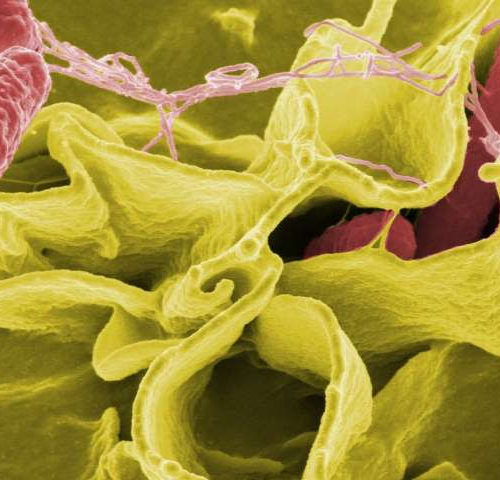
by Temple University Like the infrastructure of an apartment building, a fibrous protein known as curli amyloid that is produced by bacteria provides the supportive framework for biofilms—thick extracellular substances made by bacteria that enable multiple bacterial cells to assemble, survive, and thrive together. Curli amyloid, however, is also a key factor in diarrheal illness...
Tag: <span>infectious disease</span>
Blood test at COVID-19 diagnosis can predict disease severity, study finds
by University of Virginia Doctors can examine COVID-19 patients’ blood to identify those at greatest risk of severe illness and to pinpoint those most likely to need a ventilator, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine suggests. The discovery could lead to new treatments to prevent deadly “cytokine storms” seen in severe...
New, more infectious strain of COVID-19 now dominates global cases of virus
Researchers have shown that a variation in the viral genome of Covid-19 improved its ability to infect human cells and helped it become the dominant strain circulating around the world today. The study, published today in the journal Cell, shows the variation is more infectious in cell cultures under laboratory conditions. The variant, named ‘D614G’,...
New infectious disease test accurately diagnoses infection in minutes
by Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research Melbourne researchers have developed a fast, new test for infections and infectious diseases that could transform Australia’s ability to provide targeted clinical care and respond to pandemics and biosecurity threats. Called c-FIND, the test has the potential to rapidly and accurately detect multiple viral, bacterial or...
New vaccine holds promise in fighting diarrheal disease
OHSU research targets disease afflicting millions in developing world OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Scientists at Oregon Health & Science University have teamed up with OHSU spinoff, Najít Technologies, Inc. to develop a new vaccine that appears to confer immunity to a diarrheal disease that afflicts hundreds of millions of people in developing countries around...
Clear signs of brain injury with severe COVID-19
CREDIT: PHOTO BY JOHAN WINGBORG Certain patients who receive hospital care for coronavirus infection (COVID-19) exhibit clinical and neurochemical signs of brain injury, a University of Gothenburg study shows. In even moderate COVID-19 cases, finding and measuring a blood-based biomarker for brain damage proved to be possible. Some people infected with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 get...
HIV and TB increase death risk from COVID-19, study finds—but not by much
By Linda NordlingJun. 15, 2020 , 4:30 PM Science’s COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Pulitzer Center. CAPE TOWN, SOUTH AFRICA—Living with HIV or active tuberculosis (TB) increases a person’s likelihood of dying from COVID-19, preliminary data from South Africa show. However, the effect is small compared with other known risk factors such as old...
Breathalyzer to Detect COVID-19 in Seconds
Being able to tell, in a matter of seconds, whether someone is infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 would certainly help put a halt to the ongoing pandemic. Existing tests typically involve a deep nasal swab to obtain enough fluid sample, which has to be transferred to a laboratory machine for processing, with the...
Continuously active surface disinfectants may provide additional barrier against the spread of viruses
by Rosemary Brandt, University of Arizona In the battle to slow or prevent the transmission of viruses, such as the novel coronavirus, continuously active disinfectants could provide a new line of defense, according to a recent University of Arizona study released on the health sciences preprint server MedRxiv. While disinfecting high-contact surfaces is an important...
Researchers find one-two punch may help fight against Salmonella
by McMaster University McMaster University researchers have discovered a combination punch to treat drug-resistant infections that is showing promise based on testing in mice. Researchers found that a natural product called dephostatin is an effective partner for the antibiotic colistin in treating infections caused by the bacteria Salmonella. Colistin is considered a last-resort antibiotic for...