August 29, 2024 by University of Southampton Scientists are on the verge of a cancer breakthrough after working out how the body’s immune system targets cells devastated by the disease. A new study has discovered that our natural killer cells, from the immune system which protect against disease and infections, instinctively recognize and attack a...
Tag: <span>cells</span>
Discovery of key protein that helps cells maintain their identity
News Release 13-Aug-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationUniversity of Copenhagen – The Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences The study, published in the journal Cell, marks a step forward in the field of epigenetics and its impact on health and disease. Epigenetics, the study of how genes are turned on or off without changing the DNA itself, is...
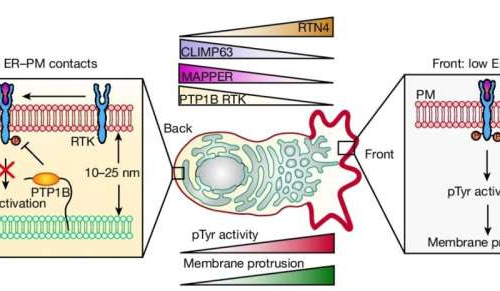
Study pushes understanding of how cells migrate
Cell & MicrobiologyHomeBiologyMolecular & Computational biology JUNE 24, 2024 by Jim Schnabel, Cornell University Model of how ER–PM contact gradients generate the observed gradient of pTyr signaling. Credit: Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07527-5Interactions between two key structures within cells help establish the front-to-back “polarity” that is essential to cell migration, according to a new study by...
Cannibalistic cells could provide an edge in future cancer treatments
By Paul McClure Researchers have added an active Rac2 protein to macrophages, causing them to cannibalize other immune cells Depositphotos Following a trail of evidence that started with a study of fruit flies nearly 25 years ago, researchers have found adding a hyperactive form of the protein Rac2 to macrophages, immune cells that eat pathogens, causes...
Cells wearing ‘backpacks’ shrink traumatic brain injury lesions by 56%
By Paul McClure Researchers have fitted “backpacks” to inflammatory cells to treat traumatic brain injury DepositphotosBy fitting microparticle ‘backpacks’ to important inflammatory cells called macrophages, researchers significantly reduced lesion size and inflammation caused by traumatic brain injury. Working with biology rather than against it, this novel approach has the potential to be an effective treatment for...
New insights into what happens in cells in early Alzheimer’s
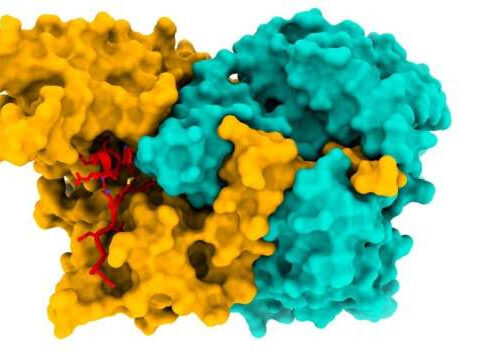
by European Synchrotron Radiation Facility The structure of the ACAD9-ECSIT_CTER complex (ECSIT in red). An international team of researchers, led by the ESRF, have elucidated the structure of the ACAD9-ECSIT_CTER complex, by using cryo-EM techniques. This complex is important in the correct functioning of the energy-producing machinery in mitochondria. Credit: ESRF/M. Soler López. Credit: ESRF/M. Soler...
Study links back pain to a subtype of cells in spinal ‘shock absorbers’
by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new Cedars-Sinai study might have cracked the mystery surrounding the cause of a specific type of back pain. Almost 40% of the adult population experiences low back pain due to degenerating disks in the spine, but medical science hasn’t understood exactly why the disks become painful. In...
New work sheds light on inner working of cells
Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF GALWAY HIGH RESOLUTION VISUALIZATION OF CELL COMPONENTS USING THREE CHEMICAL PROBES CREDIT: CÚRAM/PAU FARRAS CÚRAM researchers at University of Galway, together with colleagues at the Centre for Molecular Nanometrology at University of Strathclyde have published work unveiling the inner workings of cells. Published recently in the German scientific journal Angewandte Chemie,...
Engineered approach to remove protein aggregates from cells
UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG IMAGE: ARTHUR FISCHBACH AND THOMAS NYSTRÖM, SAHLGRENSKA ACADEMY AT THE UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG. CREDIT: PHOTO BY UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG. Protein aggregates accumulate during aging and are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. A new study by the Nyström lab at Gothenburg University, in collaboration with the Max Planck...
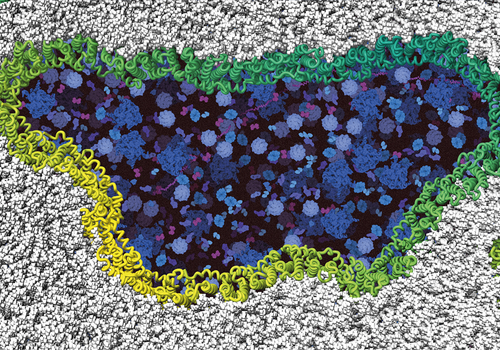
Under control to the very end – how our cells kill themselves
UNIVERSITY OF BASEL IMAGE: NINJURIN-1 PROTEINS ASSEMBLE (GREEN/YELLOW) INTO FILAMENTS AND RUPTURE THE CELL MEMBRANE (GRAY) UNTIL THE CELL DISINTEGRATES COMPLETELY. INTRACELLULAR COMPONENTS ARE SHOWN IN BLUE. CREDIT: BIOZENTRUM, UNIVERSITY OF BASEL Every day, millions of cells die in our body. Other than generally assumed, cells do not simply burst at the end of their...