For hundreds and hundreds of years people have tried to stop the aging process. However, their efforts have never yielded any positive results – there is no youth elixir. Even with the latest scientific advancement we cannot stop the damage that time does on our bodies. But now scientists from Saarland University have figured out...
Tag: <span>inflammatory</span>
Age research: A low level of the stress hormone cortisol contributes to the ageing process
SAARLAND UNIVERSITY WHY DO WE AGE? WHAT EXACTLY IS HAPPENING IN OUR BODIES? AND CAN WE DO ANYTHING ABOUT IT? MANKIND HAS SOUGHT ANSWERS TO THESE QUESTIONS SINCE TIME IMMEMORIAL. WHILE THE… view more CREDIT: IRIS MAURER Why do we age? What exactly is happening in our bodies? And can we do anything about it?...
Fat check: Yale researchers find explanation for stress’ damage in brown fat
In their search for what triggers the damaging side-effects caused by acute psychological stress, Yale researchers found an answer by doing a fat check. In the face of psychological stress, an immune system response that can significantly worsen inflammatory responses originates in brown fat cells, the Yale team reports June 30 in the journal Cell....
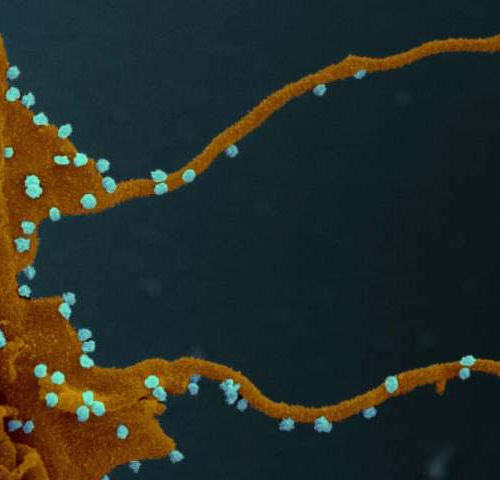
Existing drugs can prevent SARS-CoV-2 from hijacking cells
by European Molecular Biology Laboratory An international team of researchers has analyzed how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, hijacks the proteins in its target cells. The research, published in the journal Cell, shows how the virus shifts the cell’s activity to promote its own replication and to infect nearby cells. The scientists also identified...
The New JAK inhibitor Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) Shows Promise for Psoriatic Arthritis
Approved in 2019 for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, the drug may offer an oral alternative to infused or injected biologics. The JAK inhibitor upadacitinib (Rinvoq) became a treatment option in 2019 for people with rheumatoid arthritis(RA) who had not responded well to methotrexate, the disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) that is the first-line treatment for...
Star-shaped brain cells may play a critical role in glaucoma
by NYU Langone Health After a brain injury, cells that normally nourish nerves may actually kill them instead, a new study in rodents finds. This “reactive” phenomenon may be the driving factor behind neurodegenerative diseases like glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness. Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study examined what...
Promising treatment to slow kidney disease doesn’t prove out in clinical trial
Scientists find that reducing levels of uric acid in the blood does not guard against complication in type 1 diabetes. JOSLIN DIABETES CENTER BOSTON – (June 25, 2020) – Historically, half or more of people with type 1 diabetes develop kidney disease, which frequently progresses to kidney failure requiring hemodialysis or a kidney transplant for...
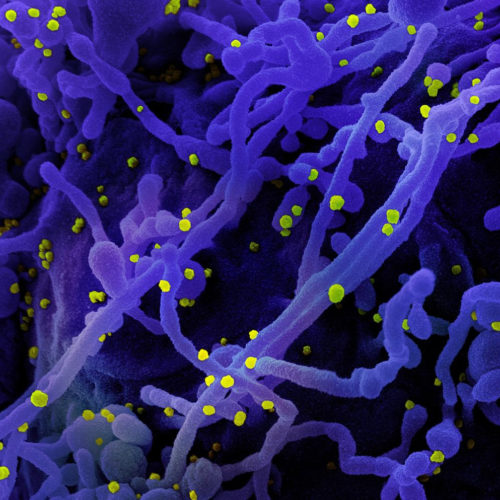
NIH investigators hope CD47 study leads to broad-spectrum infectious diseases immunotherapy
National Institutes of Health investigators and colleagues have discovered that when the immune system first responds to infectious agents such as viruses or bacteria, a natural brake on the response prevents overactivation. Their new study in mBio describes this brake and the way pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, turn it on....
AGA does not recommend the use of probiotics for most digestive conditions
New AGA guideline finds that evidence to support use of probiotics to treat digestive diseases is greatly lacking, identifying only three clinical scenarios where probiotics may benefit patients AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Bethesda, MD (June 9, 2020) — It is estimated that more than 3.9 million American adults have taken some form of probiotics, with many...
Improved gut microbiota with cholesterol-lowering medication
by Margareta Gustafsson Kubista, University of Gothenburg There is a clear link between improved gut microbiota and one of our most common cholesterol-lowering drug groups: statins. This is evident from a European study involving researchers from the University of Gothenburg. Scientists have previously found an association between the gut microbiota and various metabolism-related and cardiovascular...