Ruth Ley This week marks the tenth anniversary of the first big survey of microbial diversity in the human body, published in Nature by the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) Consortium, of which I was a member. Before then, microbiologists knew that the body played host to a large mass of microorganisms — a heady mix of bacteria,...
Tag: <span>human genome</span>
Scientists Have Finally Sequenced the Complete Human Genome – And Revealed New Genetic Secrets
By UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – BERKELEY APRIL 3, 2022 Sequencing the last 8% of the human genome has taken 20 years and the invention of new techniques for reading long sequences of the genetic code, which consists of the nucleotides C, T, G and A. The entire genome consists of more than 3 billion nucleotides. Credit: Ernesto...
First complete human genome poised to strengthen genetic analysis, study shows
by National Institute of Standards and Technology Credit: CC0 Public Domain Alongside the newly updated human genome, which fills in long-standing gaps to fully spell out the more than 3 billion letters that compose our genetic code, a separate companion study has shown it can serve as an accurate template that improves our DNA sequencing...
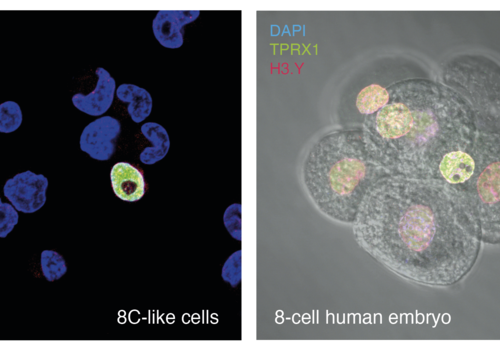
New stem cell population provides a new way to study the awakening of the human genome
BABRAHAM INSTITUTE IMAGE: IMAGES SHOWING HUMAN 8C-LIKE CELLS AMONG NAÏVE EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (LEFT) AND 8-CELL HUMAN EMBRYOS (RIGHT) FLUORESCENTLY LABELLED FOR TPRX1 (GREEN), H3.Y (RED) AND DNA (BLUE). THE IMAGE SHOWS THE ZGA MARKER PROTEINS TPRX1 AND H3.Y ARE PRESENT IN BOTH CELL POPULATIONS. CREDIT: DR. JASMIN TAUBENSCHMID-STOWERS BABRAHAM INSTITUTE, DR. FÁTIMA SANTOS BABRAHAM...
Human Genome at Super Resolution
A better understanding of the detailed structure, mechanism, and function of the human genome can illuminate biological mysteries about genetic function and yield important clues about the origins of genetic changes that give rise to dysfunction and disease. Such detailed understanding begins with the ability to see the entire genome in super-resolution at a maximum...
Scientists Finish the Human Genome at Last
By Carl Zimmer Published July 23, 2021, Updated July 26, 2021 Two decades after the draft sequence of the human genome was unveiled to great fanfare, a team of 99 scientists has finally deciphered the entire thing. They have filled in vast gaps and corrected a long list of errors in previous versions, giving us...
G4S: ANOTHER FUNCTIONAL BIT OF THE HUMAN GENOME?
Some regions of the human genome where the DNA can fold into unusual three-dimensional structures called G-quadruplexes (G4s) show signs that they are preserved by natural selection. When G4s are located in the regulatory sequences that control how genes are expressed or in other functional, but non-protein-coding, regions of the genome, they are maintained by...
Scientists use clues in the human genome to discover new inflammatory syndrome
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered a new inflammatory disorder called vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory and somatic syndrome (VEXAS), which is caused by mutations in the UBA1 gene. VEXAS causes symptoms that included blood clots in veins, recurrent fevers, pulmonary abnormalities and vacuoles (unusual cavity-like structures) in myeloid cells. The scientists reported their...