A previously unknown population of neurons in the hypothalamus could lead to new obesity treatmentsPeer-Reviewed Publication University of Maryland School of Medicine BALTIMORE, Dec. 5, 2024: Obesity affects a staggering 40 percent of adults and 20 percent of children in the United States. While some new popular therapies are helping to tackle the epidemic of obesity,...
Tag: <span>Food intake</span>
Timing of Food Intake a Novel Strategy for Treating Mood Disorders?
Batya Swift Yasgur, MA, LSW September 26, 2022 Shift workers who confine their eating to the daytime may experience fewer mood symptoms compared to those who eat both day and night, new research suggests. Investigators at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, created a simulated nightwork schedule for 19 individuals in a laboratory setting. Participants...
How food intake modifies the gut
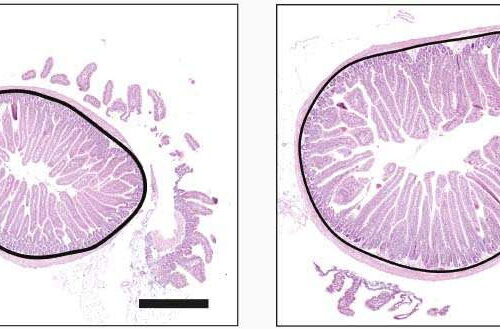
by University of Geneva Sections of mouse intestine. Up, a normal gut circumference (in black) and villi (pink convolutions). Bottom, expanded gut after overeating-induced obesity with a bigger circumference and longer villi. Credit: UNIGE / Mirko Trajkovski With more than 10% of the world’s population obese and 40% overweight, obesity constitutes one of the most...
Same nerve cell, different influence on food intake
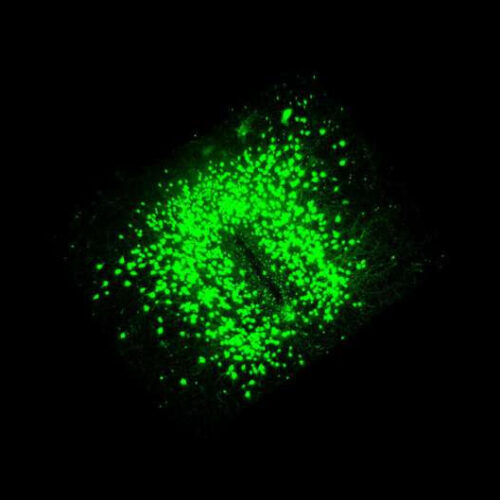
by Max Planck Society 3D rendering of POMC neurons in the hypothalamus. Credit: MPI for Metabolism Research/ Nasim Biglari The nerve cells, also called neurons, in our brain control all the basic processes of our body. For this reason, there are different types of neurons distributed over specific regions of the brain. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for...
Guidance issued for food intake in inflammatory bowel disease
(HealthDay)—In an article from the International Organization for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, published online Feb. 14 in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, recommendations are presented regarding specific food consumption for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Arie Levine, M.D., from the Wolfson Medical Center at Tel Aviv University in Israel, and colleagues reviewed the...
Ultra-Processed foods delay satiety, increase food intake and weight gain
By Dr. Ananya Mandal, MD Eating highly processed foods could be associated with weight gain finds a new study. The study was published in the latest issue of Cell Metabolism and is titled, “Ultra-Processed Diets Cause Excess Calorie Intake and Weight Gain: An Inpatient Randomized Controlled Trial of Ad Libitum Food Intake.” In the United States at present around 40 percent adults are obese says the 2015–2016 figures from the Centers...
32 Percent Of Gluten-Free Restaurant Food Contain Gluten: Study
A new study has found that about 32 percent of restaurants serving gluten-free menu may be untrue to the promise, making people with celiac disease vulnerable. The study reported that there is still a higher chance of being served with gluten food even when the menu indicates it is gluten-free. Eating Out Can Be Dangerous...
Brain hormone triggers fat burning regardless of food intake
Researchers have identified a brain hormone that triggers the burning of fat in the gut, without any obvious side effects Although the neurotransmitter serotonin has previously been shown to play a central role in regulating appetite (amongst other things), the reasons for this remained unclear. In an attempt to shed some light on the...
Neurons anticipate body’s response to food and water
Summary: A new discovery offers new insight into regulation of water and food intake. Neuroscientists recorded neuronal activity in real-time in awake mice when presented with food or water, and identified anticipatory changes in neuronal activity in the seconds prior to drinking. Using leading-edge technology, neuroscientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) gained new...