Researchers have discovered that the cells that cause goosebumps are also important for regulating the stem cells that regenerate hair. In the skin, the muscle that contracts to create goosebumps is necessary to bridge the sympathetic nerve’s connection to hair follicle stem cells. The sympathetic nerve reacts to cold by contracting the muscle and causing...
Tag: <span>homeostasis</span>
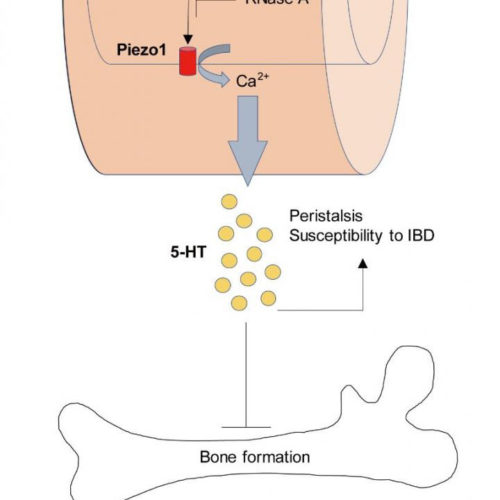
Gut Piezo1 regulates gut and bone homeostasis via RNA sensing.
NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF NATURAL SCIENCES SCHEMATIC MODEL OF FECAL RNA-MEDIATED SEROTONIN PRODUCTION. view more CREDIT: KENTA MARUYAMA In a new study published in Cell, “RNA sensing by gut Piezo1 is essential for systemic serotonin synthesis”, a research team led by Kenta Maruyama M.D., Ph.D. from National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) explored the role of...
Whoa: This Is What Happens to Your Body When You Drink Enough Water
If you’re reading this: Drink a glass of water. You likely need it, as 75 percent of Americans are described as “chronically dehydrated.” While achieving a state of hydration might seem enviable and impossible, fret not because it’s doable. And the health benefits are not only encouraging, but they are also downright inspiring in the...
Diabetes drug may protect breastfed children from future metabolic disorder
by American Physiological Society A new study suggests that treating a breastfeeding parent with a common diabetes drug may provide male offspring lifelong protection against diabetes and obesity. The study is published ahead of print in the American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. It was chosen as an APSselect article for May. Studies have shown...
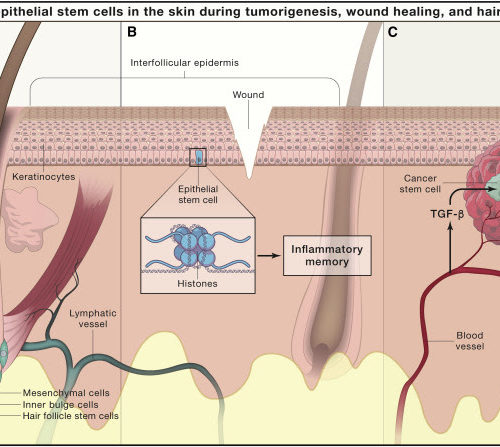
Skin in the Game: Stem Cells in Repair, Cancer, and Homeostasis
The 2020 Canada Gairdner International Award has been awarded to Elaine Fuchs for her discovery of the role of adult skin stem cells in homeostasis, wound repair, inflammation, and cancer. These insights have established a foundation for basic knowledge on how adult stem cells form, maintain, and repair tissues and have provided the groundwork for...
Restoring protein homeostasis improves memory deficits in Down syndrome model
by Baylor College of Medicine Down syndrome is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability, and currently there is no effective treatment. Memory deficits are a hallmark of this condition and a study published today in the journal Science reports that the defects in a conserved stress pathway dubbed the ‘integrated stress response,’ or...
Identifying new important players in insulin homeostasis
by La Trobe University Researchers from La Trobe University in Australia and the Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden, partner in the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD e.V.), in Germany have identified that the protein Atp6ap2 is essential for the correct functioning of pancreatic beta cells. When this protein was switched off in the beta cells...
New UCI-led study defines best time to exercise to get the most rejuvenating results
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE A new study led by researchers from the University of California, Irvine finds exercising in the morning, rather than at night, may yield better results. This study, published today in Cell Metabolism, points to daily timing as a critical variable for metabolic benefits from exercise and implications in chronobiology-based exercise therapy for patients with metabolic disorders. “Using mice, we compared the...
The ‘dynamic duo’ of enzymes in the development of cancer
Mutated helicase enzymes shown to work together to disrupt telomere homeostasis and regulation of cell division. All strands of DNA have a non-coding region at the end of the strand known as the telomere. During each replication of the gene, when the cell divides, small nucleotides are lost leading to the gradual shortening of the telomere. In...
Solving the gut inflammation puzzle
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), an umbrella term for a number of gut disorders—including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease—remains a clinical challenge. Current treatments don’t work for all patients, and many stops working over time. But despite their different responses to treatment, all IBD patients share a commonality: intestinal inflammation. A better understanding of what drives...