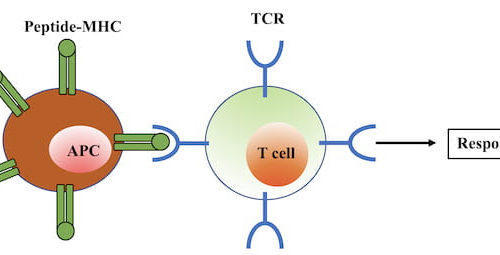
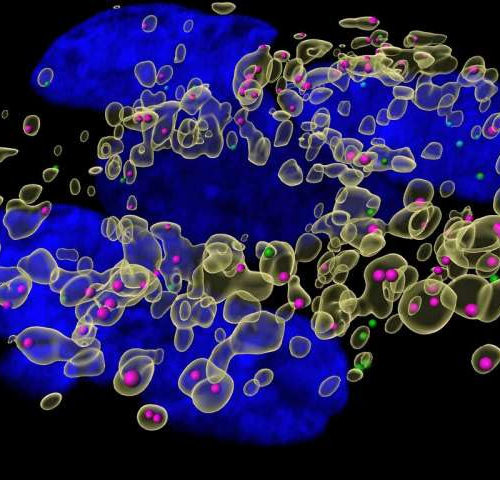
This news or article is intended for readers with certain scientific or professional knowledge in the field. Like finding that needle in the haystack every time, your T cells manage what seems like an improbable task: quickly finding a few invaders among the many imposters in your body to trigger its immune response. T cells...
Tag: <span>cells</span>
A sugar hit to help destroy cancer cells
by University of Southern California The research team has discovered that akt-type cancer cells, which are common in breast cancer, above, can be killed by a common milk sugar, galactose. Credit: Wikimedia Commons Like any cells in the body, cancer cells need sugar—namely glucose—to fuel cell proliferation and growth. Cancer cells in particular metabolize glucose...
Texas A&M researchers light cells using nanosheets for cancer treatment
A 2D nanosheet developed by scientists in the Department of Biomedical Engineering could be used to control cell response via light Scientists in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University are developing new ways to advance the field of regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. They are developing a 2D nanosheet that is 1,000...
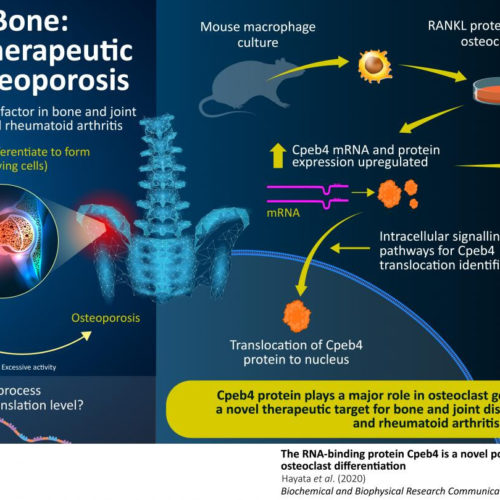
Down to the bone: Understanding how bone-dissolving cells are generated
Scientists explain the role of a certain protein in the generation of cells critical to bone maintenance Chronic bone and joint diseases, such as osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis, affect millions of people worldwide, particularly the elderly, degrading their quality of life. An important factor in both of these diseases is the excessive activity of bone-dissolving...
Teens can donate blood, but may need iron supplements after
by Alan Mozes, Healthday Reporter The concern comes as 16- to 18-year-olds have emerged as one of the fastest-growing groups of blood donors nationwide. But this study of nearly 31,000 teens who gave blood more than once between 2016 and 2018 found that roughly one in 10 were already iron-deficient when they donated for the...
Researchers discover key player in hepatitis A virus infection
by University of North Carolina Health Care Hepatitus A virus particles (pink) trapped in lysosomes (yellow intracellular organelles), unable to initiate replication in the cytoplasm of cells due to UCGC enzyme being knocked out. Credit: Maryna Kapustina, PhD, UNC School of Medicine How hepatitis A virus (HAV) manages to enter liver cells called hepatocytes and...
Brown, white and beige: understanding your body’s different fat cells could help with weight loss
by Trust Diya, The Conversation We know that carrying excess fat is bad for us and can contribute to a number of diseases, such as diabetes. But not all fat is created equal. While certain types of fat cells can accumulate in our bodies and cause health problems, other types have evolved to turn fuel...
Novel respiratory cell changes identified from cigarette smoke exposure
by Boston University School of Medicine Cigarette smoking changes the types of cells that are present in the respiratory track and some biological processes necessary for detoxification of cigarette smoke are restricted to specific types of cells. “Our study describes novel respiratory cell changes that result from cigarette smoke exposure that may be associated with...
‘EATER CELLS’ MAY PREVENT EVEN WORSE DAMAGE AFTER HEART ATTACK
POSTED BY JULIA EVANGELOU STRAIT-WUSTL Boosting the activity of specific immune cells in the heart after a heart attack can protect against developing heart failure, according to research with mice. Patients with heart failure, an invariably fatal condition, tire easily and become breathless from everyday activities because the heart muscle has lost the ability to pump...
Scientists discover how the molecule-sorting station in our cells is formed and maintained
New mechanism to explain how the cell organelle that sorts and distributes substances entering a cell is formed and maintained TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE The cells in our body are workshops that continuously operate to produce and process substances to keep us going. When a substance enters a cell for processing, it is surrounded by...