies, a University of Toronto study has found. “Several clinical trials have failed because metabolism is such an adaptive process by which cancer cells gain drug resistance,” says Michael Aregger, a co-lead author and research associate who is...
Scientists develop blood test to help improve liver cancer screening
by National Cancer Institute Scientists have developed a new test that can help identify people who are likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. The approach uses a simple blood test to check for the patient’s previous exposure to certain viruses. A study of the new approach was led...
Some types of prostate cancer may not be as aggressive as originally thought
by University of California, Los Angeles Researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center analyzed gene-expression patterns in the most aggressive prostate cancer grade group—known as Gleason grade group 5—and found that this grade of cancer can actually be subdivided into four subtypes with distinct differences. The findings may affect how people are treated for...
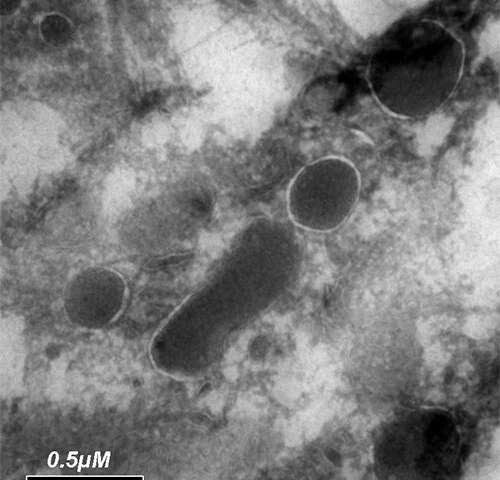
Cells inside cells: the bacteria that live in cancer cells
by Weizmann Institute of Science Cancer cells are comfy havens for bacteria. That conclusion arises from a rigorous study of over 1,000 tumor samples of different human cancers. The study, headed by researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, found bacteria living inside the cells of all the cancer types—from brain to bone to breast...
Greedy for glucose: Cancer cells rely on a primeval energy-producing pathway to proliferate and spread
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress To fuel their rapid proliferation, tumor cells rely on glycolysis, a primordial metabolic pathway that is easily exploited by cancers to gain energy to grow—and spread. Glycolysis is the oldest form of energy production in living cells. It has been around for billions of years, having emerged before oxygen...
New biomarker could flag tumors that are sensitive to common diabetes drug
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (May 19, 2020) — A newly identified biomarker could help scientists pinpoint which cancers are vulnerable to treatment with biguanides, a common class of medications used to control blood sugar in Type 2 diabetes. Biguanides, particularly a medication called metformin, have long been of interest to cancer researchers because of their ability...
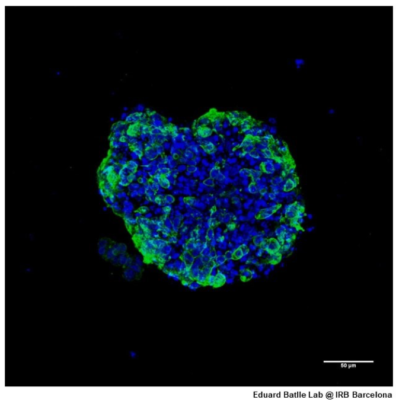
First Epigenetic Study in 3D Human Cancer Cells
Frequently, promising cancer therapies fail when applied to patients in the real clinical setting. This occurs despite many of these new treatments demonstrating promising results at the preclinical stage in the lab. One explanation is that many of the tumor models used in early research phases are established cell lines that have been growing for...