JUNE 6, 2024 by Cleveland Clinic Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainCleveland Clinic researchers found higher amounts of the sugar alcohol xylitol are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events like heart attack and stroke. The team, led by Stanley Hazen, M.D., Ph.D., confirmed the association in a large-scale patient analysis, preclinical research models and a clinical...
Tag: <span>heart attack</span>
Cannabis use linked to increase in heart attack and stroke risk
by American Heart Association Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain An analysis of 430,000 adults in the U.S. found that using cannabis, most commonly through smoking, eating, or vaporizing it, was significantly associated with a higher risk of heart attack and stroke, even after controlling for tobacco use (combustible cigarettes and other tobacco products) and other cardiovascular risk...
Niacin supplements linked to greater risk of heart attacks and strokes
People with higher levels of niacin in their blood may be more at risk of a heart attack or stroke, possibly because too much of the vitamin inflames blood vessels By Grace Wade Niacin, or vitamin B3, is a popular supplement SERSOL/Alamy People with high levels of niacin, also known as vitamin B3, in their...
How a standard blood test can predict a heart attack
by Uppsala University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainUsing the results of a standard blood test and an online tool, you can find out if you are at increased risk of having a heart attack within six months. The tool has been developed by a research group at Uppsala University in the hope of increasing patients’ motivation to...
Stroke or stroke plus neck artery tear almost doubles risk of heart attack within a year, finds research
by American Heart Association Credit: CC0 Public DomainHeart attack risk almost doubles in the first year after a stroke or when combined with a tear in a neck artery wall; however, a tear without a stroke does not seem to raise heart attack risk, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s...
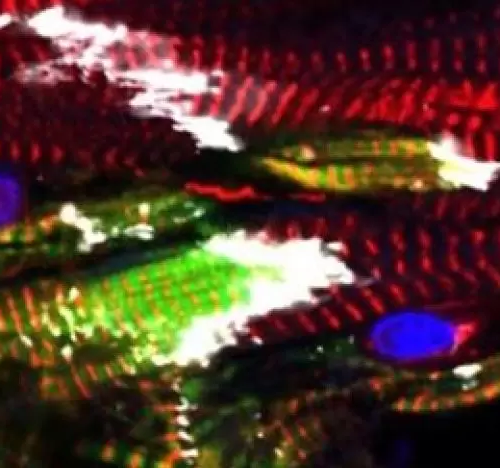
Combining Cell Types May Lead to Improved Cardiac Cell Therapy Following Heart Attack
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and other institutions have harnessed a combination of lab-grown cells to regenerate damaged heart muscle.Mixing endothelial cells with heart muscle addresses major challenges of bringing treatments to the clinic. Image Credit: Yu-Che Cheng The study, published in Circulation, addresses major challenges of using heart muscle cells grown from stem...
Wegovy cuts risk of heart attacks in milestone cardiovascular trial
By Elaine Chen This image provided by Novo Nordisk in January 2023, shows packaging for the company’s Wegovy drug.NOVO NORDISK VIA AP PHILADELPHIA — Novo Nordisk’s obesity drug Wegovy notably cut the risk of heart attacks in a landmark cardiovascular trial that affirms the treatment offers health benefits beyond weight loss. The company in August had...
Marijuana use linked with increased risk of heart attack, heart failure
by American Heart Association Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Using marijuana regularly may raise the risk for heart failure, stroke or heart attack even after accounting for other cardiovascular risk factors such as Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and obesity, according to two preliminary studies to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2023. The...
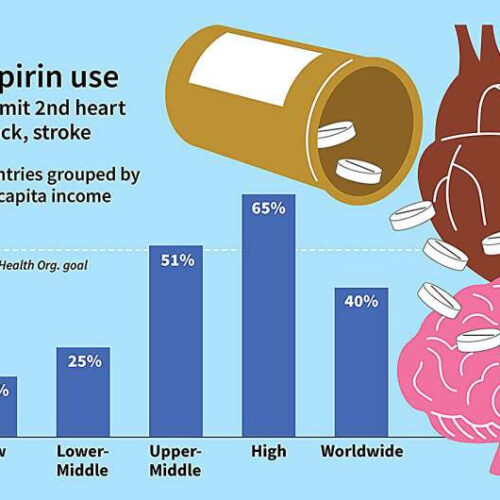
Aspirin can help prevent a second heart attack, but most don’t take it
by Washington University School of Medicine Aspirin can help prevent a second heart attack, but most don’t take itWorldwide, only 40% of eligible patients are taking daily aspirin to prevent a second heart attack or stroke, according to a new study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Grouped by per-capita income,...
New Pill Cuts Cholesterol and Heart Attacks
By Nisha Zahid New Pill Cuts Cholesterol and Heart Attacks. Credit: Daniel Foster, CC BY-NC-SA A new cholesterol-lowering drug called Nexletol has shown promise in reducing the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems in people who cannot tolerate traditional statin drugs, according to a major study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s annual meeting....