by University of Colorado at Boulder A lab scientist scans bar codes on saliva samples collected from members of the CU Boulder community. Credit: Glenn Asakawa/CU Boulder A few “super carriers” with off-the-charts viral loads are likely responsible for the bulk of COVID-19 transmissions, while about half of infected people aren’t contagious at all at the...
Tag: <span>Covid-19 virus</span>
Remdesivir disrupts COVID-19 virus better than other similar drugs: study
by Emily Ayshford, University of Chicago SARS-CoV-2 (shown here in an electron microscopy image). Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, NIH In the treatment of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, antiviral drug remdesivir has emerged as a promising candidate. Remdesivir works by disrupting the virus’s ability to replicate, but its exact mechanism has remained...
New virtual screening strategy identifies existing drug that inhibits Covid-19 virus
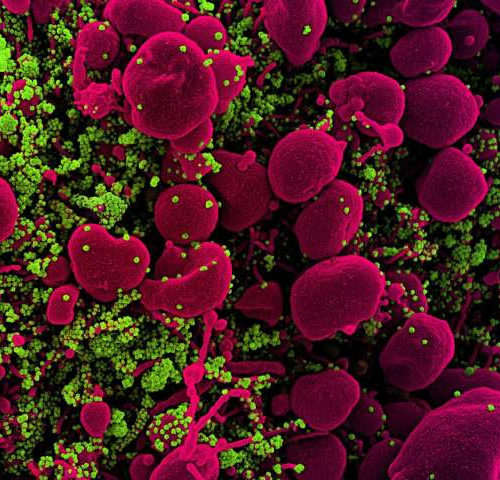
by Public Library of Science Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (pink) heavily infected with SARS-COV-2 virus particles (green), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/NIH, 2020 (CC0) A novel computational drug screening strategy combined with lab...