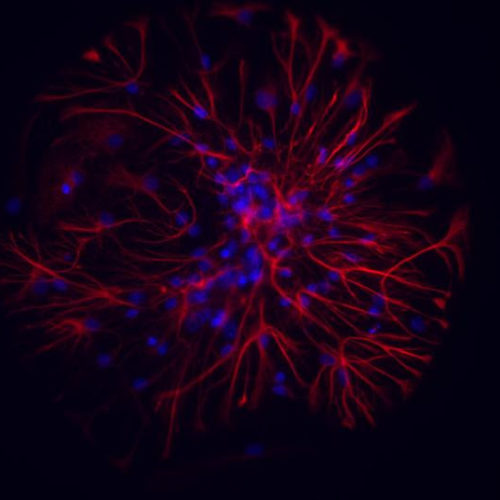
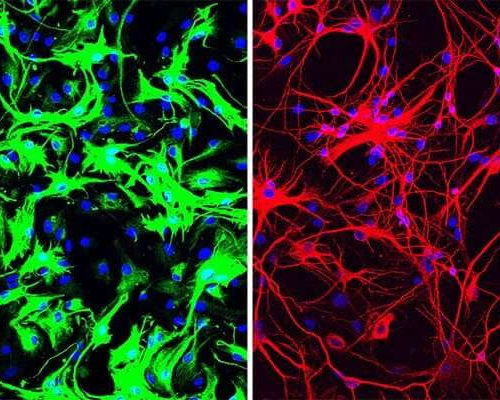
Published on ACS Nano, journal of the American Chemical Society, the study opens important perspectives for treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease, but also epilepsy, brain trauma and stroke. NEURONS AND ATROCYTES UNDER A FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE view more CREDIT: IIT-ISTITUTO ITALIANO DI TECNOLOGIA Lecce, 25th June 2020 – Gold nanoparticles have been...
Tag: <span>diseases</span>
WATCH: Drug-resistant superbugs are a slow-moving pandemic
Scientists at McMaster are warning that while the world’s attention is focused on COVID-19, another pandemic — antimicrobial resistance (AMR) — is of grave concern. “AMR is a pandemic that has been going on for a very long time. Essentially, when we started to use antibiotics, we started to see resistance to them,” says Lori...
Initial COVID-19 infection rate may be 80 times greater than originally reported
by Pennsylvania State University Many epidemiologists believe that the initial COVID-19 infection rate was undercounted due to testing issues, asymptomatic and alternatively symptomatic individuals, and a failure to identify early cases. Now, a new study from Penn State estimates that the number of early COVID-19 cases in the U.S. may have been more than 80...
Cognitive therapy has lasting effect on hypochondriacs
by University of Bergen People that suffer from health anxiety (Hypochondriacs) use very much of their time and energy on checking whether or not they have a serious disease. This has often negative effects on their social life, work, and family life, to the extent that their quality of life is strongly reduced. Researchers at...
Parkinson’s linked to overabundance of opportunistic gut pathogens
By Nick Lavars June 21, 2020 As a disease without a cure or means of prevention, there is a lot we don’t know about Parkinson’s and the way it takes hold in the human body. One school of thought is that it actually begins in the gut, and a new study has strengthened these ties...
Cancer vaccine hope: Personalised treatment designed to boost the body’s natural ability to fight the disease shows ‘promising signs’ in clinical trials
By RYAN MORRISON FOR MAILONLINE Researchers take a biopsy of a cancerous tumour to look for certain proteins Each patient has a ‘different cancer’ and the treatment is specifically targeted It is given alongside chemotherapy drugs to boost the body’s immune response So far only eight per cent of patients saw their tumour reduce but...
Urine test reveals quality of your diet — and whether it’s the best fit for your body
Scientists have completed large-scale tests on a new type of five-minute urine test that measures the health of a person’s diet, and produces an individual’s unique urine ‘fingerprint’. Scientists have completed large-scale tests on a new type of five-minute urine test that measures the health of a person’s diet, and produces an individual’s unique urine...
New vaccine holds promise in fighting diarrheal disease
OHSU research targets disease afflicting millions in developing world OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Scientists at Oregon Health & Science University have teamed up with OHSU spinoff, Najít Technologies, Inc. to develop a new vaccine that appears to confer immunity to a diarrheal disease that afflicts hundreds of millions of people in developing countries around...
One-time treatment generates new neurons, eliminates Parkinson’s disease in mice
by University of California – San Diego Xiang-Dong Fu, Ph.D., has never been more excited about something in his entire career. He has long studied the basic biology of RNA, a genetic cousin of DNA, and the proteins that bind it. But a single discovery has launched Fu into a completely new field: neuroscience. For...
Star-shaped brain cells may play a critical role in glaucoma
by NYU Langone Health After a brain injury, cells that normally nourish nerves may actually kill them instead, a new study in rodents finds. This “reactive” phenomenon may be the driving factor behind neurodegenerative diseases like glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness. Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study examined what...