by University of South Australia Eat one or more eggs per day and your risk of diabetes increases by 60 per cent. Scrambled, poached or boiled, eggs are a popular breakfast food the world over. Yet the health benefits of the humble egg might not be all they’re cracked up to be as new research from the University...
Tag: <span>Diabetes</span>
Non-obese Vietnamese Americans are 60% more likely to have diabetes
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO A new study has found that Vietnamese-American adults who were not obese were 60% more likely to have diabetes than non-obese, non-Hispanic, White Americans, after accounting for age, sex, sociodemographic factors, smoking history and exercise level. Overall, only 9% of Vietnamese Americans with diabetes in the study were obese — defined as...
Study reveals the role of our ‘second brain’ in diabetes
Researchers have uncovered new clues to the mystery of how the gut’s nervous system affects glucose metabolism in the rest of the body. Their findings could lead to new treatments for type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes causes the body’s cells to become less sensitive to signals from insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating levels of...
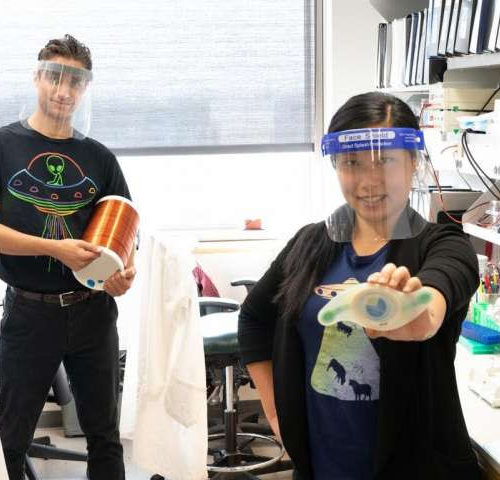
Remote control of blood sugar: Electromagnetic fields treat diabetes in animal models
by Jennifer Brown, University of Iowa Calvin Carter and Sunny Huang (pictured in their lab at the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine) may have discovered a safe new way to manage blood sugar non-invasively using electromagnetic fields (EMFs). Their findings, published in Cell Metabolism, show that exposing diabetic mice to a combination of static...
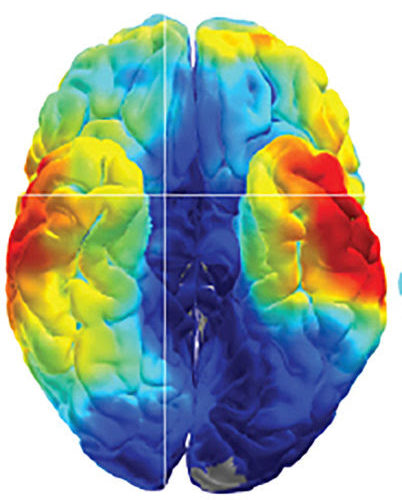
Raised blood pressure and diabetes alter brain structure to slow thinking speed and memory
In a new study published neuroscientists at Oxford University have found that raised blood pressure and diabetes in mid-life alter brain structure to slow thinking speed and memory. Looking at results from 22,000 volunteers in the UK Biobank who underwent brain scanning, the scientists found that raised blood pressure and diabetes significantly impaired the brain’s...
Diabetes dramatically reduces the kidney’s ability clean itself
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University Drs. Zheng Dong and Zhengwei Ma, MCG research associate and the study’s first author. Credit: Kim Ratliff, Augusta University photographer The kidneys often become bulky and dysfunctional in diabetes, and now scientists have found that one path to this damage dramatically reduces the kidney’s ability to clean up after itself....
HIV drugs could prevent diabetes, study suggests
UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA HEALTH SYSTEM IMAGE: JAYAKRISHNA AMBATI, MD, AND COLLEAGUES FOUND THAT PATIENTS TAKING DRUGS CALLED NRTIS TO TREAT HIV AND HEPATITIS B HAD A 33% LOWER RISK OF DEVELOPING DIABETES. A group of drugs used to treat HIV and hepatitis B could be repurposed to prevent type 2 diabetes, a new study suggests. ...
Study identifies weight-loss threshold for heart health in patients with obesity, diabetes
CLEVELAND CLINIC CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that 5 to 10 percent of surgically induced weight loss is associated with improved life expectancy and cardiovascular health. In comparison, about 20 percent weight loss is necessary to observe similar benefits with a non-surgical treatment. The findings also show that metabolic surgery may contribute health benefits...
New risk factors for type 2 diabetes uncovered
A new ‘global atlas’ study characterizes insomnia as a novel risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In total, the researchers identified 19 risk factors and dismissed 21 suggestive risk factors based on insufficient scientific evidence. New research indicates insomnia is a possible risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Globally, around 463 million adults lived with diabetes...
Enzyme insight could lead to new diabetes treatment
by Centenary Institute Credit: CC0 Public Domain Research led by the Centenary Institute has discovered that the lack of an enzyme in the liver called sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) results in pronounced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, both symptoms of early stage type 2 diabetes. The findings raises the possibility of a new treatment approach for diabetic...