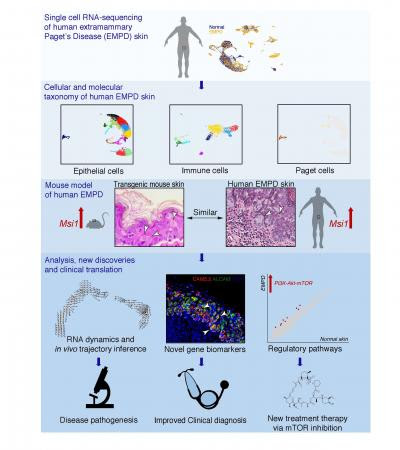
New study finds use of topical cream can alleviate skin symptoms UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE THE IMAGE IS A DIAGRAM OF THE MAJOR FINDINGS OF THE STUDY. view more CREDIT: UCI SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Irvine, Calif., June. 25, 2020 — Researchers from the University of California, Irvine, in collaboration with their colleagues from...
Tag: <span>diseases</span>
Study gives insights into how human fat cells are affected by age
by Anna Molin, Karolinska Institutet Knowledge of how human fat tissue is affected by age has long been defined by numerous mouse-based studies. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now, for the first time, been able to conduct a prospective study on humans that provides novel insights into how our fat cells reduce lipid...
Italy study shows mosquitoes cannot transmit coronavirus
A new scientific study by Italy’s national health institute ISS shows that mosquitoes are unable to transmit coronavirus to humans, the institute said Thursday. The World Health Organisation had already said there was no evidence that the virus could be transmitted by the blood-sucking insects, which spread dengue and other diseases when they bite humans....
EULAR: Early and intensive treatment of rheumatoid arthritis reduces fatigue
Better quality of life for people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases EUROPEAN LEAGUE AGAINST RHEUMATISM Kilchberg/Switzerland: Disease-related, profound fatigue impairs the quality of life of many people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. A Belgian study (1) has now concluded that early intensive treatment combining methotrexate with a bridging scheme of prednisone can reduce the onerous...
Blood sample can be used to assess the severity and prognosis of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in the future
by University of Eastern Finland Biomarkers to support the diagnosis of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and to assess the severity and expected prognosis of the disease are needed. Neurofilament light chain (NfL) measured from a blood sample strongly correlates with the duration of the disease in FTLD patients and the rate of brain atrophy, according...
Antioxidant agent may prevent chronic kidney disease and Parkinson’s disease
Oxidative stress is the result of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and can be damaging to cells and tissues. In a new study, researchers from Osaka University developed a novel dietary silicon (Si)-based antioxidant agent that suppressed the development and progression of kidney failure and Parkinson’s disease in rodents. ROS are generated as a result...
New structural ‘map’ solves mysteries of gigantic gene regulator
WALTER AND ELIZA HALL INSTITUTE Structural biology has been used to ‘map’ part of a protein called SMCHD1, explaining how some changes in SMCHD1 cause certain developmental and degenerative conditions. Publishing in the journal Science Signaling, the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute team revealed the structure of the portion of the SMCHD1 protein that is...
Could the cure for IBD be inside your mouth?
by University of Michigan While many people put off their regular trips to the dentist, recent research has shown that the consequences of doing so may go beyond cavities and root canals. From heart disease to diabetes, poor oral health is often a reflection of a person’s overall health and may even be the cause...
First report of systemic delivery of micro-dystrophin gene therapy in children with DMD
One-year data from the first four patients dosed is published in JAMA Neurology NATIONWIDE CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL Researchers from Nationwide Children’s Hospital have published in JAMA Neurology results from the first four patients treated in the first clinical trial of systemic delivery of micro-dystrophin gene therapy in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) – and initial...
Cancer’s reliance on fat could be targeted with new ‘drugs and diet’ treatment
BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE (Boston)–In an effort to improve the survival of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms, a type of leukemia, researchers inhibited a specific protein (alpha5beta1 integrin) to decrease the number of large bone marrow cells (megakaryocytes) in an experimental model. An increase in megakaryocyte numbers is thought to be the cause of many...