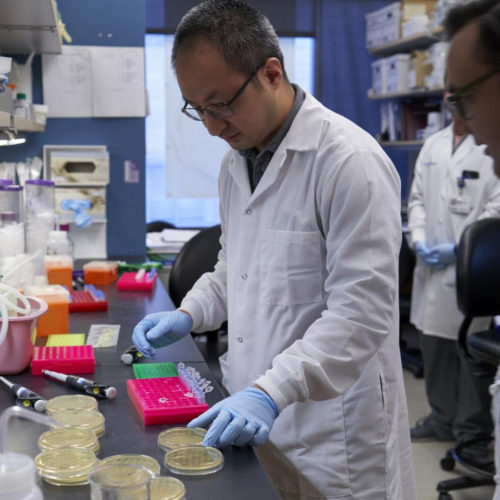
American Journal of Pathology publishes efficacy results from Houston Methodist clinical trial HOUSTON METHODIST HOUSTON METHODIST PHYSICIAN SCIENTIST ERIC SALAZAR, MD, PHD, LOOKS ON AS HIS TEAM WORKS IN THE LAB ON CONVALESCENT PLASMA RESEARCH. view more CREDIT: HOUSTON METHODIST HOUSTON-(Aug. 12, 2020) – A preliminary analysis of an ongoing study of more than 300...
Tag: <span>infectious disease</span>
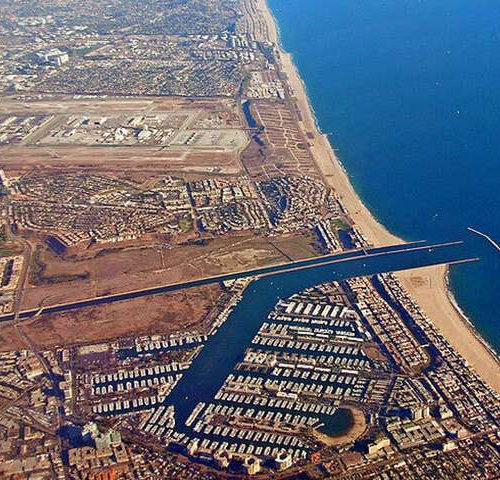
Warming climate may trigger more West Nile outbreaks in Southern California
by University of California – Berkeley California are often cooler than inland areas, granting their populations some protection against West Nile virus. Credit: Public domain photo As climate change brings hotter weather to Southern California, coastal populations from San Diego to Santa Barbara may face an increased risk of contracting West Nile virus and other...
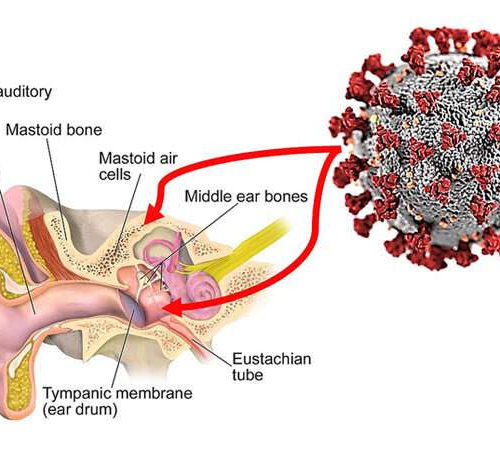
Have you heard? Middle ear, mastoid harbor SARS-Cov-2 and may pose risk for medical staffs
by Johns Hopkins University A cutaway diagram of the ear showing the two regions — the middle ear and mastoid air cells (as indicated by the red arrows) — from where Johns Hopkins researchers recently isolated the SARS-CoV-2 virus (seen at upper right), the cause of COVID-19. Credit: Graphic by M.E. Newman, Johns Hopkins Medicine,...
CBG May Be The New CBD, But Proceed With Caution
If you think CBD has taken over our lives these past few years, you’d be right. It’s in our bathroom cabinets, our beauty drawers, and it’s even infiltrated our tampons — yes, really. But CBD is just one of the many cannabinoid compounds found in the hemp plant. In fact, there are over 100 of...
Phage therapy shows potential for treating prosthetic joint infections
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Bacteriophages, or phages, may play a significant role in treating complex bacterial infections in prosthetic joints, according to new Mayo Clinic research. The findings suggest phage therapy could provide a potential treatment for managing such infections, including those involving antibiotic-resistant microbes. The research is published in the July issue of Clinical Infectious...
Rapid COVID-19 test detects neutralising antibodies with high specificity and sensitivity
by Duke-NUS Medical School As the current COVID-19 pandemic continues to adversely impact communities and economies across the world, efficiency in testing for the infection and antibodies is vital. A unique and rapid SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test (sVNT), developed in Singapore, may be the much-needed boost to current COVID-19 investigations to determine infection rate,...
Driving immunometabolism to control lung infection
by Ciara O’shea, Trinity College Dublin When drugs to kill microbes are ineffective, host-directed therapy uses the body’s own immune system to deal with the infection. This approach is being tested in patients with COVID-19, and now a team of researchers at Trinity College Dublin has published a study showing how it might also work...
Single-dose drug can reduce flu’s spread within households, study finds
A single dose of the flu drug baloxavir marboxil can reduce the spread of the illness within households, new research concludes. A study examining 752 household contacts of 545 patients with the flu found that flu infections were much less common in household members who received the drug than among those who received a placebo....
COVID-19 DRUG MAY CUT DEATH RISK BY 45% FOR SEVERE CASES
In a new study, patients who received single intravenous dose of tocilizumab were also more likely to leave the hospital or be off a ventilator within a month, despite double the risk of additional infection. Critically ill COVID-19 patients who received a single dose of a drug that calms an overreacting immune system were 45%...
Adults with obesity more likely to develop H1N1 influenza
by Nardy Baeza Bickel, University of Michigan Adults with obesity are more susceptible to influenza A/H1N1pdm—the swine flu virus, according to a new study that did not, however, find a similar association with the seasonal flu. The results could be relevant in understanding the mechanisms by which infectious diseases such as influenza or the ongoing...