July 26, 2024 by Lori Solomon Hydroxychloroquine appears to be a safe and effective treatment option for anogenital lichen sclerosus that only has mild adverse effects, according to a study published online July 19 in the International Journal of Dermatology. Christeebella O. Akpala, from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues analyzed the demographic...
Tag: <span>Hydroxychloroquine</span>
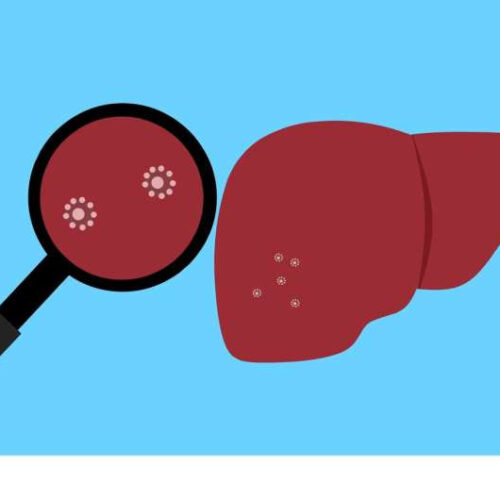
Study finds hydroxychloroquine lowers risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients
by American College of Rheumatology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain New research at ACR Convergence 2023, the American College of Rheumatology’s (ACR) annual meeting, shows that treating rheumatoid arthritis with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) reduced the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, especially in women and men who are 50 years old and younger. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a...
Long-term low-dose hydroxychloroquine use associated with low risk for retinopathy
by American College of Physicians Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A cohort study of more than 3,000 persons who received hydroxychloroquine for 5 or more years with guideline-recommended serial retinopathy screening found that the overall risk for incident retinopathy was low, with most documented cases being mild. Higher hydroxychloroquine dose was associated with progressively greater risk....
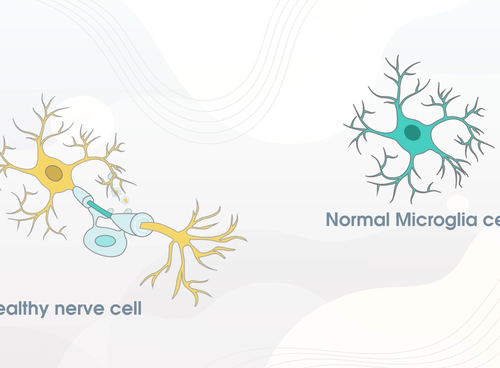
Study finds hydroxychloroquine delays disability for least treatable form of multiple sclerosis
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY VIDEO: A UCALGARY STUDY HAS FOUND PROMISING RESULTS FOR THE GENERIC DRUG HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE WHEN USED TO REDUCE THE WORSENING OF DISABILITY OF PRIMARY PROGRESSIVE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS (MS), THE LEAST TREATABLE FORM OF THE AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE. MS AFFECTS ABOUT 90,000 CANADIANS, ONE OF THE HIGHEST RATES IN THE WORLD WITH ABOUT 15 PER...
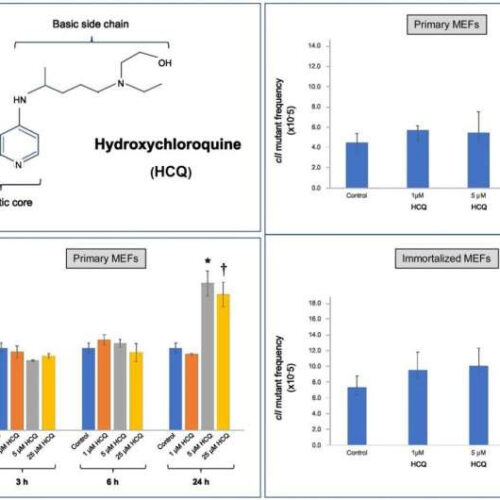
Study points to toxic potential of hydroxychloroquine in mammalian cells
by Jeremy Deutchman, University of Southern California Graphical abstract. DNA damage and mutation-induced by hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in mouse cells in vitro. Induction of oxidative DNA damage (8-oxodG) and cII mutant frequency in Big Blue® mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) treated with increasing concentrations of HCQ or control (solvent). Credit: DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103180 During the height of the pandemic,...
Can hydroxychloroquine treat COVID-19?
Hydroxychloroquine is a medication that doctors prescribe to treat a variety of conditions, including malaria, arthritis, and lupus. Recently, some doctors had been using hydroxychloroquine to treat severe cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. Its use for this purpose has been controversial and conflicting, with some researchers reporting heart problems among those taking the drug....
Coronavirus: Dexamethasone proves first life-saving drug
By Michelle Roberts Health editor, BBC News online A cheap and widely available drug can help save the lives of patients seriously ill with coronavirus. The low-dose steroid treatment dexamethasone is a major breakthrough in the fight against the deadly virus, UK experts say. The drug is part of the world’s biggest trial testing existing...
From the research lab to your doctor’s office – here’s what happens in phase 1, 2, 3 drug trials
For COVID-19, like all illnesses, the drugs and vaccines to treat or prevent the disease must be backed by rigorous evidence. Clinical trials are the source of this evidence. With vaccines and drugs for the coronavirus already entering human testing, it is important to know what the different phases of clinical trials are testing for....
Cancer, coronavirus are a dangerous mix, new studies find
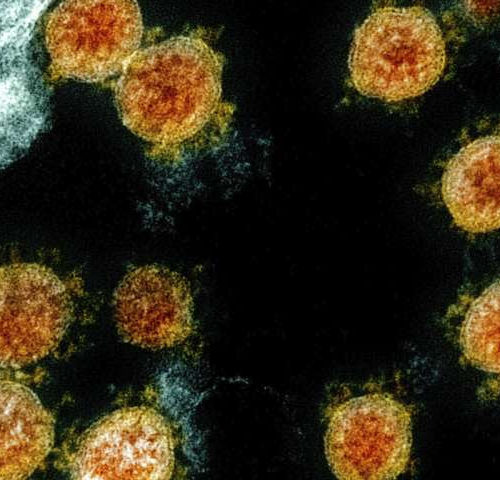
by Marilynn Marchione This electron microscope image made available and color-enhanced by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Md., shows Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, orange, isolated from a patient. Research released on Thursday, May 28, 2020 shows how dangerous the coronavirus is for current and former...
Addition of zinc may benefit some being treated for COVID-19
(HealthDay)—For hospitalized patients with COVID-19, the addition of zinc sulfate to hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin may improve some outcomes, according to a study not yet peer reviewed and posted on medRxiv.org. Philip M. Carlucci, from New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, and colleagues collected data from electronic medical records for COVID-19...
- 1
- 2