by Lancet Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Two years after infection with COVID-19, half of patients who were admitted to hospitals still have at least one symptom, according to the longest follow-up study to date, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The study followed 1,192 participants in China infected with SARS-CoV-2 during the first phase of the...
Tag: <span>COVID-19</span>
Cognitive impairment from severe COVID-19 equivalent to 20 years of aging, study
by Craig Brierley, University of Cambridge Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Cognitive impairment as a result of severe COVID-19 is similar to that sustained between 50 and 70 years of age and is the equivalent to losing 10 IQ points, say a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London. The findings,...
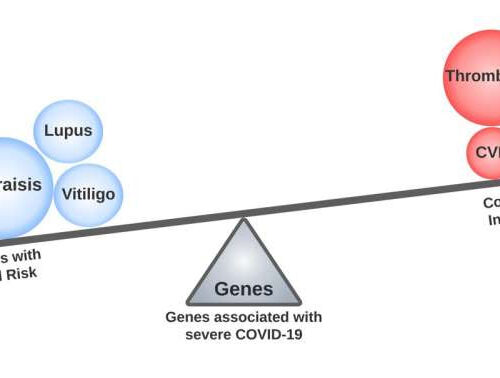
Genetic links revealed between severe COVID-19 and other diseases
by Public Library of Science While genes linked to severe COVID-19 were associated with established risk factors and adverse outcomes, including deep vein thrombosis, a significant subset of these genes had opposite associations with reduced risk of immune-mediated disorders such as psoriasis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis. Credit: Anurag Verma, Katherine Liao, and Scott Damrauer (CC-BY...
Study links telomere length to risk of death from COVID-19
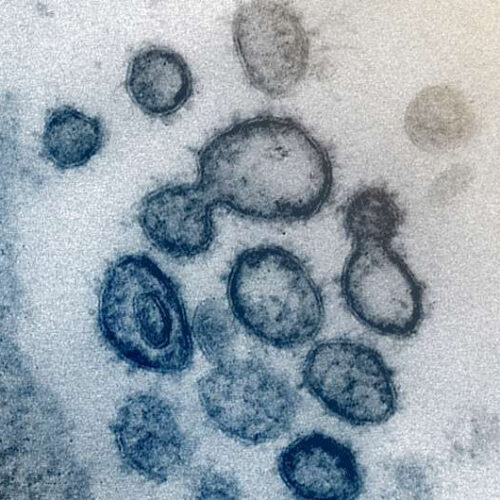
by European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases This transmission electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 — also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19 — isolated from a patient in the US. Virus particles are shown emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab. The spikes on the outer edge of...
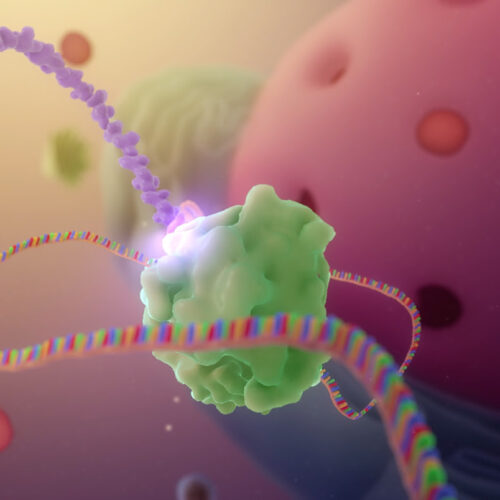
An mRNA vaccine with a twist—it copies itself—protects against COVID-19
21 APR 2022 6:35 PM BY JON COHEN The Arcturus Therapeutics COVID-19 vaccine contains a strand of messenger RNA (multicolored) that self amplifies after injection and then is translated by cells into the viral spike protein (purple). A third messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine appears to have proved its worth against COVID-19. And although it is...
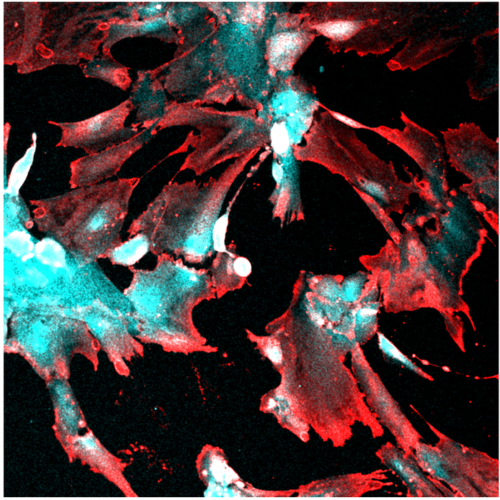
COVID-19 can directly infect and damage human kidney cells
DUKE UNIVERSITY IMAGE: FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPY IMAGE SHOWING ROBUST UPTAKE OF SARS-COV-2 BY HUMAN STEM CELL-DERIVED KIDNEY PODOCYTES. THE INFECTED CELLS EXPRESS VIRAL NUCLEOCAPSID PROTEIN (RED) AND THE PODOCYTE CELL LINEAGE IDENTIFICATION MARKER, NEPHRIN (CYAN). CREDIT: TITILOLA KALEJAIYE, DUKE UNIVERSITY DURHAM, N.C. – The virus that causes COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, can directly infect a specialized type of kidney...
How Do I Know If It’s Allergies or COVID-19?
Written by Merin Kuruvilla, MD | Reviewed by Mandy Armitage, MDPublished on February 7, 2022 Key takeaways: Allergies and COVID-19 can cause similar respiratory symptoms, making it difficult to tell them apart. The main difference is that COVID-19 can cause fever, whereas allergies do not. The only way to tell for sure whether you have...
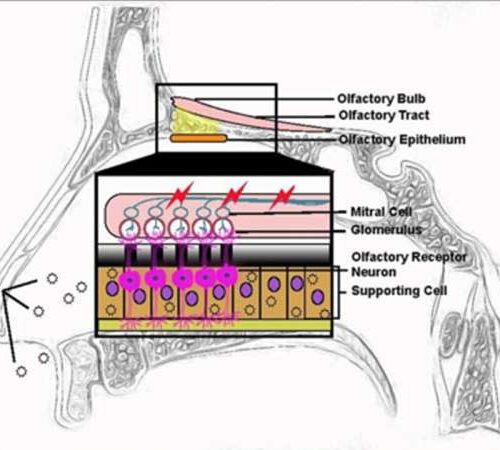
Inflammation caused by COVID-19, rather than the virus itself, may lead to loss of smell
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Graphic showing how SARS-CoV-2 infection in the nasal passages leads to inflammation, which in turn, damages nerve cells and reduces the number of axons (impulse transmitters) available to send odor signals to the olfactory bulb (which helps the brain process them). This often results in weakening or complete...
COVID-19: Inflammatory Insights
A study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital explains for the first time why COVID-19 causes severe inflammation in some people, leading to acute respiratory distress and multi-organ damage. Surprisingly, the study also finds that antibodies that people develop when they contract COVID-19 sometimes lead to more inflammation, while antibodies generated by...
A way to prevent loss of smell and taste from COVID-19
by Carrie MacMillan, Yale University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Loss of smell and taste—a hallmark symptom of COVID-19—was not on the minds of a group of Yale School of Medicine researchers when they embarked on a study in the spring of 2020. The scientists, led by Joseph Vinetz, MD, an infectious diseases specialist, were interested...