By Dr. Chinta SidharthanReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.Nov 21 2024 From cells to solutions: The Human Cell Atlas pioneers a global effort to map human biology and bridge health inequities with cutting-edge genomics. Perspective: The commitment of the human cell atlas to humanity. Image Credit: Sinhyu Photographer / Shutterstock In a recent perspective article published in the journal Nature Communications, over...
Tag: <span>Human cells</span>
Scientists Awaken the Force in Our Cells
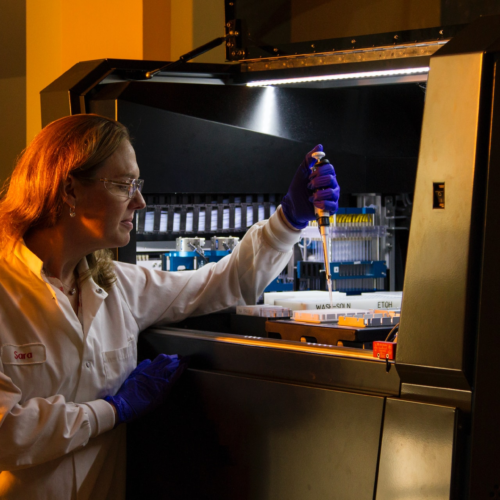
Researchers at the Yale Nanobiology Institute have developed a new tool to measure how our cells transmit physical force – a trigger for molecular messages and regulating major cellular functions. Working with human cells in a biotechnology lab – associative photo. Image credit: NCI via Unsplash, free license Published in Science Advances, the findings cast...
Antisense therapy restores fragile X protein production in human cells
by Jim Fessenden, UMass Chan Medical School (A) Volcano plot of log2FC of RNA levels (FXS vs TD). Statistically significant changes (P value <0.0002) are shown as blue dots (down-regulated) and red dots (up-regulated). Gray dots refer to unchanged RNAs. (See also Dataset S2). (B) Histograms for TPM values for RNAs that are up or...
Scientists shine a spotlight on yet another shrewd maneuver HIV uses to commandeer human cells
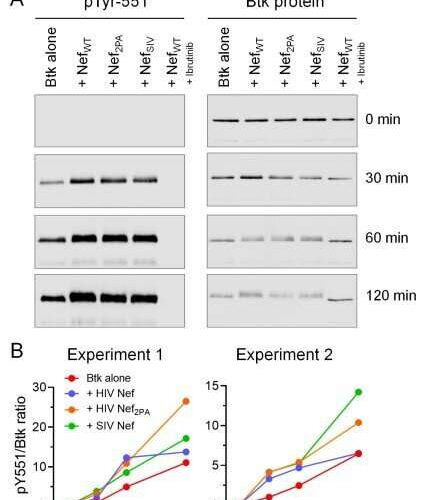
by Delthia Ricks, Medical Xpress Nef induces Btk autophosphorylation at Tyr551 in the activation loop. Each kinase reaction was performed with Btk alone or in presence of HIV‐1 Nef wild‐type (WT), the PxxP to AxxA mutant (2PA), SIV Nef, or wild‐type Nef plus 1 µM ibrutinib as a negative control. Aliquots collected at 0, 30, 60,...
Doctors Transplant 3-D Printed Ear Made of Human Cells
June 2, 2022 in News A 20-year-old woman who was born with a small and misshapen right ear has received a 3-D printed ear implant made from her own cells, the manufacturer announced on Thursday. Independent experts said that the transplant, part of the first clinical trial of a successful medical application of this technology,...
Researchers use CRISPR to build melanoma models from scratch using human cells
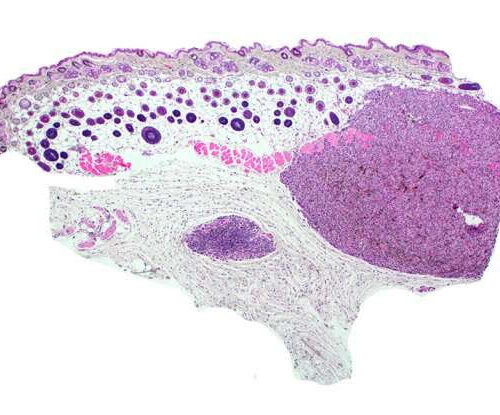
by Allessandra Dicorato, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard A histology image of a melanoma model. Credit: Science (2022). DOI: 10.1126/science.abi8175 By introducing cancer-causing mutations into healthy skin cells step-by-step, Broad scientists have created models of skin cancer that can reveal the effects of mutations. Over the last two decades, researchers have discovered thousands of genetic mutations in cancer, but...
Study reveals how ribosomes are assembled in human cells
All cells need ribosomes to make the proteins necessary for life. These multi-component molecular machines build complex proteins by stitching building blocks together according to instructions encoded in the cell’s messenger RNAs. But ribosomes are themselves composed of small and large subunits, each of which is made up of ribosomal proteins and RNA. Before they can manufacture proteins, these subunits must be manufactured...
Q&A: Nanobots could explore human cells – but their size is an engineering challenge
Scientists are developing virus-sized robots that could defuse blood clots, explore human cells or even scrub water of impurities. Image credit: Pixabay (Free Pixabay license) But as these inventions get smaller, the laws of motion that govern these machines are not very intuitive, so researchers are drawing inspiration from nature, says Brad Nelson, professor of robotics at...
New discovery shows human cells can write RNA sequences into DNA
by Thomas Jefferson University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Cells contain machinery that duplicates DNA into a new set that goes into a newly formed cell. That same class of machines, called polymerases, also build RNA messages, which are like notes copied from the central DNA repository of recipes, so they can be read more efficiently into...
Fascinating new videos capture human RNA like it’s ‘never been seen in nature’
by Chris Melore EVANSTON, Ill. — The human body has trillions of cells. Each one contains the building blocks of life and now, for the first time, a study has discovered how some of those building blocks operate. Researchers from Northwestern University say they’ve created the first-ever, data-driven videos which reveal how RNA molecules twist and fold to...