OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER COLUMBUS, Ohio – The findings of a new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) could refine an important set of prognostic and treatment recommendations for younger adult patients...
Tag: <span>diseases</span>
Impact and resistance training boosts bone strength and muscle function in those with Crohn’s disease
by Northumbria University Research from Northumbria University, Newcastle, has shown the important role specific types of exercise can play in the management of bone loss, fatigue and muscle dysfunction for those with Crohn’s disease. Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease which is estimated to affect about one in every 650 people in...
Drug-induced interstitial lung disease in breast cancer patients
A lesson we should learn from multi-disciplinary integration Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this case report the authors Zijun Zhao, Zhanghai He, Hongyan Huang, Jiewen Chen, Shishi He, Ailifeire Yilihamu and Yan Nie from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China consider drug-induced interstitial lung disease in breast cancer patients. Taxanes represented...
Proteins — and labs — coming together to prevent Rett syndrome
This news or article is intended for readers with certain scientific or professional knowledge in the field. Disruption of condensates in the neurodevelopmental disorder provides insights into how cells compartmentalize chromosomes, as well as new potential therapies. New discoveries about the disruption of condensates in the neurodevelopmental disorder Rett syndrome provide insights into how cells...
Gut microbiome translates stress into sickle cell crises
ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE July 30, 2020–(BRONX, NY)–A new study shows how chronic psychological stress leads to painful vessel-clogging episodes–the most common complication of sickle-cell disease (SCD) and a frequent cause of hospitalizations. The findings, made in mice, show that the gut microbiome plays a key role in triggering those episodes and reveals possible...
A safer cell therapy harnesses patient T cells to fight multiple myeloma
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCE A treatment for multiple myeloma that harnesses the body’s cancer-fighting T cells was safe in humans and showed preliminary signs of effectiveness, according to a clinical trial involving 23 patients with relapsed or treatment-resistant disease. Although more research is needed to determine how well the treatment works, the...
Pimavanserin reduced symptoms of dementia-related psychosis in phase 3 trial
A large-scale trial has found a treatment with pimavanserin substantially reduced psychotic symptoms and reduced risk of relapse of those symptoms compared to placebo in people with dementia, a condition for which no treatments are currently licensed UNIVERSITY OF EXETER A large-scale trial has found a treatment with pimavanserin substantially reduced psychotic symptoms and reduced...
Dry powder inhalation could be a potent tool in COVID-19 antiviral treatment
by Nick Nobel, University of Texas at Austin A microscopic image of remdesivir powder formulations after the thin-film freezing process. All formulations exhibited a brittle matrix structure of highly porous particles. Credit: University of Texas at Austin The only antiviral drug currently used to treat SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, is remdesivir, but administering...
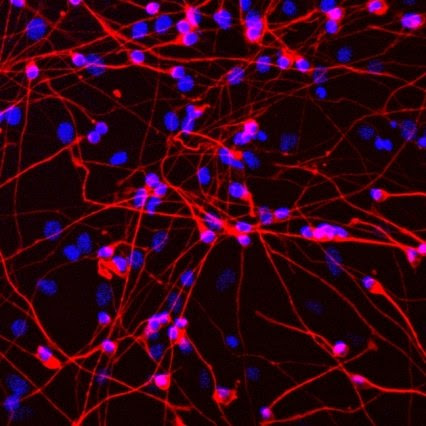
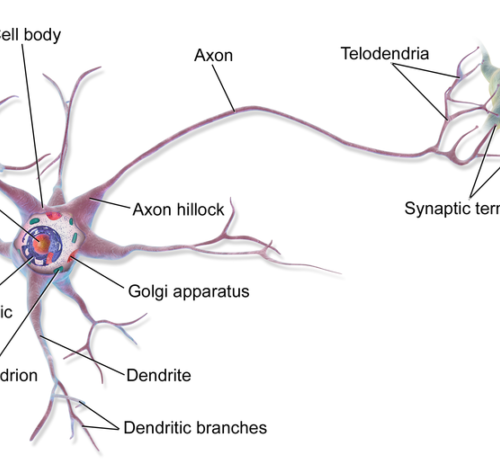
Neurons are genetically programmed to have long lives
When our neurons — the principal cells of the brain — die, so do we. Most neurons are created during embryonic development and have no “backup” after birth. Researchers have generally believed that their survival is determined nearly extrinsically, or by outside forces, such as the tissues and cells that neurons supply with nerve cells....
Talbot helps ID muscle gene that, when altered, causes joint disease
UNIVERSITY OF MAINE Jared Talbot is part of a 32-member international research team that identified a gene that, when altered, can cause bent fingers and toes, clubfoot, scoliosis, and short stature. The team discovered that partial loss of the protein coding gene MYLPF (myosin light chain, phosphorylatable, fast skeletal muscle) results in a disorder called...