by University of Nottingham Credit: CC0 Public Domain Exercise increases the body’s own cannabis-like substances, which in turn helps reduce inflammation and could potentially help treat certain conditions such as arthritis, cancer and heart disease. In a new study, published in Gut Microbes, experts from the University of Nottingham found that exercise intervention in people with arthritis, did not...
Tag: <span>chronic inflammation</span>
Landmark study points to source of rapid aging, chronic inflammation in people living with HIV
by Ryan O’byrne, University of Alberta Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry Shokrollah Elahi led a new study showing that short-lived white blood cells called neutrophils play a role in impaired T cell functions and counts in people with HIV, as well as the chronic inflammation that is common with the virus. Credit: Najmeh Bozorgmehr In...
Stem Cell Transplantation to Treat Chronic Inflammation and Frailty
Today’s open access commentary is a good companion piece to a recent paper covering the use of mesenchymal stem cell therapies to suppress age-related chronic inflammation. These first-generation stem cell therapies have proven to be unreliable when it comes to the original goal of regeneration of organ function, but they do reliably reduce excessive inflammation for some months. Transplanted stem...
Chronic Inflammation Negatively Impacts Proteostasis in Aging Tissues
Proteostasis describes the steady-state of a cell, maintaining an appropriate balance of various forms of protein machinery in order to enable continued normal function. With advancing age, proteostasis becomes disrupted in numerous complicated ways. This is a downstream outcome of underlying molecular damage, the reactions to that damage, and the immediate consequences of that damage....
HIV: An antidiabetic drug to reduce chronic inflammation
UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL HOSPITAL RESEARCH CENTRE (CRCHUM) Metformin, a drug used to treat type-2 diabetes, could help reduce chronic inflammation in people living with HIV (PLWH) who are being treated with antiretroviral therapy (ART), according to researchers at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM). Although ART has helped improved the health of PLWH,...
Immune protein may link chronic inflammation and frailty in older adults
by Johns Hopkins University Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have identified an immune system protein called interleukin-6 as a possible link between chronic inflammation and frailty in older adults. Credit: Public domain image Chronic inflammation in people age 65 and older may be marked by frequent infections, pain, injuries and slow healing wounds. To make matters worse, the negative...
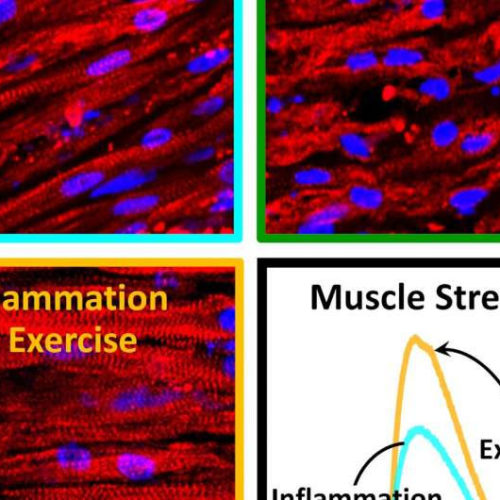
Exercising muscle combats chronic inflammation on its own
by Duke University School of Nursing Long, thin, well-defined muscle fibers (top left) are in shambles after prolonged inflammation (top right), but maintain their structure (bottom left) and strength (bottom right) when exercised during the inflammation. Credit: Zhaowei Chen, Duke University Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that human muscle has an innate ability to...
Likelihood of severe and ‘long’ COVID may be established very early on following infection
by Craig Brierley, University of Cambridge SARS-CoV-2 virus particles are shown emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab Credit: NIH Image Gallery New research provides important insights into the role played by the immune system in preventing—and in some cases increasing the severity of—COVID-19 symptoms in patients. It also finds clues to why...
Opening a new door into kinder, gentler therapies for chronic inflammation
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress A structural model of TNFR2 and the antibody agonist. Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) A naturally occurring antibody capable of stimulating the body’s immune-suppressing regulatory T cells has been discovered by a team of Harvard scientists, a finding...
A balancing act between immunity and longevity
by Max Planck Society As we age, the immune system gradually becomes impaired. One aspect of this impairment is chronic inflammation in the elderly, which means that the immune system is constantly active and sends out inflammatory substances. Such chronic inflammation is associated with multiple age-related diseases including arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease, and impaired immune...