BOSTON COLLEGE Chestnut Hill, Mass. (4/13/2022) – Gut microbes can regulate the exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas and hormone production of the gastrointestinal tract, findings that may help develop potential treatments for diabetes and other diseases, a team of researchers from Boston College, Joslin Diabetes Center, and Maastricht University, Netherlands, report in the...
Tag: <span>Gut microbiota</span>
Scientists discover link between gut microbiota and chronic inflammatory diseases like arthritis
by Laval University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain An international research team has established a link between gut microbiota and chronic inflammatory diseases such as arthritis. The team led by Éric Boilard of Université Laval has discovered that a protein naturally present in the gut acts on the microbiota and causes the formation of molecules that...
Neutral mutants can prevail in gut microbiota, enhancing diversity
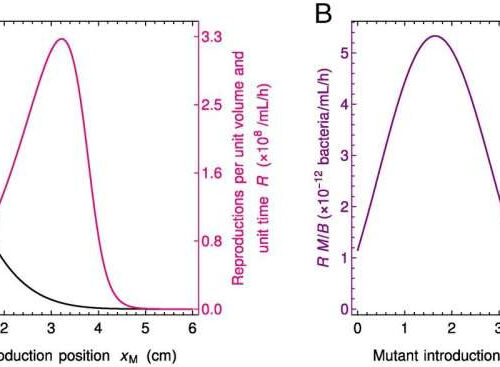
by Nik Papageorgiou, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Fate of neutral mutants appearing at various locations in the gut. (A) Steady-state ratio M / B of mutant to wild-type bacteria concentrations and number of reproduction events R per unit volume and unit time vs. position xM of the mutant introduction. The ratio M / B yields...
How changing gut microbiota can affect lupus disease activity in mice
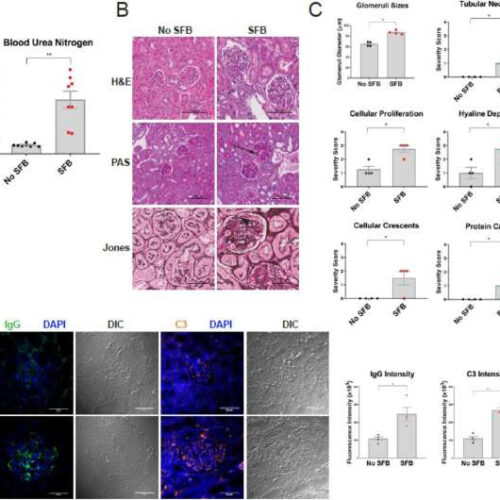
by The Ohio State University Figure 1. NZM2410 colonized with SFB exhibit intensified kidney disease with elevated immune-complex deposition. 10-week old mice were oral gavaged with fecal matter from mice harboring SFB or control mice and sacrificed at 30-weeks of age and subjected to biochemical analysis. (A) Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN). (B) Kidney disease...
With age, insufficient tryptophan alters gut microbiota, increases inflammation
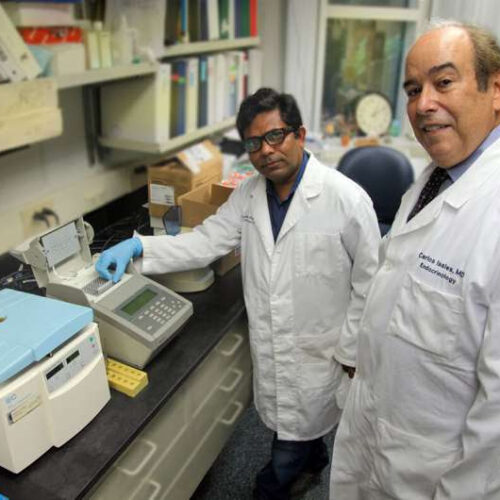
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University Drs. Sadanand Fulzele and Carlos Isales. Credit: Augusta University With age, a diet lacking in the essential amino acid tryptophan—which has a key role in our mood, energy level, and immune response—makes the gut microbiome less protective and increases inflammation body-wide, investigators report. In a normally reciprocal relationship...
The role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory skin diseases
SAY COMMUNICATIONS LUGANO, 7 May, 2021- Findings presented at today’s EADV 2021 Spring Symposium suggest that an imbalance in gut microbiota (dysbiosis), could play a significant role in the progression of inflammatory skin disease, Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS). HS is a painful, long-term skin condition, with a chronic and relapsing nature that significantly impacts patients’ quality...
Study examines fermented milks’ potential benefits for decreasing high blood pressure through modulation of gut microbiota
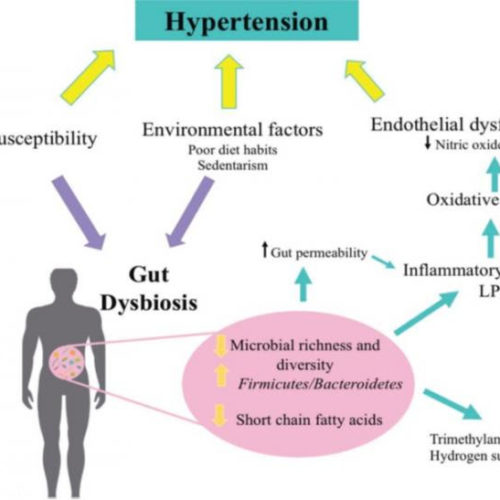
ELSEVIER IMAGE: ASSOCIATION BETWEEN DYSBIOSIS OF GUT MICROBIOTA AND HYPERTENSION CREDIT: JOURNAL OF DAIRY SCIENCE Philadelphia, March 19, 2021 – In recent years, fermented dairy foods have been gaining attention for their health benefits, and a new review published in the Journal of Dairy Science indicates these foods could help reduce conditions like hypertension (high...
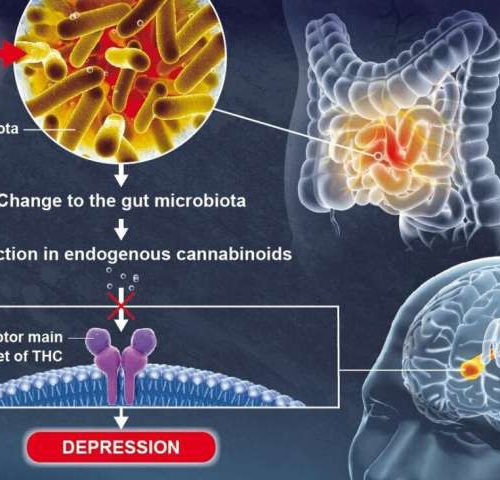
Gut microbiota plays a role in brain function and mood regulation
by Pasteur Institute Credit: Pascal Marseaud Depression is a mental disorder that affects more than 264 million people of all ages worldwide. Understanding its mechanisms is vital for the development of effective therapeutic strategies. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur, Inserm and the CNRS recently conducted a study showing that an imbalance in the gut bacterial community...
Effects of a Gluten-Free Diet on the Gut Microbiota
By Dr. Maho Yokoyama, Ph.D.Reviewed by Michael Greenwood, M.Sc. Why a Gluten Free Diet? Gluten is a protein found in grains such as wheat, barley, and rye, and is comprised of gliadins. For some people, eating foods that contain gluten can cause digestive problems due to gluten-related disorders. Gluten-related disorders can range from mild to severe in symptoms, and include celiac disease...
Microbiome may be involved in mechanisms related to muscle strength in older adults
by Tufts University A novel new study suggests that the gut microbiome has a role in mechanisms related to muscle strength in older adults. The work, led by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts, is available as a pre-proof in advance of print in Experimental Gerontology....