JANUARY 21, 2022 by University of Arkansas Credit: CC0 Public Domain For people who hate exercising, here comes some more bad news: it may also keep you younger. Not just looking younger, but actually younger, on an epigenetic level. By now, the benefits of exercise have been well established, including increased strength of bones and muscles,...
Tag: <span>exercise</span>
How Exercise May Tame Our Anxiety
January 12, 2022 in News To better cope with all the dispiriting news this winter about rising Covid-19 cases and so much else, you might want to get out and play in the snow, according to a new report. The large-scale study of almost 200,000 cross-country skiers found that being physically active halves the risk of developing...
Uncovered: Key to how exercise protects against consequences of ageing
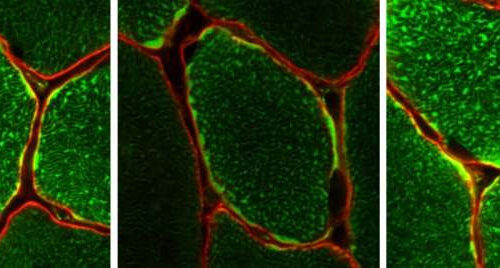
by Monash University Staining showing mitochondria within individual muscle fibres. Credit: Monash University Monash University, Australia scientists have discovered an enzyme that is key to why exercise improves our health. Importantly this discovery has opened up the possibility of drugs to promote this enzyme’s activity, protecting against the consequences of aging on metabolic health, including...
Heat therapy can mimic some of the vascular benefits of exercise
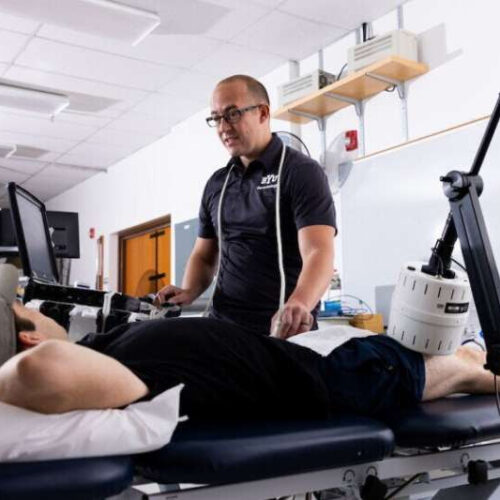
by Trevor Jones, Brigham Young University BYU exercise sciences professor Jayson Gifford administers heat therapy to a study subject. Credit: BYU Photo Data consistently shows that exercise is key to well-being in nearly every facet of life; its positive impact is unquestioned. But what about when people, perhaps not by choice, need to sit on...
Exercise helps women with arm and shoulder problems after breast cancer surgery
BMJ Exercise helps women with arm and shoulder problems after breast cancer surgery Early post-operative exercise appears to help women recover better than receiving standard care only, study shows Women who exercise shortly after having non-reconstructive breast cancer surgery appear to regain better shoulder and arm mobility and experience less pain than those who receive...
Anxiety effectively treated with exercise
by University of Gothenburg Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Both moderate and strenuous exercise alleviate symptoms of anxiety, even when the disorder is chronic, a study led by researchers at the University of Gothenburg shows. The study, published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, is based on 286 patients with anxiety syndrome, recruited from primary care services in Gothenburg...
Can exercise play a role in the link between the gut and the brain?
by Jamie Wetherbe, University of Southern California Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Until about 10 years ago, most clinicians only looked at the brain when finding ways to treat patients with Parkinson’s Disease. “Neurologists and researchers try to improve brain function and use treatment strategies that target the brain,” said Kaylie Zapanta MS ’17 Ph.D. ’23. “As an exercise physiologist, I’m...
Exercise may stop cancer in its tracks
by Edith Cowan University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Forget bedrest, research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has shown exercise may be a key weapon in cancer patients’ battle against the disease. Exercise causes muscles to secrete proteins called myokines into our blood—and researchers from ECU’s Exercise Medicine Research Institute have learned these myokines can suppress tumor growth and even help actively fight cancerous...
Walking is good. But moderate-vigorous exercise boosts fitness three times more
IMAGE: WITH HELP FROM 2,000 FRAMINGHAM HEART STUDY PARTICIPANTS, BU RESEARCHERS STUDIED HOW MUCH BEING SEDENTARY, WALKING, AND ROUTINE EXERCISE IMPACTS FITNESS. CREDIT: PHOTO BY FITSUM ADMASU ON UNSPLASH: HTTPS://UNSPLASH.COM/PHOTOS/OGV9XIL7DKY Exercise is healthy. That is common knowledge. But just how rigorous should that exercise be in order to really impact a person’s fitness level? And, if...
A year of committed exercise in middle age reversed worrisome heart stiffness
by Karen Schmidt, American Heart Association Credit: CC0 Public Domain A year of exercise training helped to preserve or increase the youthful elasticity of the heart muscle among people showing early signs of heart failure, a small study shows. The new research, published Monday in the American Heart Association journal Circulation, bolsters the idea that “exercise is medicine,”...