September 28, 2024 by University of Michigan Researchers at Michigan Medicine have developed a composite hydrogel capable of achieving sustained, steady drug release using ultrasound as a trigger. The team behind the breakthrough believes it could revolutionize drug delivery for various medical applications, in which constant drug levels are crucial for optimal therapeutic outcomes. The...
Tag: <span>hydrogel</span>
Hydrogel with ultrasound activation enables sustained drug release
September 28, 2024 by University of Michigan Researchers at Michigan Medicine have developed a composite hydrogel capable of achieving sustained, steady drug release using ultrasound as a trigger. The team behind the breakthrough believes it could revolutionize drug delivery for various medical applications, in which constant drug levels are crucial for optimal therapeutic outcomes. The...
Injectable hydrogel electrodes open door to a novel painless treatment regimen for arrhythmia
by Texas Heart Institute Design of injectable hydrogel electrode. Redox initiation reaction of polyether urethane diacrylamide (PEUDAm) macromer + N-acryloyl glycinamide (NAGA) delivered using double barrel syringe with a mixing head. Ammonium persulfate (APS) and iron gluconate (IG) are used as initiator and reducing agents. Resulting hydrogels display bidentate hydrogen bonding at netpoints for improved...
Revolutionary Seaweed and Carbonated Water Based Hydrogel for Treating Skin Wounds
Acting as the main interface between the internal and the external world, the skin is the largest and most important organ of the human body. It is frequently exposed to many types of physical injuries or wounds, including cuts, scrapes, scratches, infections, and ulcers.Unfortunately, as one ages, the skin becomes more frail and less capable...
Novel hydrogel finds new aptamers, or ‘chemical antibodies,’ in days
by Tim Schley, Pennsylvania State University A new method for selecting aptamers, or ‘chemical antibodies,’ created by Penn State engineers takes only days to complete, instead of the months typically needed for traditional methods. Credit: Kate Myers/Penn StateOne double-helix strand of DNA could extend six feet, but it is so tightly coiled that it packs an...
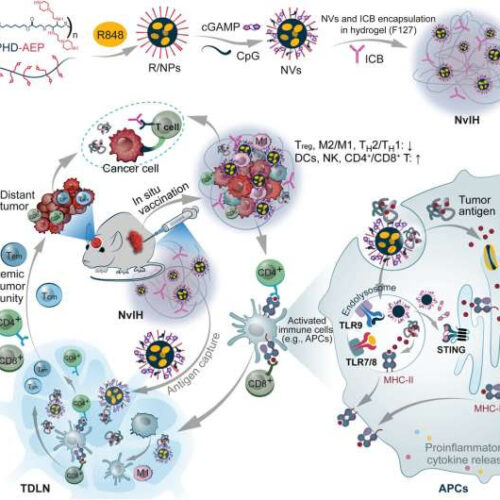
Single-dose injectable nanovaccine-in-hydrogel for robust cancer immunotherapy
by Thamarasee Jeewandara , Medical Xpress In situ vaccination with single-dose NvIH reduced TME immunosuppression, enhanced TME antitumor immune milieu, and elicited systemic antitumor immunity, resulting in robust immunotherapy of large poorly immunogenic tumors with abscopal effect. NvIH is composed of injectable (NVs + ICBs)-in-hydrogel that was loaded with triple immunostimulants (TLR7/8/9 and STING agonists...
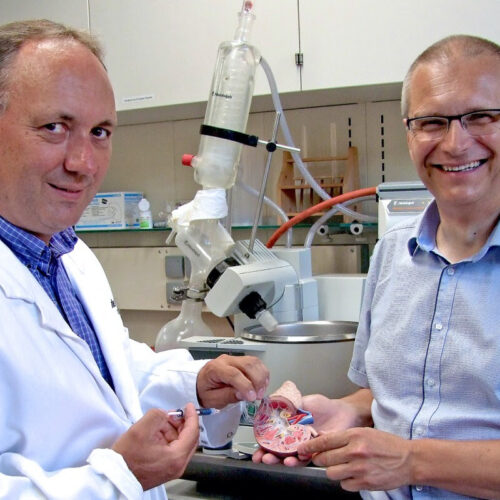
Hydrogel designed to remove every bit of those “blasted” kidney stones
By Ben Coxworth April 04, 2022 Purenum founders Prof. Ingo Grunwald (left) and Manfred PeschkaPurenum GmbH Although some kidney stones can be treated with medication, larger ones are often broken up with an endoscopic laser. A new hydrogel is now claimed to be capable of removing even the smallest of the resulting fragments, instead of...
A new injectable hydrogel for cartilage repair
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions in China has developed an injectable hydrogel for use in repairing damaged cartilage. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes how they made their hydrogel, how it can be applied and how well...
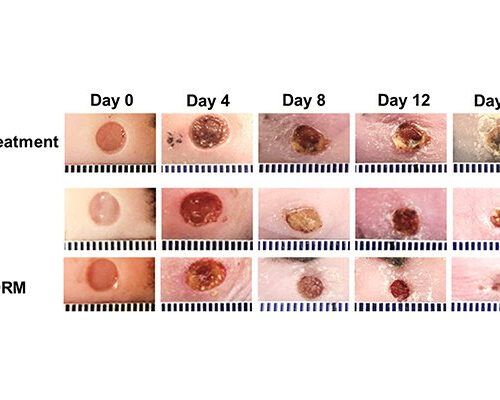
Oxygen-delivering hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing
About one-fourth of people with diabetes develop painful foot ulcers, which are slow to heal due to low oxygen in the wound from impaired blood vessels and increased inflammation. These wounds can become chronic, leading to poor quality of life and potential amputation. Representative images of wounds treated with or without gel and oxygen-release microspheres...
New hydrogel that cuts in half recovery time from muscle injuries
UNIVERSITAT POLITÈCNICA DE VALÈNCIA IMAGE: PATRICIA RICO AND ANA RODRÍGUEZ (UPV-CIBERBBN) CREDIT: UPV A team from the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the CIBER Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN) has designed and tested, at a preclinical level, a new biomaterial for the treatment and recovery of muscle injuries. It is a boron-loaded alginate hydrogel,...