Roberta Villa, MD DISCLOSURES | December 09, 2024 22320 Added to Email Alert It’s been a while since I’ve discussed the H5N1 avian influenza clade 2.3.4.4b and its rapid spread in North America. I hope the facts prove me wrong, but many experts have been warning for some time that ideal conditions are forming for this virus, which for now only...
Tag: <span>influenza</span>
Key influenza-severity risk factor found hiding in plain sight on our antibodies
Antibody composition shapes flu severity Peer-Reviewed Publication Stanford Medicine Sialic acid (blue links) at the end of sugar chains attached to antibodies (red) induce the antibodies to bind to receptors (light blue) that promote an anti-inflammatory response in alveolar macrophages. When sialic acid is absent, the sugar chains attach to receptors (yellow) that promote inflammation,...
New vaccine design uses immunity against influenza to offer faster protection against emerging pathogens
by Iqbal Pittalwala, University of California – Riverside Credit: CC0 Public DomainAfter COVID vaccination, it usually takes weeks for our bodies to develop protective antibody responses. Imagine, however, a vaccine that speeds up the production of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that spreads COVID-19. A research team led by Rong Hai, an associate professor of microbiology...
WHY THIS YEAR’S VIRUS SEASON COULD BE DIFFERENT
AUGUST 21ST, 2023POSTED BY JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY Margaret LaRaviere gets an influenza vaccine during an event hosted by the Chicago Department of Public Health at the Southwest Senior Center on September 09, 2022 in Chicago, Illinois. Epidemiologist David Dowdy says vaccines and a preventive drug for RSV offer hope for a healthier fall and winter...
Nanobodies from alpacas could steer immune attacks on influenza
by Nancy Fliesler, Children’s Hospital Boston Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain While conventional flu vaccines are designed to anticipate the influenza strains projected to dominate in the next flu season, they’re only partially effective. And while antiviral drugs are available to treat active flu cases, the body quickly clears them, requiring high, frequent doses. Coupling one existing flu...
New universal flu vaccine offers broad protection against influenza A virus infections, researchers find
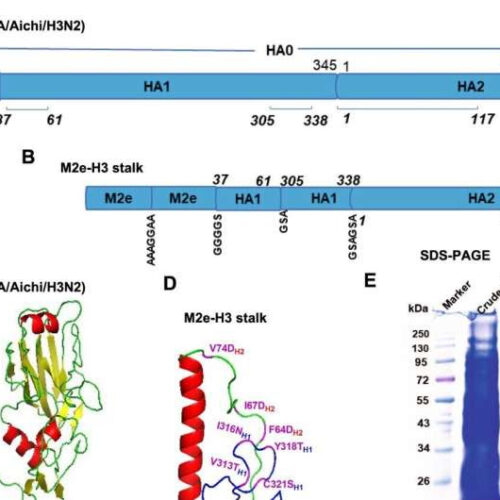
by Georgia State University Rationale design of chimeric M2e-H3 stalk protein, purification, and confirmation. A Schematic of full-length HA gene of influenza A virus (A/Aichi/H3N2), and the selective domains as a vaccine target are numbered in amino acid (aa 37-61, 305-338, 1-117) residues. B M2e-H3 stalk vaccine construct with flexible and soluble linker sequences (AAAGGAA; GGGGS;...
Dietary cholesterol worsens inflammation, sickness in mice with influenza
UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURAL, CONSUMER AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES IMAGE: A UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS RESEARCH TEAM FINDS HIGH LEVELS OF DIETARY CHOLESTEROL MAKE MICE SICKER WHEN INFECTED WITH INFLUENZA. L TO R: JOSEPH TINGLING, DREW STEELMAN, AND ALLISON LOUIE CREDIT: LAUREN D. QUINN, UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS URBANA, Ill. – New research from the University...
Study: It is safe for people to be vaccinated against COVID-19 and influenza at the same time
by University of Bristol Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Research has found that it is safe for people to receive a flu vaccine at the same time as a COVID-19 vaccine. Reported side effects were mainly mild to moderate, and there were no negative impacts on the immune response produced by either vaccine when both were given on...
New vaccine strategy harnesses ‘foot soldier’ T-cells to provide protection against influenza
As Americans begin pulling up their sleeves for an annual flu vaccine, researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have provided new insights into an alternative vaccine approach that provides broader protection against seasonal influenza. In a study published in Cell Reports Medicine, scientists describe a T-cell-based vaccine strategy that is effective against multiple strains of influenza virus. The...
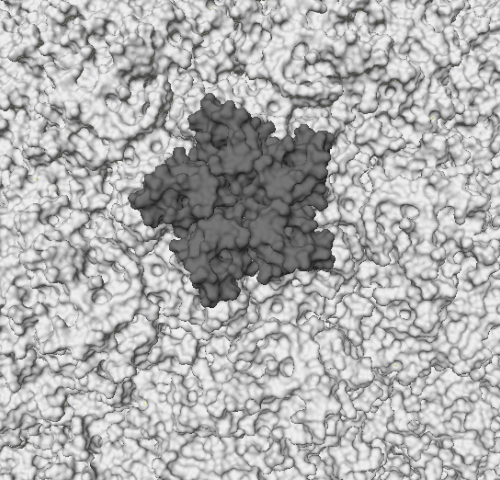
Common cold combats influenza
by Yale University A representation of the molecular surface of one variant of human rhinovirus. Credit: Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 As the flu season approaches, a strained public health system may have a surprising ally—the common cold virus. Rhinovirus, the most frequent cause of common colds, can prevent the flu virus from infecting airways by jumpstarting the body’s antiviral...