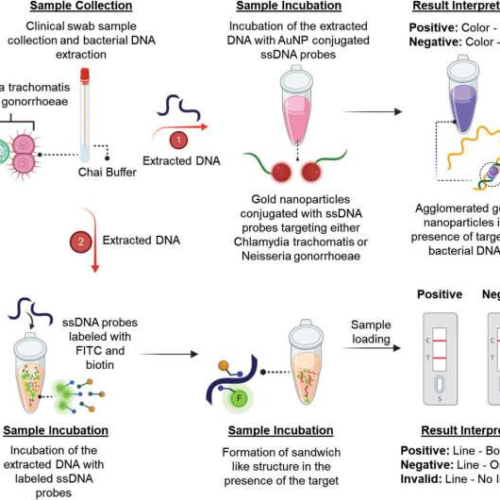
by Ashley WennersHerron, Pennsylvania State University Schematic representation of two approaches based on changes in absorbance and lateral flow methods, utilizing novel oligonucleotide probes targeted toward Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, for the clinical determination of chlamydia and gonorrhea. The addition of genetic material (bacterial DNA from either Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae) will result in...
Tag: <span>chlamydia</span>
Chlamydia’s stealthy cloaking device identified
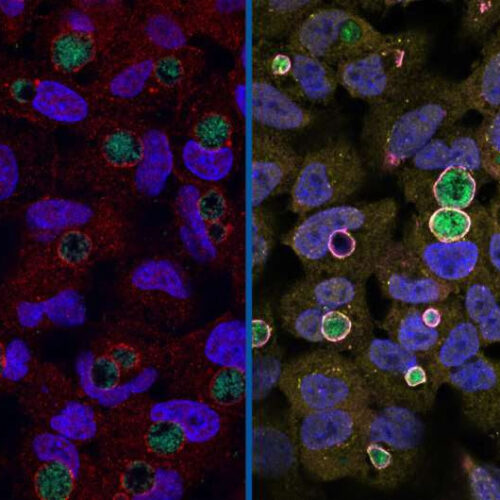
by Duke University At left: A wild type Chlamydia (green) surrounded by the GarD protein (red) that cloaks it from detection inside human cells. Right: Chlamydia with GarD knocked out (green) are enveloped by the antimicrobial proteins ubiquitin (yellow) and RNF213 (magenta). Credit: Stephen C. Walsh, Duke University Chlamydia, the leading cause of sexually transmitted...
New hypothesis proposed for how chlamydia might increase cancer and ectopic pregnancy risk
A review of evidence by researchers at the University of Bristol and University of Edinburgh has suggested a possible new means by which chlamydia could lead to an increased risk of cancer and ectopic pregnancy. The hypothesis also provides a possible explanation for how pelvic inflammatory disease may be triggered in some women. The review, published in...
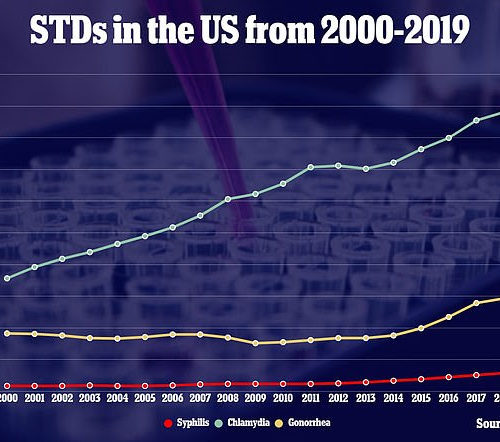
STDs reach all-time in the US for sixth consecutive year with 2.5 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis
By MARY KEKATOS SENIOR HEALTH REPORTER FOR DAILYMAIL.COM PUBLISHED: 16:29 EDT, 13 April 2021 | UPDATED: 17:40 EDT, 13 April 2021 The number of sexually transmitted diseases reached an all-time high in the U.S. for the sixth consecutive year, a new report finds. In 2019, there were 2.5 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis, the three most commonly reported...
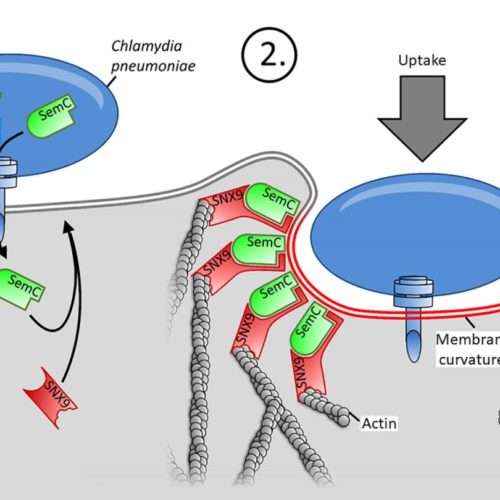
Chlamydia build their own entrance into human cells
Infection biology: Publication in PNAS HEINRICH-HEINE UNIVERSITY DUESSELDORF Together with scientists from Paris and Munich, a team of researchers working under Prof. Dr. Johannes Hegemann and Dr. Katja Moelleken has published these findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS). There are two types of...
Most common 3 STDs on the rise, according to CDC report
By Tim Newman Fact checked by Paula Field According to a report published this week by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the number of people with chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis is rising. Yesterday, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) releasedits annual Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance Report, containing data from 2018. Yesterday,...
FDA Gives Thumbs Up To 2 New Extragenital Tests For Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the marketing of two extra genital diagnostic testings for the sexually transmitted infections chlamydia and gonorrhea. FDA Clears 2 New STI Testing Devices The Aptima Combo 2 Assay and the Xpert CT/NG can detect the presence of the bacteria Chlamydiatrachomatis and Neisseria gonnorrhoeae through the examination of extragenital specimens. The two devices are the first to...
Syphilis rates soar across the US – with cases up by 50 percent in hot spots for the STD
For the fourth year in a row, rates of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia all hit a record high in the US in 2017 California has one of the highest rates of the syphilis Palm Springs, California has a rate over 10-times higher than the national average A health official from the county Palm Springs resides in says that a false sense of security...
A cure for chlamydia? Scientists discover key genes that control our immune response to the infection and could pave the way for new treatments
‘Switching off’ two key genes makes immune cells more susceptible to infection The genes could be a useful target for new chlamydia therapies, helping to combat antibiotic resistance that increasingly limits STI treatment options The researcher’s model demonstrates how chlamydia interacts with our immune system, which could also have important implications for other infections Scientists may...