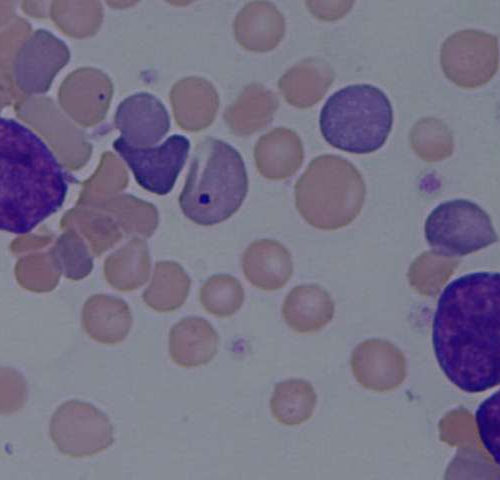
by QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute New QIMR Berghofer research has identified how an early genetic change in blood and bone marrow cells paves the way for the development of some blood cancers. The discovery provides a new target for treatment of the blood cancers myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). MDS is...
Tag: <span>Genetics</span>
Skin cancer: men are genetically more prone
As COVID-19 restrictions loosen this summer, Canadians will spend more time outdoors and make the most of the sunshine. A new study from McGill University suggests why men may be more genetically prone to develop skin cancer. The research led by Professor Ian Watson of McGill’s Goodman Cancer Research Centre (GCRC), published in the journal...
Cancer’s reliance on fat could be targeted with new ‘drugs and diet’ treatment
by Institute of Cancer Research Cancers are often heavily reliant on breaking down fats for their growth and spread, and could be treated by a highly innovative combination of new drugs and dietary changes, a major new study concludes. The landmark research used a surgical ‘iKnife’ to analyze vaporized cancer tissue—and identified a metabolic weakness...
Seeing corneal degeneration in a new light
by UT Southwestern Medical Center The molecular changes that lead to Fuchs’ endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) occur decades before the disease causes blurry vision and other noticeable symptoms in patients, new research by UT Southwestern scientists shows. This insight into this earliest stage of FECD may eventually lead to new ways of screening for and...
Ten reasons why immunity passports are a bad idea
Restricting movement on the basis of biology threatens freedom, fairness and public health. Imagine a world where your ability to get a job, housing or a loan depends on passing a blood test. You are confined to your home and locked out of society if you lack certain antibodies. It has happened before. For most...
Gene therapy with a new base editing technique restores hearing in mice
Repairing a single mutation in the Tmc1 gene restored partial hearing in mice Key Findings: This is the first example of repairing a recessive gene mutation Repairing a single mutation in the Tmc1 gene restored partial hearing in mice The technique required the use of two viral vectors to deliver the base editing machinery Cells...
Study uncovers link between psoriasis and joint disease
Reviewed by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) A team led by Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine researchers has made two major discoveries involving psoriasis, a chronic and debilitating skin disease with no known cure. The researchers found that an overabundance of a protein known as KLK6 can produce and worsen the skin inflammation characteristic...
For acute myeloid leukemia, genetic testing is often worth the wait
Study suggests the benefits of a more personalized therapy typically outweigh the risks of delaying treatment to await test results AMERICAN SOCIETY OF HEMATOLOGY PRINT E-MAIL New tailored therapies offer exciting prospects for treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but taking advantage of them may require waiting a week or more for genetic testing before starting...
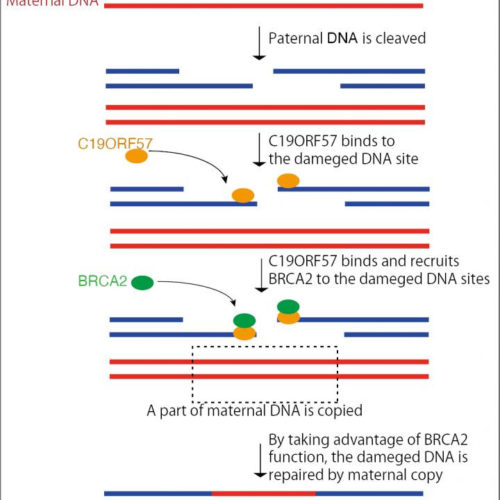
Discovery of a novel gene involved in DNA damage repair and male fertility
Clarifying the mechanisms for meiotic recombination in sperm production KUMAMOTO UNIVERSITY A research group from the Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG)at Kumamoto University, Japan has discovered that the gene C19ORF57 plays a critical role in meiosis. The gene appears to be related to the cause of male infertility and could be a big...
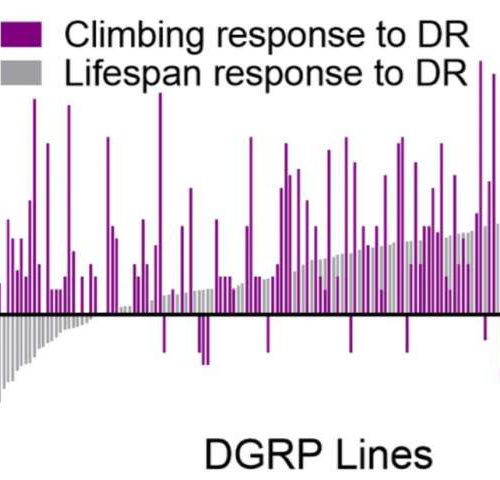
Eat less and live a long healthy life? Study shows ‘not in all cases’
by Buck Institute for Research on Aging Each of the analyzed fly strains arranged by response to dietary restriction. The overlapping bars show the increase or decrease in lifespan (grey bars) or healthspan (purple bars) when that fly strain underwent dietary restriction. Most strains show positive responses, but a number of strains show negative responses...