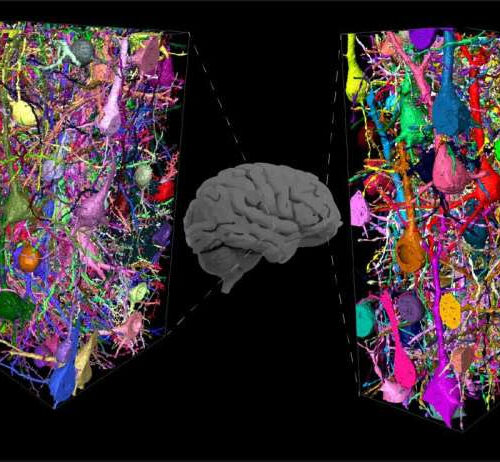
by Max Planck Society Human neuronal networks, mapped from different parts of the cerebral cortex. Connectomic comparison to mouse revealed massively expanded interneuron-to-interneuron networks in human. Credit: Loomba, Helmstaedter, MPI for Brain Research The analysis of the human brain is a central goal of neuroscience. However, for methodological reasons, research has largely focused on model...
Tag: <span>Human Brain</span>
Scientists create highly detailed 3D reconstructions of the human brain
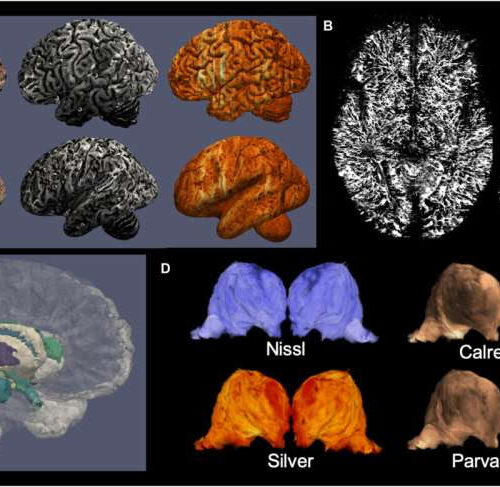
by University of Amsterdam Examples of information derived from the dataset of specimen no. 15-2017. (A) Cortical maps from the dataset: blockface (left), quantitative R2* (middle), and parvalbumin immunohistochemistry (right), sampled at the midcortical surface in fully folded (top) or inflated (bottom) views; (B) reconstructed blood vessels extracted from the coregistered stainings; (C) automated cortical...
Human brain doesn’t slow down until after 60
You used to be able to make snap judgments in your 20s, but now it feels like you take a lot longer to react to questions, decisions and challenges put before you. Don’t fret, it’s not that you’re losing brain power. Your response time does tend to slow down as you age, but a new study...
Microglial methylation “landscape” in human brain
ELSEVIER Philadelphia, December 28, 2021 – In the central nervous system, microglial cells play critical roles in development, aging, brain homeostasis, and pathology. Recent studies have shown variation in the gene-expression profile and phenotype of microglia across brain regions and between different age and disease states. But the molecular mechanisms that contribute to these transcriptomic...
Human brain replays new memories at 20 times the speed during waking rest
CELL PRESS Neural replay during waking rest may contribute to memory consolidation of action sequences in humans, according to a study published June 8 in the journal Cell Reports. Brain imaging results revealed fast, repeated reactivation of a neural network representing a behavioral sequence that people were learning–approximately 20 times the speed of the new memory–especially...
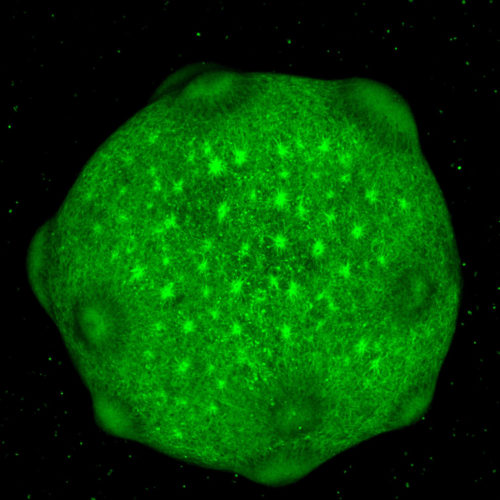
Tiny clusters of lab-grown cells are a new window into the human brain
Alison Snyder Clumps of brain cells grown in the lab provide a way to study the organ that is central to our species but is largely inaccessible in living people. Why it matters: Brain-related disorders — from autism spectrum disorders to schizophrenia to Parkinson’s disease — are a leading contributor to disability in people around the world. These...
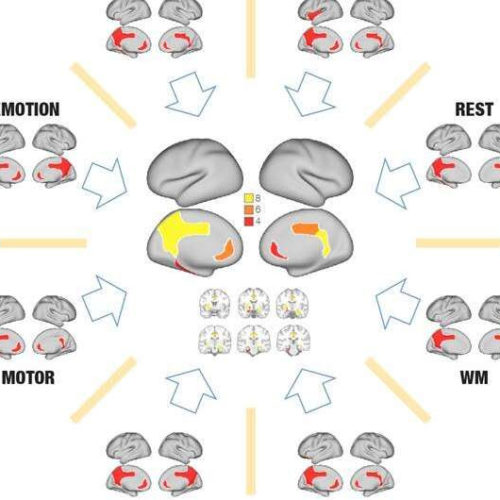
Revisiting the Global Workspace orchestrating the hierarchical organisation of the human brain
by Universitat Pompeu Fabra – Barcelona The new identification of the global workspace results from the intersection of key causal brain regions involved in orchestrating the performance of seven cognitive tasks and the resting state. Credit: Universitat Pompeu Fabra – Barcelona The celebrations in the 250th anniversary of the birth of Ludwig van Beethoven would...
New form of neuronal communication is discovered in the human brain
We don’t quite understand how our own brain works – it is actually quite a big mystery. However, scientists are improving our knowledge of our central nervous system all the time. For example, now researchers from the University of Helsinki and Aalto University, in collaboration with the University of Glasgow and the University of Genoa, have identified...
New model of human brain ‘conversations’ could inform research on brain disease, cognition
INDIANA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: RICHARD BETZEL A team of Indiana University neuroscientists has built a new model of human brain networks that sheds light on how the brain functions. The model offers a new tool for exploring individual differences in brain networks, which is critical to classifications of brain disorders and disease, as well as for...
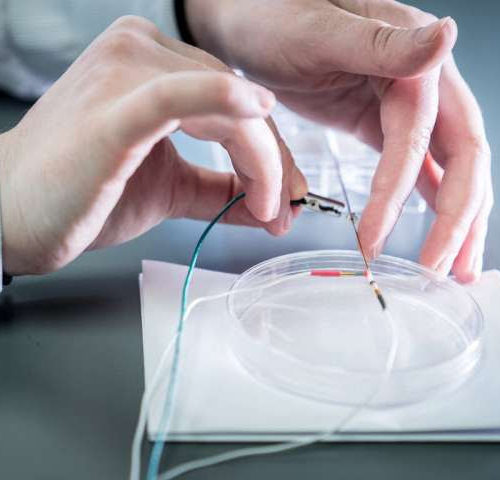
Scientists find neurochemicals have unexpectedly profound roles in the human brain
by Virginia Tech Virginia Tech researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute Center for Human Neuroscience Research construct carbon fiber microelectrodes for real-time detection of dopamine and serotonin activity in human patients. In first-of-their-kind observations in the human brain, an international team of researchers has revealed two well-known neurochemicals—dopamine and serotonin—are at work at sub-second speeds to shape...