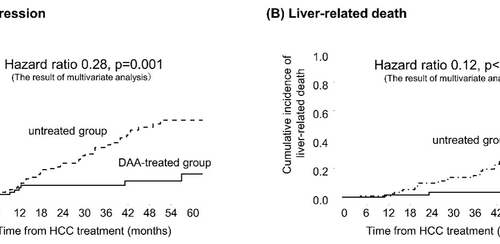
IMAGE: CUMULATIVE INCIDENCE OF TUMOR PROGRESSION (A) AND LIVER-RELATED MORTALITY (B) BY KAPLAN-MEIER ANALYSIS. TUMOR PROGRESSION WAS DEFINED AS WHEN HCC PROGRESSES TO MULTIPLE NODULES IN THE LIVER, PORTAL INVASION OR METASTASIZES TO OTHER PARTS OF THE BODY, BRINGING THE DISEASE FROM EARLY- TO ADVANCED-STAGE HCC, ACCORDING TO THE BARCELONA CLINIC LIVER CANCER STAGING SYSTEM....
Tag: <span>Hepatitis C</span>
Exploring a key to hepatitis C entry into cells
by NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases A transmission electron microscopic image of hepatitis virus particles. Credit: CDC/ E.H. Cook, Jr. In a new paper published in Nature, scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, describe the structure of a key protein on the surface...
Hepatitis C and joint pain: What is the link?
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) often does not always cause symptoms, but if the infection becomes chronic, it can cause complications over time. One of these is joint inflammation and pain. Sometimes, joint pain is the first symptom that people with HCV notice, and in some cases, it may indicate arthritis. HCV is also associated with other...
X-ray study explores potential of hepatitis C drugs to treat COVID-19
by Oak Ridge National Laboratory The heart-shaped SARS-CoV-2 main protease enables the virus to reproduce by cutting long chains of proteins that activate the replication process. Experiments show existing drugs used to treat hepatitis C may have potential to treat COVID-19 by stopping the “heart” of the virus. Experiments led by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak...
New method developed for non-invasive risk assessment following hepatitis C recovery
by Johannes Angerer, Medical University of Vienna The chronic viral inflammation of the liver that occurs in hepatitis C results in the formation of inflexible scar tissue in the form of fibrosis/cirrhosis of the liver. This impedes the flow of blood through the organ, with resulting hypertension in the portal vein. In the majority of...
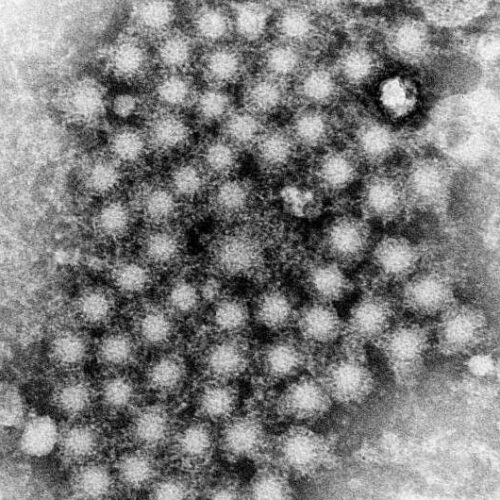
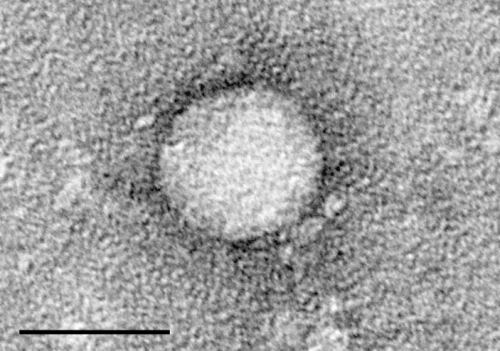
Evidence review shows new therapy for Hepatitis C is highly effective
by Oregon Health & Science University Electron micrographs of hepatitis C virus purified from cell culture. Scale bar is 50 nanometers. Credit: Center for the Study of Hepatitis C, The Rockefeller University. New direct-acting antiviral therapies are highly effective at eliminating the Hepatitis C virus infection, according to a systematic evidence review by researchers at...
Study shows that hepatitis C drug EPCLUSA has the potential to inhibit coronaviruses
by Columbia University Columbia Engineering researchers have been developing strategies to cope with the new strain of coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, that has caused a global public health emergency. In their latest study, “Nucleotide analogues as inhibitors of viral polymerases,” posted now in bioRxiv, the researchers recognized that the hepatitis C virus and coronaviruses use a similar...
What to know about false positives in hepatitis C testing
Hepatitis C is a viral liver infection that can become chronic. Some people have antibodies associated with the virus in their blood but do not have an active hepatitis C infection. These antibodies can lead to false-positive results on blood tests for the infection. A person can have hepatitis C for a number of years, or sometimes...
For older adults, new hepatitis C treatments are safe and effective
by American Geriatrics Society Viral hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the liver. There are three viruses responsible for most cases of the disease: hepatitis A, B, and C. Hepatitis A is typically caused by consuming contaminated food or water. Hepatitis B and C usually occur when someone comes in contact with infected...
What hepatitis C genotypes mean for treatment
By Jenna Fletcher Reviewed by Cameron White, MD, MPH Hepatitis C is liver inflammation that results from a viral infection. It may not cause symptoms, so it can go undetected for years. As the infection progresses over many years, it can cause liver damage. This may take the form of scarring, permanent damage called cirrhosis,...