by Melinda Krigel, University of California, San Francisco Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a leading cause of sudden death in adolescents and initial detection is often difficult. A new UC San Francisco study finds that Artificial Intelligence-enhanced (AI)-Electrocardiograms (ECG) may help identify the condition in its earliest stages and monitor important disease-related...
Tag: <span>electrocardiogram</span>
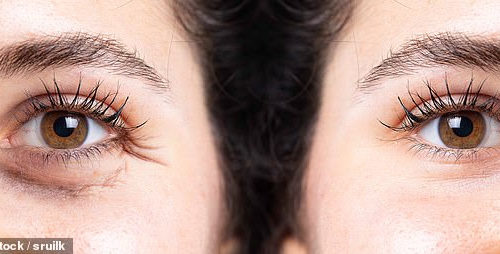
No use hiding your age: Scientists develop an eye scanner that can detect and track biological ageing in humans for the first time by analysing proteins in their lenses
he team created an eye scanner that can tell someone’s ‘real’ or biological age There is no universal method for tracking a person’s biological age, authors say By building this new scanner they were able to create one method to see the age The team say that biological age is a more accurate health measure...
Scientists discover more than 200 genetic factors that cause heart arrhythmia
by Queen Mary, University of London Hundreds of new links have been found between people’s DNA and the heart’s electrical activity, according to a study of almost 300,000 people led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. The results could one day lead to advanced screening...
Novel necklace detects abnormal heart rhythm
“The wearable necklace-ECG (electrocardiogram) provides a new and easy method for detecting an abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation, which is a fast-growing public health problem,” said study author Mr. Elmeri Santala, a medical student at the University of Eastern Finland. One of the major causes of stroke is unrecognised and untreated atrial fibrillation. Approximately...
Electrocardiogram shows value in college athletes’ screens
Over the past 30 years, colleges and universities have increasingly screened athletes for health conditions that may pose undue risk to sports participation. Sudden cardiac death is the leading cause of death among college athletes, so a primary function of these screenings is to reveal unknown heart conditions. The National Collegiate Athletic Association requires a...
Chloroquine COVID-19 trial stopped after patient deaths
Researchers in Brazil were testing chloroquine in 81 hospitalized COVID-19 patients. About half were prescribed 450 mg twice daily for five days, and the others were prescribed 600 mg for 10 days, The New York Times reported. But within three days, some patients taking the higher dose developed serious heart rhythm disorders, resulting in 11...
ELECTRONIC ‘TATTOO’ MONITORS HEART FOR DAYS
New wearable technology made from stretchy, lightweight material could make heart health monitoring easier and more accurate, a new study reports. Existing electrocardiogram (ECG) technology hasn’t changed much in almost a century, researchers say. The new device is so lightweight and stretchable that it can remain over the heart for extended periods with little or no discomfort. It measures...
Novel electrocardiogram uses signals from ear and hand to check heart rhythm
A novel electrocardiogram (ECG) method which uses signals from the ear and hand to check heart rhythm is revealed today at EHRA 2011 a European Society of Cardiology (ESC) congress. The ECG does not require two hands and could be used by drivers, athletes, and the military. Study author Dr. Raffaele De Lucia, of the University Hospital of Pisa, Italy, said: “Mobile ECG devices present a major opportunity to...