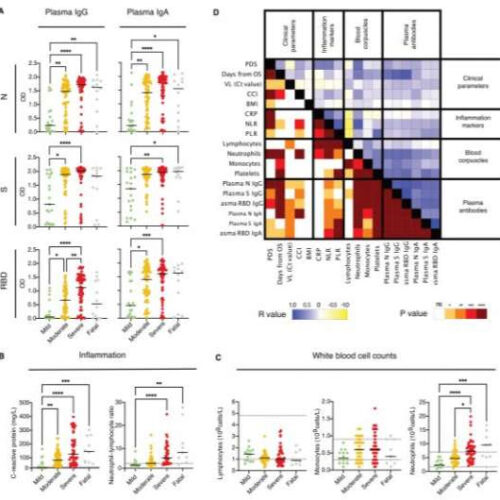
by Karolinska Institutet Systemic antibody responses, inflammation markers and other clinical parameters in relation to COVID-19 severity during acute disease. (A) Plasma IgG and IgA responses (n=19 for mild, n=58 for moderate, n=58 for severe and n=12 for fatal) against N, S and RBD are shown together with the levels of (B) C-reactive protein and the...
Tag: <span>COVID-19</span>
Monoclonal antibody therapy and COVID-19
by Samantha Bochenek, University of Kentucky Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Monoclonal antibody therapy is an infusion treatment that can reduce the severity of COVID-19. Here are some of the commonly asked questions about the treatment. Q: What are monoclonal antibodies and how do they work? A: Monoclonal antibodies are proteins created in a lab. The proteins mimic your...
High effectiveness of mix-and-match COVID-19 vaccines
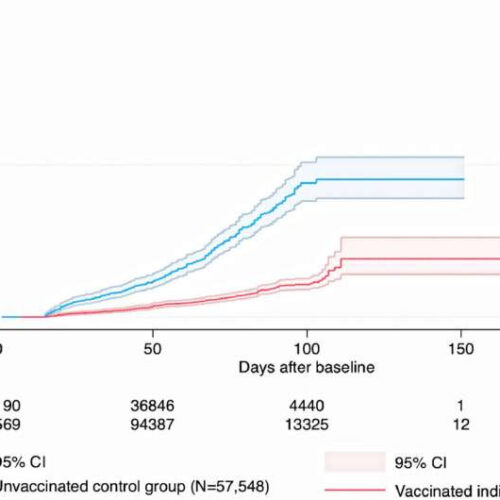
by Ola Nilsson, Umea University Fig. 1. Cumulative incidence and 95% confidence intervals for symptomatic Covid-19 infection in individuals given a heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 / BNT162b2 schedule and in corresponding controls. Credit: DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100249 People who had received a first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine and received an mRNA vaccine for their second dose had...
Missing link between severe COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s disease discovered
By Rich Haridy October 10, 2021 The gene variant plays a role in heightened inflammatory responses influencing both Alzheimer’s disease and severe COVID-19steilemas/Depositphotos Early in the pandemic researchers saw disproportionately high rates of dementia patients suffering from severe COVID-19. A common hypothesis was that memory impairments associated with neurodegeneration affect a person’s ability to consistently...
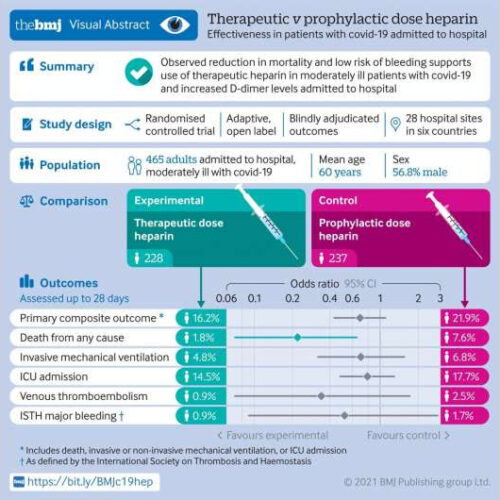
High-dose of readily available blood thinner reduces risk of death for moderately ill COVID-19 patients
by Ana Gajic, St. Michael’s Hospital Graphical abstract. Credit: DOI: 10.1136/bmj.n2400 A high dose of an inexpensive and globally available blood-thinning medication reduces the risk of death in hospitalized patients who are moderately ill with COVID-19, suggests a new study led by St. Michael’s Hospital. Published today in the BMJ, the international RAPID Trial compared the effects...
FDA panel supports Moderna COVID-19 booster shots for older Americans and other adults at higher risk of infection
Karen Weintraub Elizabeth Weise USA TODAY A federal advisory panel voted Thursday to support booster shots of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for people 65 and up, as well as younger adults with certain medical problems or jobs that put them at increased risk for infection. The booster shot will be a half-dose of the same...
Kids with MIS-C mount normal T cell response to COVID-19
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO IMAGE: ALESSANDRA FRANCO, MD, PH.D., ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS AT UC SAN DIEGO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. CREDIT: UC SAN DIEGO HEALTH SCIENCES Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a serious condition associated with a recent COVID-19 infection. The syndrome is rare, and it remains unclear how the viral...
One-third of Long Beach COVID-19 patients have long COVID symptoms
by Andy Fell, UC Davis Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain One-third of recovered COVID-19 patients reported new or continuing symptoms two months after their positive tests, according to a study by graduate students in epidemiology at the University of California, Davis, in collaboration with the Long Beach Department of Health and Human Services. Women, people over 39,...
Study: It is safe for people to be vaccinated against COVID-19 and influenza at the same time
by University of Bristol Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Research has found that it is safe for people to receive a flu vaccine at the same time as a COVID-19 vaccine. Reported side effects were mainly mild to moderate, and there were no negative impacts on the immune response produced by either vaccine when both were given on...
Could vitamin A help to regain your smell loss after COVID-19?
By Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Sep 29 2021 Researchers at the University of East Anglia and James Paget University Hospital are launching a new project to see whether Vitamin A could help people regain their sense of smell after viral infections including COVID-19. We also spoke exclusively to Professor Carl Philpott who is leading the study to find...