By Michael Irving April 04, 2022 A phase 1 trial for an RNA gene therapy has shown promise in reducing levels of a lipoprotein that can lead to cardiovascular disease Depositphotos In phase 1 trials, an experimental siRNA therapy has shown promise for reducing levels of a lipoprotein associated with a higher risk of premature...
Tag: <span>heart disease risk</span>
Gene map may identify heart disease risk for people with type 2 diabetes
by American Heart Association Credit: CC0 Public Domain A risk score based on a gene map predicted the likelihood of high blood pressure leading to heart problems or stroke in people with Type 2 diabetes, according to a study published today in the American Heart Association’s peer-reviewed journal Hypertension. This tool may be especially useful in...
Biomarker discovery measures COVID-19 heart disease risk
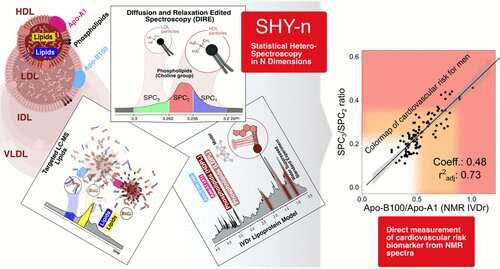
by Murdoch University Graphical abstract. Credit: Analytical Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05389 Researchers at Murdoch University’s Australian National Phenome Centre have discovered a new set of biomarkers for increased risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with COVID-19 infections. COVID-19 infection has previously been associated with significantly elevated risks of multiple types of cardiovascular disease and cardiac insufficiency, and...
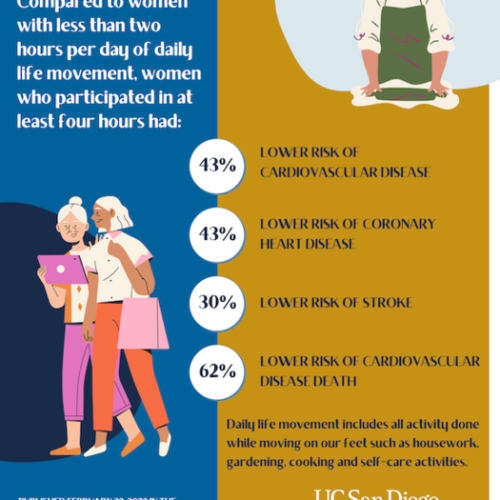
Daily activities like washing dishes reduced heart disease risk in senior women
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO IMAGE: DAILY LIFE MOVEMENT INCLUDES ALL ACTIVITY DONE WHILE MOVING ON ONE’S FEET DURING ACTIVITIES SUCH AS HOUSEWORK, GARDENING, COOKING AND SELF-CARE ACTIVITIES. CREDIT: HERBERT WERTHEIM SCHOOL OF PUBLIC HEALTH AND HUMAN LONGEVITY SCIENCE AT UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN DIEGO Seniors take note, running or brisk walking is not...
Heart-disease risk soars after COVID — even with a mild case
The risk of 20 diseases of the heart and blood vessels is high for at least a year after a COVID-19 diagnosis. Credit: Living Art Enterprises/Science Photo Library Even a mild case of COVID-19 can increase a person’s risk of cardiovascular problems for at least a year after diagnosis, a new study shows. Researchers found...
Social isolation and loneliness increase heart disease risk in senior women
by University of California – San Diego As social networks shrink, older adults are more at risk for social isolation and loneliness. Credit: Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego During the current pandemic, social distancing has been one tool used to reduce the spread of...
Depression and anxiety worsened during the pandemic, putting patients at higher heart disease risk, study finds
INTERMOUNTAIN HEALTHCARE IMAGE: A PATIENT IS TREATED AT AN INTERMOUNTAIN HEALTHCARE EMERGENCY ROOM. CREDIT: INTERMOUNTAIN HEALTHCARE The COVID-19 pandemic has not only affected the physical health of millions of Americans, but it’s also taken a toll on the country’s mental health. A new study by researchers at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City finds that...
Heart disease risk in women increases leading up to menopause; early intervention is key
by American Heart Association Credit: CC0 Public Domain The menopause transition, the years leading up to menopause, is a time of increasing heart disease risk for women. Monitoring women’s health and lifestyle, while integrating early intervention strategies for good cardiovascular health, are important, especially during midlife and during menopause to help prevent heart disease, according to...
New study confirms combo pill alone and with aspirin lowers heart disease risk
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION Embargoed until 12:10 p.m. CT/1:10 p.m. ET, Friday, Nov. 13, 2020 DALLAS, Nov. 13, 2020 — A single, daily pill combining blood pressure and cholesterol medications, along with the addition of a daily dose of aspirin, reduced cardiovascular disease events in people at risk for heart disease, according to late-breaking research presented...
Studies reveal mutations that boost blood stem cell growth and increase leukemia and heart disease risk
by Sarah C.p. Williams, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard As people grow older, certain genetic mutations in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)—which give rise to blood and immune cells—can eventually cause cancer or predispose people to cardiovascular disease. Now, two teams of scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston Children’s...