by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) A new synthetic paper for finger-prick blood tests could provide accurate point-of-care diagnostics for cancer, COVID-19, and other serious diseases. Researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology say the innovation allows the detection of important biomarker proteins that might otherwise evade the blood plasma screening process. There are proteins in...
Tag: <span>COVID-19</span>
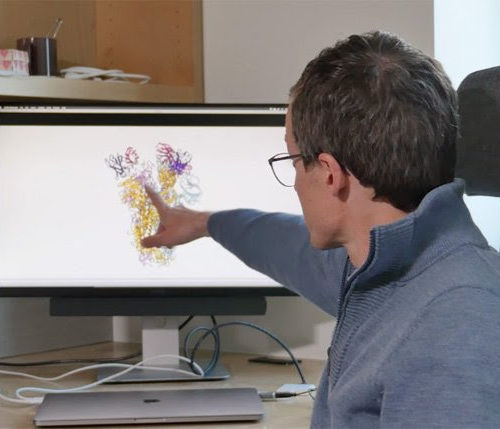
Antibody neutralizes SARS and COVID-19 coronaviruses
The neutralizing antibody, called S309, is on an accelerated path toward clinical trials. An antibody first identified in a blood sample from a patient who recovered from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in 2003 inhibits related coronaviruses, including the cause of COVID-19. The antibody, called S309, is now on a fast-track development and testing path at...
COVID-19 cytokine storm: Possible mechanism for the deadly respiratory syndrome
by Hokkaido University Research into how the SARS-CoV-2 virus induces death is suggesting potential treatments for its most destructive complications. Leading immunologists in Japan are proposing a possible molecular mechanism that causes massive release of proinflammatory cytokines, or a cytokine storm, leading to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19 patients. Their suggestions, published...
Potential new treatment approach to fatal COVID-19
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc Researchers from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and Pathways Bioscience in the United States have found that activating a transcription factor involved in oxidative stress regulation, antiviral activity, and inflammation may serve as a new treatment approach to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The scientists propose that the antiviral and...
Scientists in China believe new drug can stop pandemic ‘without vaccine’
by Qian Ye and Matthew Knight A Chinese laboratory has been developing a drug it believes has the power to bring the coronavirus pandemic to a halt. The outbreak first emerged in China late last year before spreading across the world, prompting an international race to find treatments and vaccines. A drug being tested by...
Research shows electroceutical fabric eradicates coronaviruses on contact
by Nicole Wilkins, Indiana University The electroceutical technology offers clinicians a non-antibiotic solution for infection risk reduction and potentially increases its value for use in face masks and possibly other surface treatments. Credit: Chandan Sen With the number of novel coronavirus infections at 4 million and growing as of May 10, use of personal protective...
Multi-drug regimen for heart failure could meaningfully extend patients’ lives
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital Patients with heart failure have substantially shorter life expectancies than people without this condition. Approximately 6.5 million people in the U.S. and over 64 million people worldwide have heart failure, and about half of them have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). In the last three decades, there have...
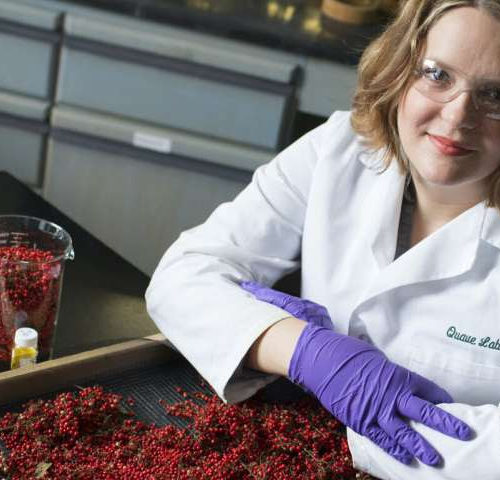
Scientists identify chemicals in noxious weed that ‘disarm’ deadly bacteria
by Carol Clark, Emory University Scientists have identified specific compounds from the Brazilian peppertree—a weedy, invasive shrub in Florida—that reduce the virulence of antibiotic-resistant staph bacteria. Scientific Reports published the research, demonstrating that triterpenoid acids in the red berries of the plant “disarm” dangerous staph bacteria by blocking its ability to produce toxins. The work...
Preventing ‘cytokine storm’ may ease severe COVID-19 symptoms
For some COVID-19 patients, the body’s immune response may be as destructive as the virus that causes the disease. The persistent high fevers, severe respiratory distress, and lung damage seen in some critically ill patients are all signs of an immune system in overdrive. Now, a new clinical trial will test a treatment that targets...
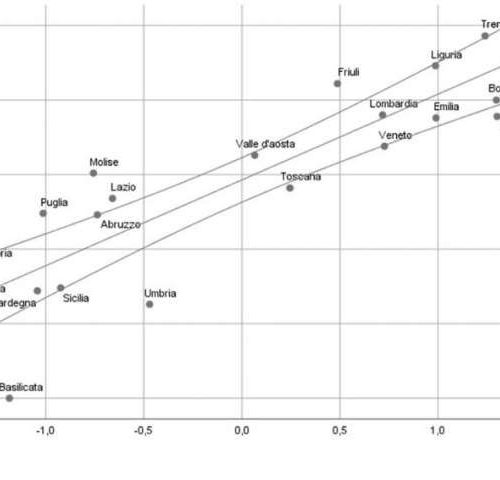
Social isolation linked to more severe COVID-19 outbreaks
by Public Library of Science Regions of Italy with higher family fragmentation and a high number of residential nursing homes experienced the highest rate of COVID-19 infections in people over age 80, according to a new study published May 21, 2020 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Giuseppe Liotta of the University of Rome,...