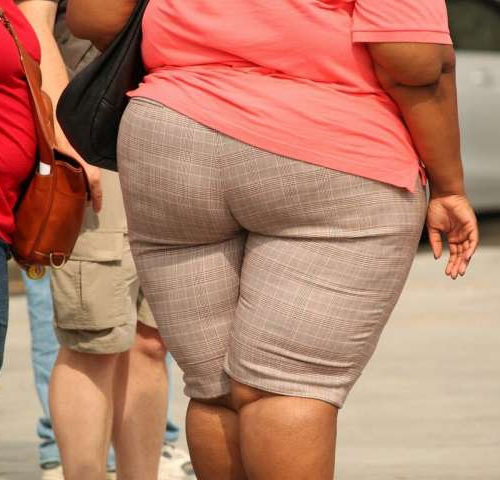
Adults with obesity are more susceptible to influenza A/H1N1pdm—the swine flu virus, according to a new study that did not, however, find a similar association with the seasonal flu. The results could be relevant in understanding the mechanisms by which infectious diseases such as influenza or the ongoing coronavirus pandemic might affect different segments of...
Tag: <span>influenza</span>
Fast-spreading mutation helps common flu subtype escape immune response
by Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health Strains of a common subtype of influenza virus, H3N2, have almost universally acquired a mutation that effectively blocks antibodies from binding to a key viral protein, according to a study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. The results have implications for flu...
Single-dose drug can reduce flu’s spread within households, study finds
A single dose of the flu drug baloxavir marboxil can reduce the spread of the illness within households, new research concludes. A study examining 752 household contacts of 545 patients with the flu found that flu infections were much less common in household members who received the drug than among those who received a placebo....
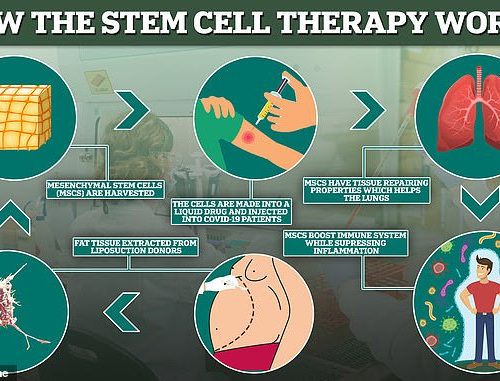
Liposuction treatment hope for coronavirus: Stem cells taken from fat-reduction donors boosts survival rates FIVE-fold for critically-ill patients hooked up to ventilators
Of a small number of patients, 15% died compared with the 85% expected Overall 70% of patients who were on the brink of death saw improvements The researchers admitted they did not expect such positive results The treatment works by injecting patients with cells taken from fat tissue The stem cells are known to bolster...
Scientists find no virus risk based on blood type.
A pair of recent studies found that people with Type A blood are no more at risk of getting the virus or falling dangerously ill than others, contradicting preliminary evidence based on a relatively small sample of people. Over the past few months, after looking at thousands of additional patients with Covid-19, scientists are reporting...
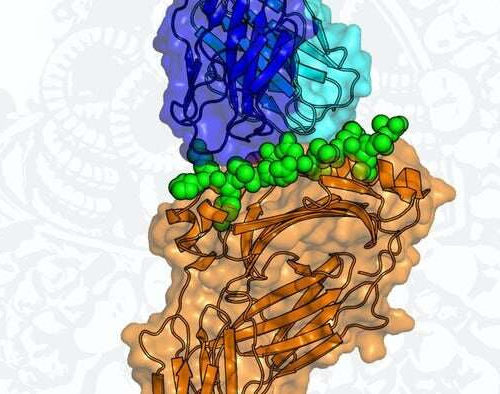
Discovery of new immune targets inside flu virus offers hope for universal vaccine
by Cardiff University New markers hidden inside the influenza virus have been discovered by scientists at Cardiff University. The researchers from the School of Medicine worked with an international team of experts—including collaborators in Moscow, Russia and Melbourne, Australia—to look at how people’s immune systems responded to the new proteinmarkers. They showed for the first...
Type 1 interferon deficiency: Biomarker of patients at risk of severe COVID
INSERM (INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA SANTÉ ET DE LA RECHERCHE MÉDICALE) Approximately 5% of people with Covid-19 progress to a severe or critical form, including the development of severe pneumonia that progresses to acute respiratory distress syndrome. While these forms sometimes occur early in the course of the disease, clinical observations generally describe a two-stage...
Fast-spreading mutation helps common flu subtype escape immune response
by Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health Strains of a common subtype of influenza virus, H3N2, have almost universally acquired a mutation that effectively blocks antibodies from binding to a key viral protein, according to a study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. The results have implications for flu...
The Aging Gut Microbiome Produces More Trimethylamine, Harming Arterial Function
In recent years academic interest has grown in the study of the gut microbiome. Researchers are making inroads into understanding the considerable influence of these microbial populations over the progression of health and aging. The gut microbiome may be as influential as physical activity in these matters. The balance of microbial populations shifts unfavorably over...
Adults with obesity more likely to develop H1N1 influenza
by Nardy Baeza Bickel, University of Michigan Adults with obesity are more susceptible to influenza A/H1N1pdm—the swine flu virus, according to a new study that did not, however, find a similar association with the seasonal flu. The results could be relevant in understanding the mechanisms by which infectious diseases such as influenza or the ongoing...