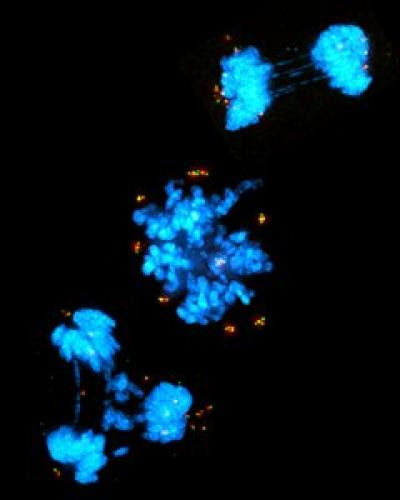
Heidelberg neurobiologists successfully test novel drug principle in a mouse model and in brain organoids of ALS patientsPeer-Reviewed Publication HEIDELBERG UNIVERSITY A new pharmacological inhibitor can intervene in a central cell death mechanism that is responsible for the death of motor neurons and hence important for the progression of the motor neuron disease amyotrophic lateral...
Tag: <span>inhibitor</span>
Newly developed inhibitor shows potential for prostate cancer
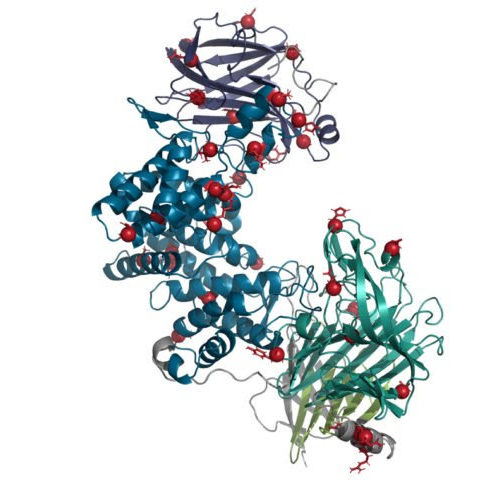
by Albert Ludwigs University of Freiburg Identification of a bi-substrate inhibitor of KMT9. a Chemical structure of compound 1a with predicted binding mode. b MST assay to determine the dissociation constant (Kd) of compound 1a and SAM binding to KMT9. c FTSA for compound 1a binding to KMT9. d Chemical structure of SAM. e FTSA for...
New way to target some rapidly dividing cancer cells, leaving healthy cells unharmed
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE IMAGE: CANCER CELLS WITH EXCESS CENTROSOMES. DNA IS SHOWN IN BLUE, AND CENTROSOMES ARE SHOWN AS GREEN AND RED. Scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine and the University of Oxford say they have found a new way to kill some multiplying human breast cancer cells by selectively attacking the core of their cell...
Re-engineered enzyme could help reverse damage from stroke, spinal cord injury: U of T study
A team of researchers from the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering and the University of Michigan has redesigned and enhanced a natural enzyme that shows promise in promoting the regrowth of nerve tissue following injury. The new version of the enzyme is more stable and could lead to treatments for reversing...
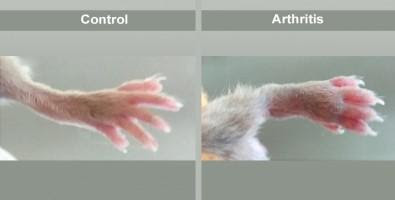
Lab-created molecule achieves positive results in the treatment of arthritis
Tested in mice with genetically induced arthritis, the substance decreased the area affected, reduced local swelling, and assuaged the pain associated with the inflammatory process. ARTHRITIC MOUSE PAW TREATED WITH TPPU (LEFT) AND UNTREATED PAW OF ANOTHER ARTHRITIC MOUSE. By José Tadeu Arantes | Agência FAPESP – Arthritis affects almost 2% of the world’s population,...
