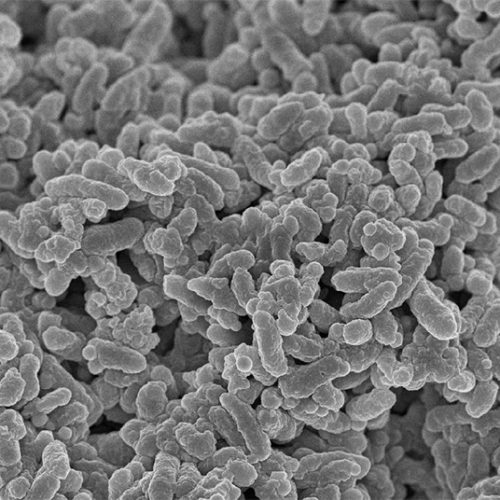
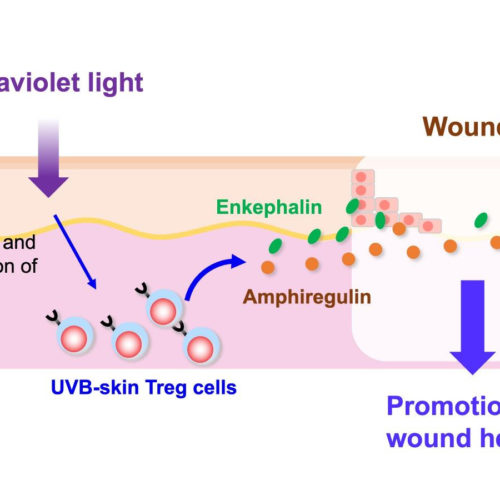
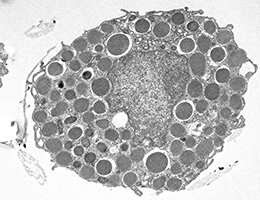
Proenkephalin+ regulatory T cells expanded by ultraviolet B exposure maintain skin homeostasis with a healing function NAGOYA CITY UNIVERSITY UVB IRRADIATION INDUCES PROLIFERATION AND ACTIVATION OF SKIN TREG CELLS. UVB-EXPANDED SKIN TREG (UVB-SKIN TREG) CELLS PROMOTE WOUND HEALING BY PRODUCING ENKEPHALIN AND AMPHIREGULIN(AREG), WHICH ENHANCE KERATINOCYTE GROWTH/PROLIFERATION TO REPAIR… view more CREDIT: DEPARTMENT IMMUNOLOGY, NAGOYA...
Tag: <span>cells</span>
Breast cancer cells use message-carrying vesicles to send oncogenic stimuli to normal cells
by The Wistar Institute According to a study by The Wistar Institute, breast cancer cells starved for oxygen send out messages that induce oncogenic changes in surrounding normal epithelial cells. These messages are packaged into particles called extracellular vesicles (EVs) and reprogram mitochondrial shape and position within the recipient normal cells to ultimately promote deregulated...
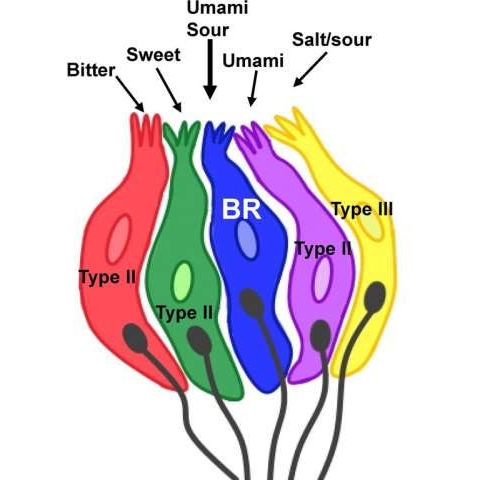
New type of taste cell discovered in taste buds
by Public Library of Science Most taste cells selectively respond to a specific stimulus type while broadly responsive cells respond to multiple taste qualities. Credit: Jhanna Flora and Kathryn Medler Our mouths may be home to a newly discovered set of multi-tasking taste cells that—unlike most known taste cells, which detect individual tastes—are capable of...
