“Regular endurance training and good fitness seem to protect against serious cardiovascular events and early mortality for people diagnosed with atrial fibrillation,” says exercise physiologist Lars Elnan Garnvik. Garnvik recently completed his doctorate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. His latest article was recently published in the prestigious European Heart Journal. Garnvik and...
Tag: <span>diseases</span>
Advanced X-ray technology tells us more about Ménière’s disease
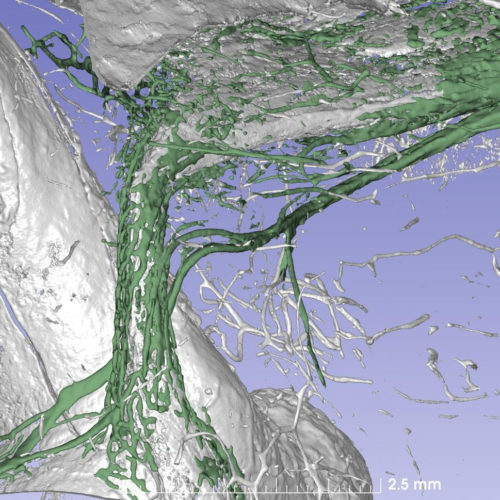
CREDIT: NORDSTRÖM ET AL. The organ of balance in the inner ear is surrounded by the hardest bone in the body. Using synchrotron X-rays, researchers at Uppsala University have discovered a drainage system that may be assumed to play a major role in the onset of Ménière’s disease, a common and troublesome disorder. These results...
HKBU scientists eliminate drug side effects by manipulating molecular chirality
Scientists from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) have developed a novel technique that can produce pure therapeutic drugs without the associated side effects. The approach, which uses a nanostructure fabrication device, can manipulate the chirality of drug molecules by controlling the direction a substrate is rotated within the device, thus eliminating the possible side effects...
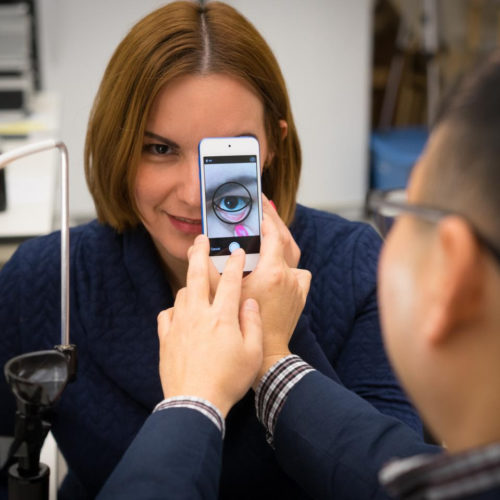
New mobile health tool measures hemoglobin without drawing blood
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a way to use smartphone images of a person’s eyelids to assess blood hemoglobin levels. The ability to perform one of the most common clinical lab tests without a blood draw could help reduce the need for in-person clinic visits, make it easier to monitor patients who are in critical...
How the Lyme disease epidemic is spreading and why ticks are so hard to stop
by Durland Fish, The Conversation In the 1970s, an epidemic of mysterious arthritis-like symptoms began spreading among children in the lushly wooded area around Lyme, Connecticut. Scientists traced the cause to tick bites and named it Lyme disease, but why it had suddenly appeared there was a mystery. Similar symptoms had been documented on Long...
Transcranial direct current stimulation is a safe treatment
by University of Eastern Finland Transcranial direct current stimulation, tDCS, is a promising treatment for conditions such as depression and addictive disorders. New evidence on the safety of transcranial direct current stimulation was recently offered by a new study showing that tDCS does not affect metabolism. Transcranial direct current stimulation is a non-invasive method for...
Unraveling one of prion disease’s deadly secrets
AMHERST, Mass. – A molecular biologist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst who has for decades studied the nightmarish group of fatal diseases caused by prions – chronic wasting disease in deer, mad cow in cattle and its human analog – credits a middle-of-the-night dream for a crucial insight, a breakthrough she hopes could lead...
Interleukin-12 electroporation may sensitize ‘cold’ melanomas to immunotherapies
by American Association for Cancer Research Combining intratumoral electroporation of interleukin-12 (IL-12) DNA (tavokinogene telseplasmid, or TAVO) with the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab (Keytruda) led to clinical responses in patients with immunologically quiescent advanced melanoma, according to results from a phase II trial published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for...
COVID-19 may increase blood clotting and blockage of brain blood vessels
Clinical observations of COVID-19 patients, who went on to have a stroke, suggest coronavirus may cause clots within blood vessels (arteries) in the brain, finds a team of neurologists from UCL and UCLH (the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery), London. The findings suggest early testing for D-dimer, a protein fragment in the blood associated...
Small study of patients with severe COVID-19 treated with the arthritis drug anakinra finds clinical improvements
by Lancet The first study to report use of the rheumatoid arthritis drug anakinra to treat COVID-19 patients found that high-dose anakinra was safe and was associated with respiratory improvements and reduced signs of cytokine storm in 72% (21/29) of patients, according to results from patients studied for 21 days (enrolled from 17 to 27...