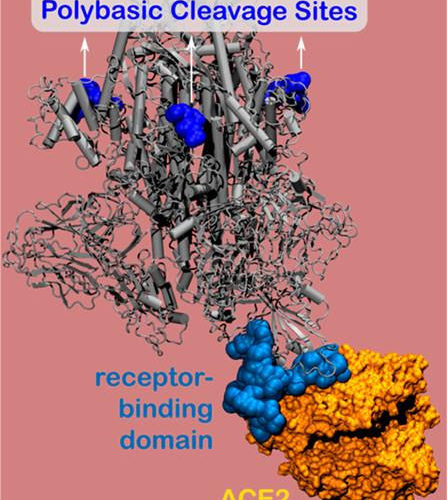
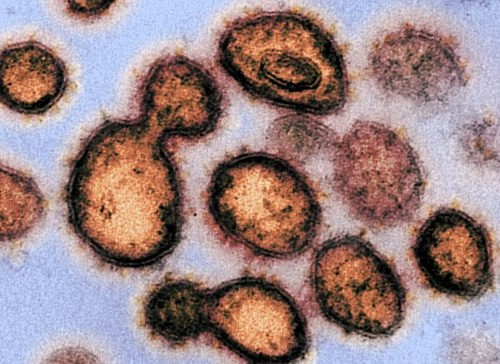
Research exposes new vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2
Electrostatic interactions enhance the spike protein’s bond to host cells NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY A COMPUTER MODEL SHOWING THE POLYBASIC CLEAVAGE SITES, LOCATED ON THE NOVEL CORONAVIRUS’ PROTEIN SPIKE. view more CREDIT: NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have uncovered a new vulnerability in the novel coronavirus’ infamous spike protein — illuminating a relatively simple,...
India clears a psoriasis drug for COVID-19, and a tiny US biotech’s shares soar
Dive Brief: India’s drug regulator has granted an emergency approval to the antibody drug itolizumab to treat the potentially deadly immune response, cytokine release syndrome, that appears to affect some patients hospitalized with acute respiratory distress related to COVID-19. The Drugs Controller General of India cleared the treatment for use after itolizumab, alongside standard of...
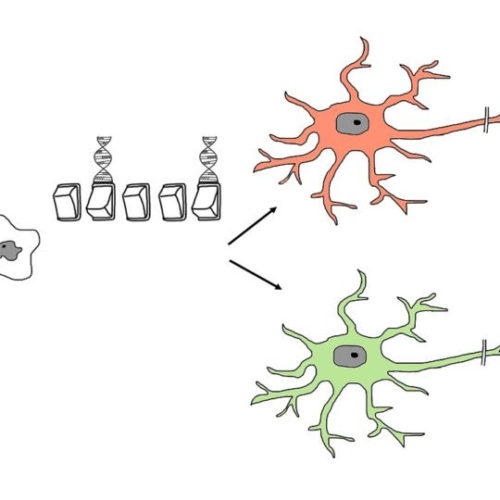
Gene yields insights into the causes of neurodegeneration
by Cornell University Across the globe, approximately 50 million people are living with dementia. The two most common forms are Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), which develop when neurons in specific parts of the brain stop functioning—triggering memory loss and other behavioral or personality changes. Without a cure, the World Health Organization predicts...
Ex Vivo Mitochondrial Transfer as a Way to Improve Stem Cell Therapy Outcomes
A sizable portion of the variable efficacy of first generation stem cell therapies as presently practiced may be due to a poor quality of cells following expansion in culture. Regardless of quality, near all such cells die shortly after transplantation. Few clinics and few approaches to cell therapy lead to lasting survival and engraftment of...
Transgenic rice containing anti-hypertensive peptides lowers blood pressure in hypertensive rats
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. In the future, taking your blood pressure medication could be as simple as eating a spoonful of rice. This “treatment” could also have fewer side effects than current blood pressure medicines. As a first step, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistryhave made transgenic rice that contains...
- 1
- 2