The bacteria, fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum), proliferates in periodontal disease and affects the gums and jawbone. If untreated, it results in unstable teeth and tooth loss. In recent years, studies have linked F. nucleatum to conditions ranging from colorectal cancer to premature delivery of babies. “In this study, our lab is the first to find that Fusobacterium nucleatum can generate systemic inflammation and...
Tag: <span>Gum disease</span>
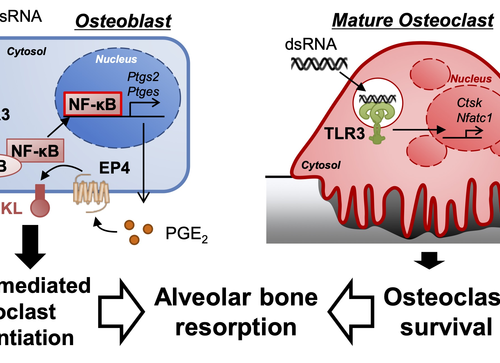
Double-stranded RNA induces bone loss during gum disease
TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE AND TECHNOLOGY IMAGE: TLR3 SIGNALING ACTIVATED BY DS RNA [POLY(I:C)] ANALOGUE INDUCES THE PGE2-MEDIATED EXPRESSION OF RANKL THAT STIMULATES OSTEOCLAST FORMATION AND DIRECTLY PROLONGS THE LIFE SPAN OF MATURE OSTEOCLASTS, THAT WAS LEADING ALVEOLAR BONE RESORPTION IN PERIODONTAL DISEASE. CREDIT: MASAKI INADA, TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE AND TECHNOLOGY Tokyo University of...
Evidence grows for vaping’s role in gum disease
by New York University Credit: CC0 Public Domain A series of new studies by researchers at NYU College of Dentistry highlights how e-cigarettes alter oral health and may be contributing to gum disease. The latest, published in mBio, finds that e-cigarette users have a unique oral microbiome—the community of bacteria and other microorganisms—that is less healthy...
Disarming a blood-clotting protein prevents gum disease in mice
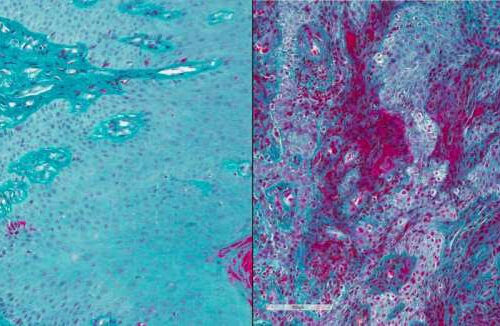
by National Institutes of Health Compared with healthy volunteers (left), gum tissue from people with severe periodontal disease (right) shows high levels of fibrin (magenta). Credit: Lakmali Silva, NIDCR Blocking function of a blood-clotting protein prevented bone loss from periodontal (gum) disease in mice, according to research led by scientists at the National Institute of...
Gum disease increases risk of other illness such as mental health and heart conditions, study finds
by University of Birmingham Credit: CC0 Public Domain A University of Birmingham-led study shows an increased risk of patients developing illnesses including mental ill-health and heart conditions if they have a GP-inputted medical history of periodontal (gum) disease. Experts carried out a first of its kind study of the GP records of 64,379 patients who...
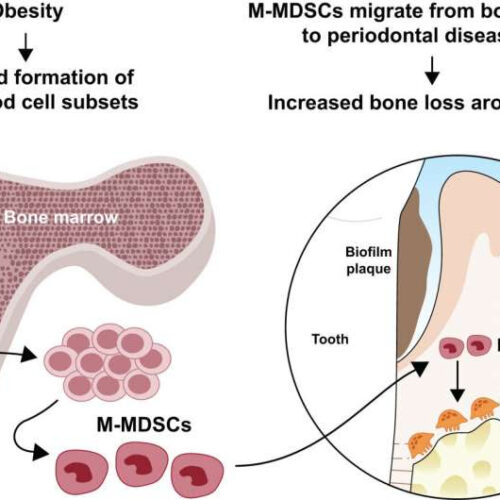
Obesity raises the risk of gum disease by inflating growth of bone-destroying cells
by Marcene Robinson, University at Buffalo The graphic demonstrates how MDSC expansion during obesity to become bone destroying osteoclasts during gum disease is tied to increased bone loss around teeth. Credit: Keith Kirkwood Chronic inflammation caused by obesity may trigger the development of cells that break down bone tissue, including the bone that holds teeth...
HEARTBURN DRUGS MAY CUT GUM DISEASE SEVERITY
The researchers found that patients who used proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)—a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers—were more likely to have smaller probing depths in the gums (the gap between teeth and gums). When gums are healthy, they fit snuggly against the teeth. However, in the presence of harmful bacteria, the...
Study finds that heartburn drugs may provide unexpected benefits for those with gum disease
by University at Buffalo Credit: CC0 Public Domain The use of heartburn medication is associated with decreased severity of gum disease, according to a recent University at Buffalo study. The research found that patients who used proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)—a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers—were more likely to have...
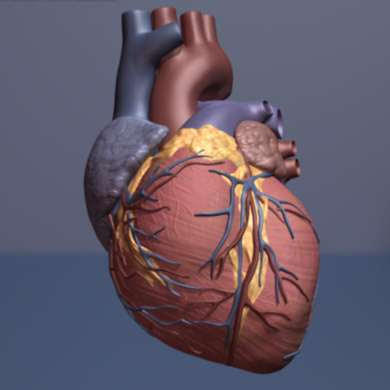
Gum disease linked with new onset heart disease
by European Society of Cardiology Human heart. Credit: copyright American Heart Association Gum disease is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease: the more severe the periodontitis, the higher the risk. The findings are presented at ESC Congress 2021. The association was particularly evident among patients who had experienced a heart attack in the past....
Gum disease linked to severe COVID-19 outcomes
Written by Robby Berman on April 25, New research finds a link between COVID-19 severity and gum disease. Nes/Getty Images Researchers at McGill University find a strong link between periodontitis, a common form of gum disease, and severe COVID-19 outcomes. Periodontitis produces an inflammatory response that may spread through the body — scientists have previously linked the...