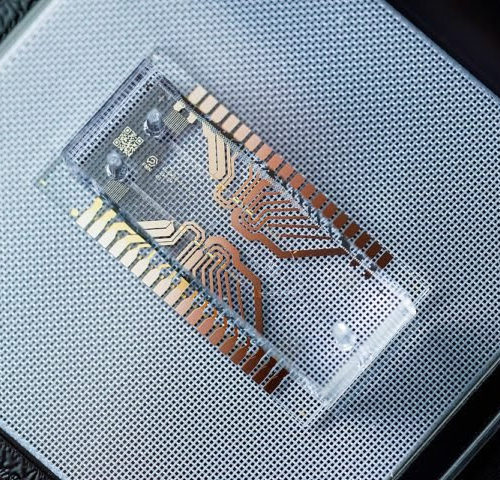
Scientists use acoustic microfluidic devices to separate and sort components in fluids, such as red and white blood cells, platelets and tumour cells in the blood, to better understand diseases or to develop new treatments. However, technologies developed in research labs often lack the consistent performance needed for use in clinical and industrial settings. A team of researchers at...