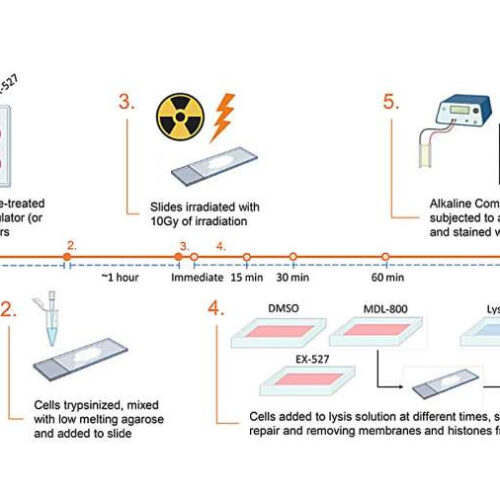
by Impact Journals LLC Experimental design for the results shown in Figures 3 and 4. Credit: 2023 Copp et al. A new research paper titled “Sirtuin 6 activation rescues the age-related decline in DNA damage repair in primary human chondrocytes” has been published in Aging. While advanced age is widely recognized as the greatest risk...
Tag: <span>DNA Damage Repair</span>
Suntanner, heal thyself: Exosome therapy may enable better repair of sun, age-damaged skin
NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIVERSITY In the future, you could be your very own fountain of youth – or at least your own skin repair reservoir. In a proof-of-concept study, researchers from North Carolina State University have shown that exosomes harvested from human skin cells are more effective at repairing sun-damaged skin cells in mice than popular retinol or stem cell-based treatments currently in...
Immunotherapy could offer hope for some men with aggressive prostate cancers
A group of men with especially aggressive prostate cancer may respond unusually well to immunotherapy, a major new study reports. Micrograph showing prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (the most common form of prostate cancer) Credit: Wikipedia The research offers the possibility of effective treatment for men with prostatecancer who currently die from their disease much more rapidly...
Key cancer-fighting gene’s secret weapons revealed
The findings revealed that a special group of genes that function within the body’s normal DNA repair process were vital to the effectiveness of p53. This new information could help doctors to better identify patients with an increased risk of developing certain cancers. It could also help to develop safer, more effective treatments for patients....
Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent or Embryonic Stem Cells Decreases the DNA Damage Repair by Homologous Recombination
Highlights Spontaneous and S-phase-specific chromosome aberrations in differentiated cells Higher frequency of residual γ-H2AX foci after exposure to DNA-damaging agents Higher frequency of cells with 53BP1 and RIF1 co-localization in differentiated cells Higher frequency of cells with a reduced number of RAD51 or BRCA1 foci Summary The nitric oxide (NO)-cyclic GMP pathway contributes to human...