COVID-19 has been torturing the world for this entire year, but we are still learning about it and the ways it spreads. Researchers at the University of Sydney together with their colleagues in China have now found an association between lower humidity and an increase in community transmission. The fact that COVID-19 spreads easier in...
Tag: <span>COVID-19</span>
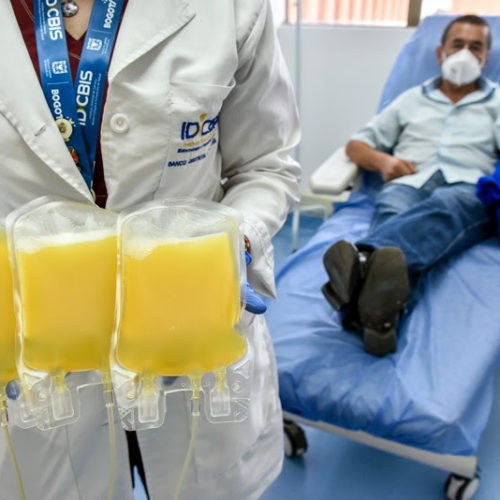
Is convalescent plasma safe and effective? We answer the major questions about the Covid-19 treatment
By LEV FACHER AUGUST 23, 2020 WASHINGTON — The Food and Drug Administration on Sunday issued an emergency authorization for doctors to treat Covid-19 using blood plasma from patients who’ve recovered from the disease. Below, STAT answers the major questions surrounding convalescent plasma as a Covid-19 treatment and the science supporting its use. What is convalescent plasma,...
Mount Sinai study finds COVID patients were most commonly readmitted to hospital for respiratory complications
Authors: Girish Nadkarni, MD, Co-Chair; Anuradha Lala, MD, Member; Benjamin Glicksberg, PhD, Member; and other coauthors of the Mount Sinai COVID Informatics Center at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Bottom Line: This study describes characteristics of patients with COVID-19 who returned to the ER or required readmission to the hospital within 14...
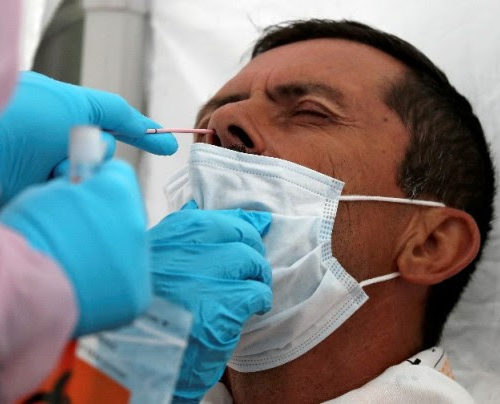
COVID-19 NEW Update: Yale Creates an FDA-Approved Saliva-Based Virus Test That Costs $10 With 94% Accuracy
Researchers from Connecticut-based Yale University has created a new way to determine if a person has acquired SARS-CoV-2, causing COVID-19. It turns out, a person’s saliva contains parts of the virus strands. Due to this conclusion, the university created its very own saliva-based COVID-19 test, and it is now approved by the United States Food...
Evidence lags behind excitement over blood plasma as a coronavirus treatment
Researchers call for more rigorous clinical trials as rumours abound that US regulators are considering widening access to the potential therapy. Plasma is a yellow liquid left behind after cells are removed from donated blood. It contains antibodies and immune-regulating proteins that could help treat disease.Credit: Guillermo Legaria/Getty US President Donald Trump has called on...
WORRIES ABOUT TELEHEALTH ARE DOWN, BUT BARRIERS REMAIN
One in four older Americans had a virtual medical visit in the first three months of the COVID-19 pandemic, most of them by video, a new telehealth poll finds. That’s much higher than the 4% of people over 50 who said they had ever had a virtual visit with a doctor in a similar poll...
Low humidity increases COVID risk; another reason to wear a mask
Dry air could prompt further disease spread A study focused on the Greater Sydney area during the early epidemic stage of COVID-19 found an association between lower humidity and an increase in community transmission. Now a second study by the same team confirms the risk. The study is published today in Transboundary and Emerging Diseases....
Childhood syndrome linked to COVID-19 causes profound immune changes
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH RESEARCH Researchers have uncovered how the immune system is altered in a rare COVID-19 related illness in children referred to as paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS-TS). PIMS-TS is a rare syndrome which has emerged in a small number of children during the COVID-19 pandemic. The condition causes severe inflammation in blood...
Multivitamin, mineral supplement linked to less-severe, shorter-lasting illness symptoms
by Steve Lundeberg, Oregon State University Older adults who took a daily multivitamin and mineral supplement with zinc and high amounts of vitamin C in a 12-week study experienced sickness for shorter periods and with less severe symptoms than counterparts in a control group receiving a placebo. The findings by Oregon State University researchers were...
New study: Hydroxychloroquine ineffective as a preventive antiviral against COVID-19
CLEVELAND–Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have added to the growing body of understanding about how hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is not a possible defense against COVID-19. Specifically, they found that HCQ is not effective in preventing COVID-19 in patients with lupus and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), suggesting a broader interpretation of HCQ as ineffective preventive medicine for...