Tweaking the adenovirus spike protein induces a more robust immune reaction for a cancer vaccine against gastric, pancreatic, esophageal and colon malignancies in animal models. THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIVERSITY PHILADELPHIA – Jefferson researchers developing a cancer vaccine to prevent recurrences of gastric, pancreatic, esophageal and colon cancers have added a component that would make the vaccine...
Tag: <span>cancers</span>
Anorexia may stunt young women’s growth
Study highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment WASHINGTON–Girls with anorexia nervosa can have stunted growth and may not reach their full height potential, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. Anorexia nervosa is a condition in which a person loses an unhealthy amount of...
Too Much Rice Could Kill: Study Shows Arsenic Exposure Could Lead to Fatal Diseases
A study found that eating too much rice could lead to heart disease and death. A research team from the University of Manchester and the University of Salford analyzed the link between rice consumption and heart diseases in England and Wales, which are caused by arsenic exposure, according to Daily Mail. The research findings were...
Adverse effects from cancer drug trials explained
NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY A team of researchers investigating how a certain type of drugs can kill cells has discovered that these drugs can do more harm than good when used in combination with other cancer treatments. The researchers wanted to know more about how the drugs, which are called pan-Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL-specific...
Precision medicine identifies key recurring mutation in head and neck cancers
by University of California – San Diego Head and neck cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) account for the majority of these cases. In a new study, based on preclinical research and published July 29, 2020 in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, a journal of the American...
New, remote weight-loss method helped slash pounds
Losing weight during COVID-19 pandemic is urgent as obesity increases risk of severe disease and death NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY CHICAGO — Losing weight during the COVID-19 pandemic has increasing urgency because obesity increases the risk of severe disease and death. Two-thirds of U.S. adults are overweight or obese, according to the Centers for Disease Control and...
NUS researchers uncover a novel protein which drives cancer progression
PRINT E-MAIL Cancers arise when the genetic code of normal cells is altered, causing excessive growth. Researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have discovered a protein that drives the growth of cancers of the esophagus or liver by altering the genetic code in a...
The New JAK inhibitor Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) Shows Promise for Psoriatic Arthritis
Approved in 2019 for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, the drug may offer an oral alternative to infused or injected biologics. The JAK inhibitor upadacitinib (Rinvoq) became a treatment option in 2019 for people with rheumatoid arthritis(RA) who had not responded well to methotrexate, the disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) that is the first-line treatment for...
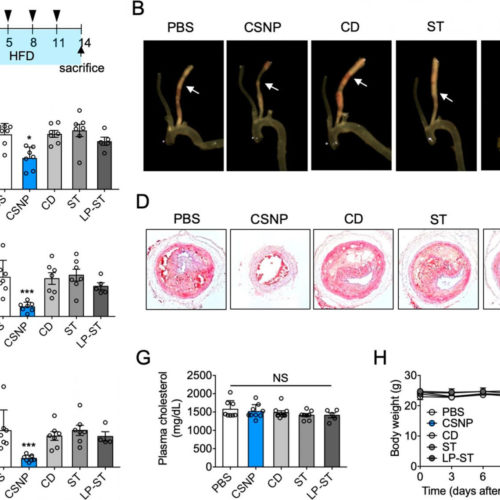
New nanoparticle drug combination for atherosclerosis
THE KOREA ADVANCED INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KAIST) CREDIT: PROFESSOR JI-HO PARK, KAIST Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation. The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory,...
Scientists reveal how mutations in metabolism can drive cancers
by Yale University Our cells have several ways to repair DNA that breaks when the cells divide. However, genetic mutations can disable these DNA repair mechanisms, destabilize the cells, and trigger cancer. In a paper published today in the journal Nature, Yale Cancer Center (YCC) scientists have identified mutations in metabolite-producing genes as a disruption...