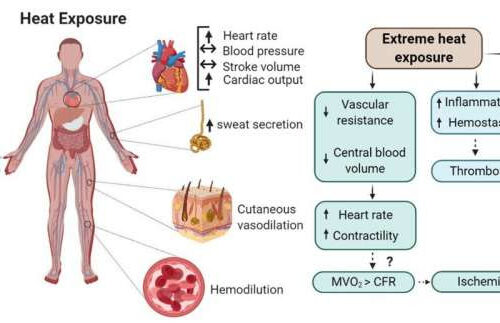
by Elsevier Extreme heat is associated with a greater risk of adverse cardiovascular (CV) outcomes, albeit the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. Cutaneous vasodilation during heat exposure reduces peripheral vascular resistance and is paralleled by a redistribution of blood flow and volume towards the skin circulation. Consequently, central blood volume is decreased and can be further reduced...
Tag: <span>extreme heat</span>
Post
Researcher examines extreme heat, multiple sclerosis link
With sweltering temperatures still enveloping much of the nation, a University of Miami public health scientist has released the results of a new study that shows patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) may experience a worsening of their symptoms when exposed to extreme heat. “We’ve known for quite some time that neurological symptoms of multiple sclerosis...