2 immunotherapies merged into single, more effective treatment
Mouse study suggests strategy may work against variety of cancers WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RESEARCHERS AT WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IN ST. LOUIS HAVE COMBINED TWO TYPES OF IMMUNOTHERAPY INTO A SINGLE TREATMENT THAT MAY BE MORE EFFECTIVE AND POSSIBLY SAFER THAN CURRENT… view more CREDIT: JULIA WAGNER Some of the most promising...
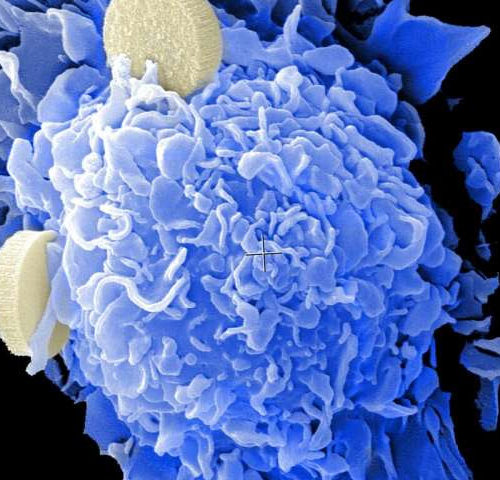
The immune system: Knocked off balance
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich The immune system: Knocked off balanceInstead of protecting us, the immune system can sometimes go awry, as in the case of autoimmune diseases and allergies. An LMU team has dissected how mast cells regulate their calcium levels to keep the immune response under control. Credit: IMCES UK Essen/LMU Instead...
How a memory game could help us understand brain injury
After a traumatic brain injury, why do some people regain skills quickly while others face long-lasting setbacks? Boston University neuroscientist Jerry Chen of BU’s Center for Systems Neuroscience and colleagues have been trying to answer this question by understanding which parts of the brain process sensory information and which remember different skills. The latest research...
Synthetic Melanin Protects from Radiation Damage
JULY 14TH, 2020 SIAVASH PARKHIDEHCARDIAC SURGERY, DENTISTRY, DERMATOLOGY, MATERIALS, NUCLEAR MEDICINE, ONCOLOGY, ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY, PUBLIC HEALTH, RADIATION ONCOLOGY, RADIOLOGY, SPACE MEDICINE Researchers at Northwestern University have developed a new biomaterial, selenomelanin, that can help protect people from radiation. The new substance, chemically synthesized and produced by bacteria, helps protect cells from radiation more effectively than...
Study finds fatty acid that kills cancer cells
by Washington State University Researchers have demonstrated that a fatty acid called dihomogamma-linolenic acid, or DGLA, can kill human cancer cells. The study, published in Developmental Cell on July 10, found that DGLA can induce ferroptosis in an animal model and in actual human cancer cells. Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent type of cell death that...
Adaptive therapy based on Darwin’s evolutionary principles could help fight cancer
by Avni Shah, University of Southern California Computational models developed by USC researchers show adaptively controlling tumor cell populations to keep them in competition can more effectively treat cancer. Evolutionary theory is at the crux of civilization, from the trees that populate our forests to the animals in our backyards. Little by little, over time,...
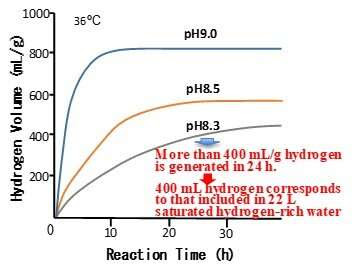
Antioxidant agent may prevent chronic kidney disease and Parkinson’s disease
Oxidative stress is the result of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and can be damaging to cells and tissues. In a new study, researchers from Osaka University developed a novel dietary silicon (Si)-based antioxidant agent that suppressed the development and progression of kidney failure and Parkinson’s disease in rodents. ROS are generated as a result...