Imagine visiting the doctor, answering a few basic questions, and getting an on-the-spot estimate of whether you’ll experience heart failure in the next 30 years. Such a model now exists, thanks to a new Northwestern Medicine study, which derived and validated the first set of risk prediction models for lifetime risk of heart failure. The ability...
Tag: <span>heart failure</span>
Research team develops first model to predict lifetime risk of heart failure
by Northwestern University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Imagine visiting the doctor, answering a few basic questions and getting an on-the-spot estimate of whether you’ll experience heart failure in the next 30 years. Such a model now exists, thanks to a new Northwestern Medicine study, which derived and validated the first set of risk prediction models for lifetime risk of heart...
People with HIV are at increased risk for heart failure
KAISER PERMANENTE OAKLAND, Calif. — People with HIV are at higher risk of developing heart failure than people without HIV, a new study found. The research, published December 13 in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, is one of the largest studies to investigate heart failure risk in people with HIV and how that risk varies by age, gender, race, and...
The diabetes medication that could revolutionise heart failure treatment
by University of East Anglia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A medication originally used for patients with diabetes is the first to help people with heart failure and could revolutionize treatment, according to new research from the University of East Anglia. Early research had shown that Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors could help around half of heart failure patients—those...
Diabetes drug dapagliflozin may benefit patients with heart failure
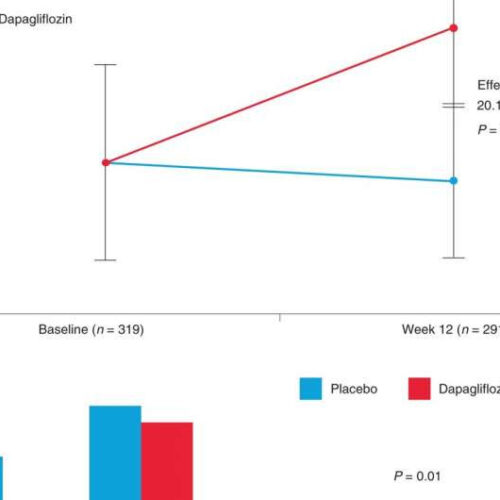
by Melissa Rohman, Northwestern University Effects of dapagliflozin on selected secondary endpoints and in supportive responder analysis. a–c, Effects of dapagliflozin on selected secondary endpoints and in supportive responder analysis. Effects of dapagliflozin versus placebo at 12 weeks on 6MWT distance (a), KCCQ-CS responder analysis (b) and KCCQ-OS (c). Data are presented as mean values with 95%...
Aspirin increases the risk of heart failure by over 25%
(© blueskies9 – stock.adobe.com)HEART HEALTH by Chris Melore SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France — Aspirin is one of the most common pain relievers in the world, but a new study finds it may be contributing to heart failure. Researchers with the European Society of Cardiology find taking aspirin raises the risk of heart failure among people with at least...
Heart failure symptoms improve with a type 2 diabetes medicine
by American Heart Association Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Canagliflozin, a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, was found to greatly improve symptoms and quality of life within 3 months for people with heart failure due to either reduced or preserved cardiac function, even if they didn’t also have type 2 diabetes, according to late-breaking...
Popular heart failure drug no better than older drug in sickest patients
A new study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that a widely used heart failure drug named sacubitril/valsartan is no better than valsartan alone in patients with severe heart failure. The study also provides evidence that the treatment with valsartan may be slightly safer for patients with advanced...
Report points to new therapeutic approach for tough-to-treat heart failure
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (10/19/2021) – Recent studies may point towards a new therapeutic mechanism for a type of heart failure that currently has no specific treatment option. Researchers from the University of Minnesota Medical School — along with the University of Vermont and the Medical University of South Carolina — looked into a condition called heart failure with...
Scientists show how AI may spot unseen signs of heart failure
by The Mount Sinai Hospital Researchers at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai developed an electrocardiogram-reading algorithm that can detect subtle signs of heart failure. Credit: Glicksberg and Nadkarni labs, Mount Sinai, N.Y., N.Y. A special artificial intelligence (AI)-based computer algorithm created by Mount Sinai researchers was able to learn how to identify subtle changes...