by University of Southern California A new study led by researchers at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology is the first to demonstrate that a tiny protein has a big impact on health and longevity in both animals and humans. The researchers examined humanin, a peptide encoded in the small genome of mitochondria—the powerhouses...
Tag: <span>DNA</span>
Premature epigenomic aging acts like a ‘sleeper cell’ that is awakened by Western-style diet
by Baylor College of Medicine The epigenome is sometimes referred to as the “software” or “operating system” of the genome. It comprises small chemical modifications to DNA and the proteins that make up our chromosomes, and controls the activity of all the genes within the genome. During early life, as our organs develop, the epigenome...
An aspirin a day keeps the bowel doctor away
by Newcastle University A regular dose of aspirin to reduce the risk of inherited bowel cancer lasts at least 10 years after stopping treatment, research has revealed. The international trial—known as CAPP2—involved patients with Lynch syndrome from around the world and revealed that two aspirins a day, for an average of two and a half...
Cancer drug: New treatment halts tumour growth
By Rachel Schraer Health reporter A drug that could stop cancer cells repairing themselves has shown early signs of working. More than half of the 40 patients given berzosertib had the growth of their tumours halted. Berzosertib was even more effective when given alongside chemotherapy, the trial run by the Institute of Cancer Research (ICR)...
Blood test to monitor cancer up to 10 times more sensitive than current methods
by University of Cambridge A new method of analyzing cancer patients’ blood for evidence of the disease could be up to ten times more sensitive than previous methods according to new research led by the University of Cambridge. In the coming years, this method and others based on this approach could lead to tests that...
Gene therapy with a new base editing technique restores hearing in mice
Repairing a single mutation in the Tmc1 gene restored partial hearing in mice Key Findings: This is the first example of repairing a recessive gene mutation Repairing a single mutation in the Tmc1 gene restored partial hearing in mice The technique required the use of two viral vectors to deliver the base editing machinery Cells...
Scientists develop blood test to help improve liver cancer screening
by National Cancer Institute Scientists have developed a new test that can help identify people who are likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. The approach uses a simple blood test to check for the patient’s previous exposure to certain viruses. A study of the new approach was led...
New method created for identifying genes behind brain tumors
by Uppsala University Researchers at Uppsala University have developed a method for identifying functional mutations and their effect on genes relevant to the development of glioblastoma—a malignant brain tumor with a very poor prognosis. The study is published in Genome Biology. The human genome consists of nearly 22,000 genes. Many studies have explored the nearly...
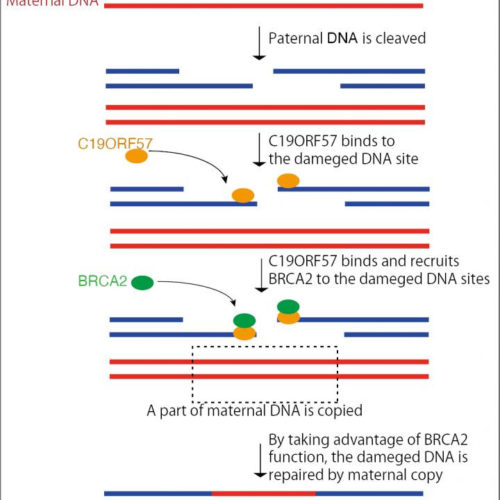
Discovery of a novel gene involved in DNA damage repair and male fertility
Clarifying the mechanisms for meiotic recombination in sperm production KUMAMOTO UNIVERSITY A research group from the Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG)at Kumamoto University, Japan has discovered that the gene C19ORF57 plays a critical role in meiosis. The gene appears to be related to the cause of male infertility and could be a big...
Scientists reveal how mutations in metabolism can drive cancers
by Yale University Our cells have several ways to repair DNA that breaks when the cells divide. However, genetic mutations can disable these DNA repair mechanisms, destabilize the cells, and trigger cancer. In a paper published today in the journal Nature, Yale Cancer Center (YCC) scientists have identified mutations in metabolite-producing genes as a disruption...